Chapter: Civil : Construction Techniques, Equipment And Practices : Construction Practices
Damp Proof Course
Damp Proof Course
1 Materials for Damp Proof Course (DPC):
An effective damp proofing material should have
the following properties;
1.
It should be impervious.
2.
It should be strong and durable, and should be
capable of withstanding both dead as well as live loads without damage.
3.
It should be dimensionally stable.
4.
It should be free from deliquescent salts like
sulphates, chlorides and nitrates.
The materials commonly used to
check dampness can be divided into the following three categories:
1.
Flexible Materials: Materials like bitumen felts
(which may be hessian based or fibre/glass fibre based), plastic sheeting
(polythene sheets) etc.
2.
Semi-rigid Materials: Materials like mastic,
asphalt, or combination of materials or layers.
3.
Rigid Materials: Materials like first class
bricks, stones, slate, cement concrete etc.
2.SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR
DAMP PROOF COURSE:
The choice of material to
function as an effective damp proof course requires a judicious selection. It
depends upon the climate and atmospheric conditions, nature of structure and
the situation where DPC is to be provided. The points to be kept in view while
making selection of DPC materials are briefly discussed below:
1.
DPC above ground level: For DPC
above ground level with wall thickness generally not exceeding 40cm, any
one of the type of materials mentioned above may be used. Cement concrete is
however commonly adopted material for DPC at plinth level, 38 to 50mm thick
layer of cement concrete M15 (1:2:4 mix) serves the purpose under normal
conditions.
In case of damp and humid
atmosphere, richer mix of concrete should be used. The concrete is further made
dense by adding water proofing materials like Pudlo, Impermo, Waterlock etc in
its ingredients during the process of mixing. It is used to apply two coats of
hot bitumen over the third surface of the concrete DPC.
1.
DPC Material for floors, roofs etc: For
greater wall thickness or where DPC is to be laid over large areas such
as floors, roofs, etc, the choice is limited to flexible materials which
provide lesser number of joints like mastic, asphalt, bitumen felts, plastic
sheets etc.
The felts when used should be
properly bonded to the surface with bitumen and laid with joints properly
lapped and sealed.
1.
DPC Material for situations where
differential thermal movements occur: In parapet walls and
other such situations, materials like mastic, asphalt, bitumen felts and metal
(copper or lead) are recommended. It is important to ensure that the DPC
material is flexible so as to avoid any damage or puncture of the material due
to differential thermal movement between the material of the roof and the
parapet.
2.
DPC material for Cavity Walls: In
cavity wall construction, like cavity over the door or window should be
bridged by flexible material like bitumen felt, strips or lead etc.
General principles to be observed while laying DPC
are:
1.
The DPC should cover full thickness of walls
excluding rendering.
2.
The mortar bed upon which the DPC is to be laid
should be made level, even and free from projections. Uneven base is likely to
cause damage to DPC.
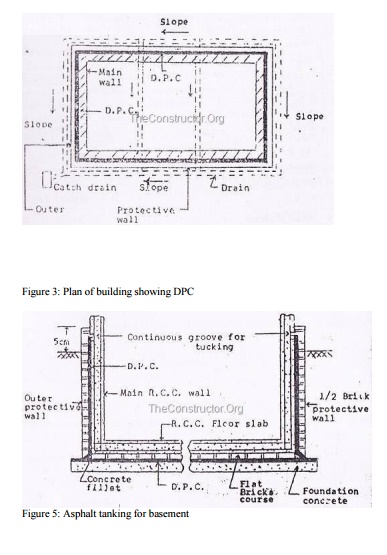
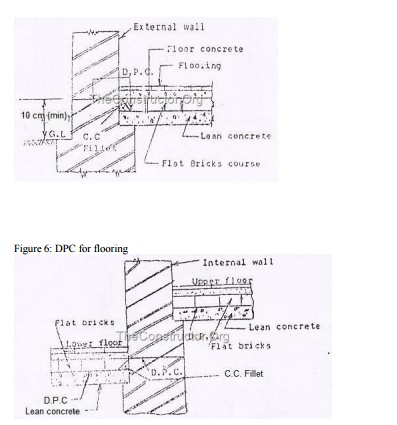
3.
When a horizontal DPC is to be continued up a
vertical face a cement concrete fillet 75mm in radius should be provided at the
junction prior to the treatment.
4.
Each DPC should be placed in correct relation to
other DPC so as to ensure complete and continuous barrier to the passage of
water from floors, walls or roof.

Related Topics