Geography - Density of Population | 12th EM Geography : Chapter 1 : Population Geography
Chapter: 12th EM Geography : Chapter 1 : Population Geography
Density of Population
Density of Population
Absolute
numbers do not give any indication of the impact of population on the land and
its resources. The number of persons living per unit of land areas gives a
better picture. This is expressed in the form of density of population per
sq.km of land area.
Density of population = Total population / Total area of the country
It
is obtained by dividing the total land area by the total population, the
quotient being the number of people per square kilometre. Compared with simple
arithmetic density, physiological or nutritional density is a more refined
method of calculating man-land ratios.
Physiological or Nutritional density is the ratio between total population and total cropped area. The total arable land in the world is 13.3% and the nutritional density of the world is 325 per sq.km of land. The total percentage of arable land is 48.83 in India and its nutritional density is 753 per sq.km of land. Singapore has the highest nutritional density of population of 440,998 per sq.km of land the world. The areas of density of population can be divided into three as follows:
1. High density areas of population
Fertile
plains with favourable climate and highly industrialised and urbanised areas
are generally densely populated. There are four major areas of high density of
population with more than 100 persons
per sq.km. Areas include:
a.
Eastern Asia, including china, Japan and Republic of Korea.
b.
Southern Asia, comprising India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
c.
North-Eastern part of the United States of America.
d.
Central and North-Western Europe.
Of
the four regions given, the first two i.e. Eastern Asia and South Asia have
high density of population due to favourable environmental conditions such as
favourable climate, fertile soil and large areas of plains which encourage the
growth of agriculture. The plains and river valleys of India and China are
densely populated. In the last two groups i.e. North Eastern United States of
America and North – Western Europe which are densely populated due to the
concentration of manufacturing industries.
2. Moderate density areas of population
The
areas of moderate density of population have between 10 and 80 persons per sq.km. The areas of moderate density
of population include Central part of the United States of America, Tropical
Western Africa, Western blocks of Russia, Eastern Europe, Deccan Plateau of
India, Central China, Southern portion of the Plateau of Mexico, North -Eastern
Brazil and Central Chile, The above areas are characterised by the well
developed agricultural activities, favourable climate, fertile soils, fishing,
etc,.
3. Low density areas of population
About
half the area of the world has population less
than 10 persons per sq.km. Certain vast areas remain completely
uninhabited. The main areas are
a) Amazon
forest region of South America and Congo forest region of Africa.
a)
Arctic area of Canada, Greenland and
the Polar regions.
b)
Great deserts of the world i.e.
Sahara, Kalahari, Arabia, Great desert of Australia, Atacama Desert of South
America, desert regions of Western United States and Thar Desert of India.
c)
High mountainous regions in all
continents.
d) Antarctica.
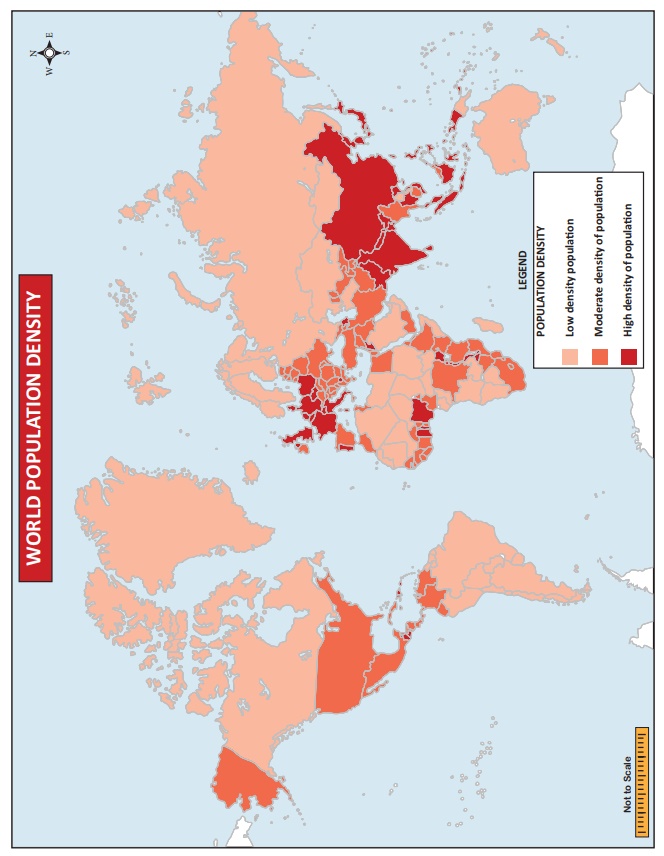
Australia with
an average density of population of 2 persons per sq.km is one of the most
sparsely populated countries of the world. However, inhabitants of these areas
have high standard of living. The reasons for low density of population are
a)
Bad and unfavourable environment
conditions for human settlement.
b)
Lack of economic activities.
c)
Lack of transport and communication.
d) Government
policy.
Terms related population
1. Population: A group of individuals of the same species occupying a particular geographic area.
2. People: The members of a particular nation, community, or ethnic group.
3. Crude Birth rate (Natality
Rate): Number of live births per thousand people in
a year.
4. Crude Death Rate (Mortality Rate): Number of deaths per thousand people in a year.
5. Net Migration Rate: the formula for net migration rate is simple:
N = 1000 × (I – E) / P
N= net migration rate
E= number of people emigrating out of the
country
I= number of people immigrating into the
country
P= the estimated mid-year population
6. Fertility Rate: is the number of live births
expected per 1000 women in their life times in a specified geographic area and
for a specific point in time, usually a calendar year. Niger has the highest fertility rate of 6.49 while Singapore has the lowest fertility rate
of 0.83. Can you guess why there is variation between these countries?
7. Dependency ratio:
Number of dependents in a population divided by
the number of working age people. It’s a calculation which groups those aged
under 15 with those over 65 years as the ‘dependants’ and classifying those
aged 15-64 years as 'the working-age population'.
8. Growth Rate: = CBR – CDR +/- Net Migration Rate/ 1000
South Sudan has the highest population growth
rate of 3.83% in 2017.
9. Rate of Natural Increase
(RNI) = CBR-CDR (No Migration)
CBR>CDR = ↑ population
RNI usually expressed as % e.g., 2% = 2/100 =
20/1000
RNI ≠ population growth if migration
significant
10. Adult Literacy Rate: The Adult literacy index (ALI) is a statistical measure used to determine how many
adults can read and write in a certain area or nation. Adult literacy is one of
the factors in measuring the Human Development Index (HDI) of each nation,
along with life expectancy, education, and standard of living. Burkina faso has
the lowest literacy rate of 21.8% ( 2015). How does literacy rate affect the
standard of living of a country?
11. Life expectancy rate: Life expectancy equals the average number of years a person born in a given country
is expected to live. As of 2015, the country with the highest life expectancy
is Monaco at 89.52 years; the country with the lowest is Chad at 49.81 years.
Related Topics