Chapter: Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing : Assessment
Data Analysis
DATA ANALYSIS
After completing the psychosocial assessment, the nurse analyzes
all the data that he or she has collected. Data analysis involves thinking
about the overall assessment rather than focusing on isolated bits of
information. The nurse looks for patterns or themes in the data that lead to
conclusions about the client’s strengths and needs and to a particular nursing
diagnosis. No one statement or behav-ior is adequate to reach such a
conclusion. The nurse also must consider the congruence of all information
provided by the client, family, or caregivers, as well as his or her own
observations. It is not uncommon for the client’s percep-tion of his or her
behavior and situation to differ from that of others. Assessments in a variety
of areas are necessary to support nursing diagnoses such as Chronic Low
Self-Esteem or Ineffective Coping.
Traditionally, data analysis leads to the formulation of nursing
diagnoses as a basis for the client’s plan of care. Nursing diagnoses have been
an integral part of the nurs-ing process for many years. With the sweeping
changes occurring in health care, however, the nurse also must articulate the
client’s needs in ways that are clear to health team members in other disciplines
as well as to families and caregivers. For example, a multidisciplinary
treatment plan or critical pathway may be the vehicle for planning care in some
agencies. A plan of care that is useful to the client’s family for home care
may be necessary. The nurse must describe and document goals and interventions
thatmany others, not just professional nurses, can understand. The descriptions
must contain no jargon or terms that are unclear to the client, family, or
other providers of care.
Psychological Tests
Psychological tests are another source of data for the nurse to use
in planning care for the client. Two basic types of tests are intelligence
tests and personality tests. Intelligence
tests are designed to evaluate the
client’s cognitive abilities and intellectual
functioning. Personality tests
reflect the client’s personality in areas such as self-concept, impulsecontrol,
reality testing, and major defenses (Adams & Culbertson, 2005). Personality
tests may be objective (constructed of true-and-false or multiple-choice
ques-tions). Table 8.1 describes selected objective personality tests. The
nurse compares the client’s answers with stan-dard answers or criteria and
obtains a score or scores.

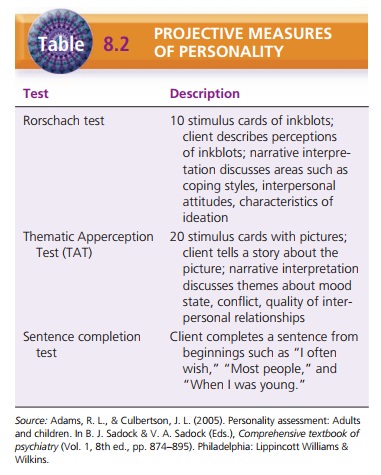
Other personality tests, called projective tests, are unstructured
and are usually conducted by the interview method. The stimuli for these tests,
such as pictures or Rorschach’s inkblots, are standard, but clients may respond
with answers that are very different. The evaluator ana-lyzes the client’s
responses and gives a narrative result ofthe testing. Table 8.2 lists commonly
used projective personality tests.
Both intelligence tests and personality tests are fre-quently
criticized as being culturally biased. It is impor-tant to consider the
client’s culture and environment when evaluating the importance of scores or
projections from any of these tests; they can provide useful information about
the client in some circumstances but may not be suitable for all clients.
Psychiatric Diagnoses
Medical diagnoses of psychiatric illness are found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders, 4th edition, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR).
This taxonomy is uni-versally used by psychiatrists and by some therapists in
the diagnosis of psychiatric illnesses. The DSM-IV-TR
clas-sifies mental disorders into categories. It describes each disorder and
provides diagnostic criteria to distinguishone from another. Although the DSM-IV-TR is not a substi-tute for a
thorough psychosocial nursing assessment, the descriptions of disorders and
related behaviors can be a valuable resource for the nurse to use as a guide.
The DSM-IV-TR uses a multiaxial
system to provide the format for a complete
psychiatric diagnosis:
·
Axis I: clinical disorders, other
conditions that may be a focus of
clinical attention
·
Axis II: personality disorders,
mental retardation
·
Axis III: general medical conditions
·
Axis IV: psychosocial and
environmental problems
·
Axis V: global assessment of
functioning (GAF).
The psychosocial and environmental problems categorized on axis IV
include educational, occupational, housing, finan-cial, and legal problems as
well as difficulties with the social environment, relationships, and access to
health care.
The GAF is used to make a judgment about the client’s overall level
of functioning. The GAF score given to the client may describe his or her
current level of func-tioning as well as the highest level of functioning in
the past year or 6 months. This information is useful in setting appropriate
goals for the client’s care.
Mental Status Exam
Often, psychiatrists, therapists, or other clinicians perform a
cursory abbreviated exam that focuses on the client’s cognitive abilities.
These exams usually include items such as orientation to person, time, place,
date, season, and day of the week; ability to interpret proverbs; ability to
per-form math calculations; memorization and short-term recall; naming common
objects in the environment; ability to follow multistep commands; and ability
to write or copy a simple drawing. The fewer tasks the client completes
accurately, the greater the cognitive deficit. Because this exam assesses
cognitive ability, it is often used to screen for dementia. However, cognition
may also be impaired (usually temporarily) when clients are depressed or
psychotic.
Related Topics