Chapter: Mechanical : Design of Transmission Systems : Spur Gears and Parallel Axis Helical Gears
Design Procedure for Helical Gear
DESIGN PROCEDURE FOR HELICAL GEAR:
1. Calculation of gear ratio (i):
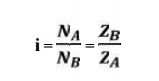
where, NA and NB = speed of the driver and driven respectively, and ZA and ZB = Number of teeth on driver and driven respectively.
2. Selection of material
Consulting Table 5.3, knowing the gear ratio i, choose the suitable material.
3. If not given, assume gear life (say 20000 hrs)
4. Calculation of initial design torque:
[Mt] = Mt . K. Kd
where, [Mt] = transmission torque
K = Load factor, Table 5.11
Kd = Dynamic load factor, Table 5.12
Assume K. Kd = 1.3 ( if not given)
5. Calculation of Eeq, [ϭb] and [ϭc]:
ü From table 5.20 Calculate Eeq
ü From table 5.16 Calculate Design bending stress [ϭb]
ü Calculate Design contact stress [ϭc] by
[ϭc] = CB . HB. Kcl (or)
[ϭc] = CR . HRC. Kcl
CB CR = Coefficient of surface hardness from table 5.18
HB HRC = Hardness number
6. Calculation if centre distance (a):
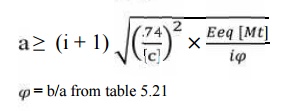
7.Select number of teeth on gear and pinion:
Ø On pinion,Z1 = Assume ≥ 17
Ø On gear, Z2 = i X Z1
8. Calculation of module:
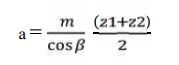
Choose standard module from table 5.8
9. Revision of centre distance (m):
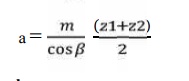
10. Calculate b, d1, v and ѱp :
Calculate face width, b = ѱ. a
Calculate pitch dia, d = (mn.z1)/ cos β
Calculate pitch line velocity, v = (πd1N1)/60
Calculate value of ѱp = b/d1
11. Selection of quality of gear:
Knowing the pitch line velocity and acosulting table 5.22, select a suitable quality
of gear.
12. Revision of design torque [Mt]: Revise K:
Using the calculated value of ѱp revise the K value by using table 5.11
Revise Kd:
Using the selected quality if gear and pitch line velocity, revise the Kd
value
[Mt] = Mt . K. Kd
13. Check for bending:
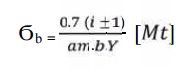
Compare Ϭb and [Ϭb].
If Ϭb ≤ [Ϭb], then design is safe.
14. Check for wear strength:
Calculate induced contact stress,

If Ϭc ≤ [Ϭc], then design is safe.
15. If the design is not satisfactory (ϭb > [ϭb] and / or ϭc > [ϭc] ), then increase the module of face width value of the gear material.
16. Check for gear:
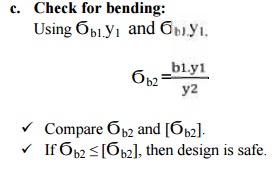
ü Compare Ϭb2 and [Ϭb2].
ü If Ϭb2 ≤ [Ϭb2], then design is safe.
d. Check for wear strength:
Calculate induced contact stress will be same for pinion and gear,
So,
Ϭc2 = Ϭc
ü Compare Ϭc and [Ϭc]
ü If Ϭc ≤ [Ϭc], then design is safe
Related Topics