Structured Query Language(SQL) - Data Types | 12th Computer Science : Chapter 12 : Database concepts and MySql : Structured Query Language(SQL)
Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 12 : Database concepts and MySql : Structured Query Language(SQL)
Data Types
Data Types
The data in a database is stored based on the
kind of value stored in it. This is identified as the data type of the data or
by assigning each field a data type. All the values in a given field must be of
same type.
The ANSI SQL standard recognizes only Text and
Number data type, while some commercial programs use other datatypes like Date
and Time etc. The ANSI data types are listed below in Table 12.1
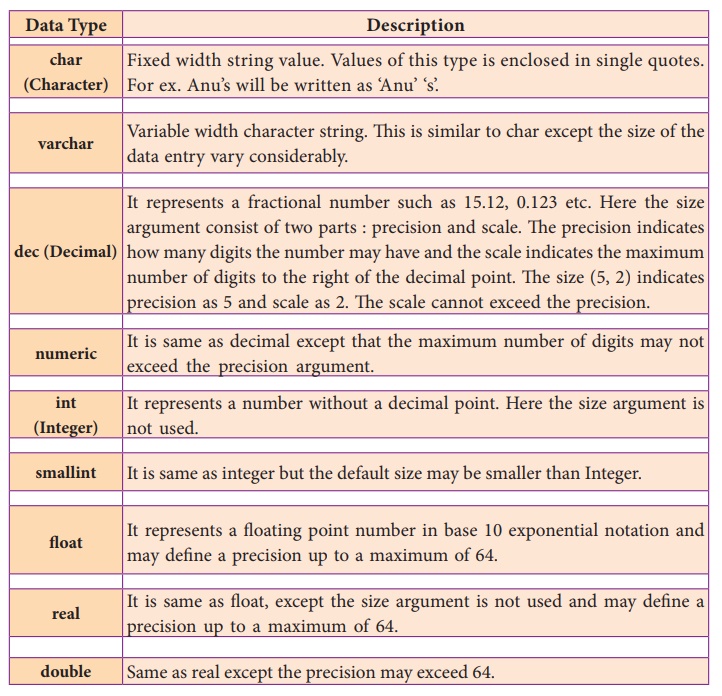
Data : Type Description
char (Character) : Fixed width string value. Values of this type
is enclosed in single quotes. For ex. Anu’s will be written as ‘Anu’ ‘s’.
varchar : Variable width character string. This is
similar to char except the size of the data entry vary considerably.
dec (Decimal) : It represents a fractional number such as
15.12, 0.123 etc. Here the size argument consist of two parts : precision and
scale. The precision indicates how many digits the number may have and the
scale indicates the maximum number of digits to the right of the decimal point.
The size (5, 2) indicates precision as 5 and scale as 2. The scale cannot
exceed the precision.
numeric : It is same as decimal except that the maximum
number of digits may not exceed the precision argument.
int (Integer) : It represents a number without a decimal
point. Here the size argument is not used.
smallint : It is same as integer but the default size may
be smaller than Integer.
float : It represents a floating point number in base
10 exponential notation and may define a precision up to a maximum of 64.
real : It is same as float, except the size argument
is not used and may define a precision up to a maximum of 64.
double : Same as real except the precision may exceed
64.
Related Topics