Pathogenesis and Pathology, Clinical Features, Laboratory Diagnosis | Medical Mycology - Cutaneous Mycoses | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 9 : Medical Mycology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 9 : Medical Mycology
Cutaneous Mycoses
Cutaneous Mycoses
Dermatophytoses
are the most common cutaneous fungal infection seen in man and animals
affecting skin, hair and nails. The fungi can invade the keratinized tissues of
skin and its appendages and they are collectively known as Dermatophytes or Tinea
or ring worm infection. The
dermatophytes are hyaline septate molds. They are divided into three main
anamorphic genera depending on their morphological characteristics.
i. Trichophyton [Cause infection in skin, hair and nails]
ii. Microsporum
[Cause
infection in skin and hair]
iii .Epidermophyton
[cause
infection in skin and nail]
The
fungal species affecting humans are known as anthropophilic. Those inhabitating domestic and wild animals as
well as birds are called zoophilic.
Fungi species from soil are known as geophilic
dermatophytes.
HOTS: What are the sources of dermatophytes?
Pathogenesis and Pathology
The
dermatophytes grow within dead keratinized tissue and produce keratinolytic
proteases, which provide means of entry into living cells. Fungal metabolic
products cause erythema, vesicles and pustule on the site of infection. Some
dermatophytes species like soil saprobes digest the keratinaceous debris in soil
and are capable of parasitizing keratinous tissues of animals
Clinical Features
The clinical manifestations of Dermatophytoses are
also called Tinea or Ringworm depending on the anatomical site involved. Following are the
common clinical conditions produced by dermatophytes:
1. Tinea
Capitis: This is an infection of
the shaft of scalp hairs. It can be
inflammatory (eg. Kerion, Favus) or non - inflammatory (Black dot, Seborrheic
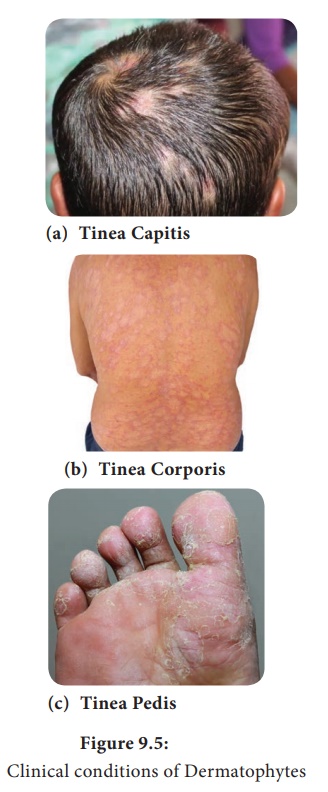
dermatitis). The infected hairs appear dull and grey (Figure 9.5a). Breakage of
hair at follicular orifice which creates patches of alopecia with black dots of
broken hair. It is caused by Trichophyton
species.
2. Tinea
Corporis: This is an infection on the glabrous (non - hairy) skin of body. Erythematous scaly lesions with sharply marginated raised
border appear on the infected areas (Figure 9.5b). It is caused by Trichophyton rubrum.
3. Tinea
Imbricata: It forms concentric rings of scaling on the glabrous
skin, leading to lichenification. It is caused by Trichophyton concentricum
4. Tinea
Gladiatorum: This infection
is common among wrestlers and athletes. Lesions are seen on arms, trunk or head and neck. It is caused by Trichophyton tonsurans.
5. Tinea Incognito: It is steroid modified Tinea caused as a result of misuse of corticosteroids in combination with topical antimycotic drugs.
6. Tinea Faciei: This is an infection of skin of face except beard. Erythematous annular plaques are formed.
It is one of the forms of Tinea incognito.
7. Tinea Barbae: This is the infection of the beard and moustache areas of the face. This is also called barber’s itch. It is caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum and Microsporum canis. Erythematous patches on the face with scaling appear and these
develop folliculitis.
8. Tinea
Pedis: This is an infection of
the foot, toes and interdigital web spaces. This is seen among the individuals wearing shoes for long
hours and known as Athlete’s foot (Figure 9.5c). Erythema and scaling associated with itching and
burning sensation appear with thin fluid discharging from small vesicles. It is
caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes,Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum.
9. Tinea Cruris: This is an infection of the groin in men who use long term tight fitting garments. Erythematou sharp
margin lesions known as Jock itch. It is caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum.
10. Tinea
Manuum: This is an infection of the skin of palmar aspect of hands. It
causes hyperkeratosis of the palms and fingers. It is caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton
rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum.
11. Tinea
Unguium: This is an infection of the nail plates. The infection spreads on
the entire nail plate infecting the nail bed. It results in opaque, chalky or
yellowish thick ended nail. It is caused by
Trichophytonmentagrophytes, Trichophyton
rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum
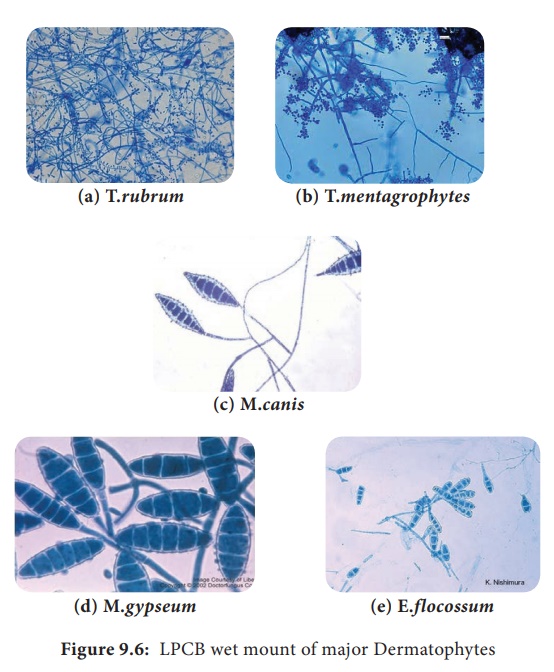
Figure
9.6 shows the microscopic view of major determatophytes
Infobits:
How do dermatophytes cause disease in
humans?
Dermatophytosis is a common contagious disease caused by fungi
known as dermatophytes. Dermatophytes belong to a group of organisms that are
able to break down the keratin in tissues such as the epidermis, hair, nails,
feathers, horns and hooves.
Laboratory Diagnosi
i. Samples
Skin
scrapings, hair and nail samples were collected
a. Direct Examination
Samples
are subjected to KOH (10%) wet mount, the affected site were disinfected with
alcohol before collecting the clinical specimen.
b. Fungal culture
The
samples are inoculated on Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) with antibiotics and
cycloheximide and are incubated at 25°C–35°C. The colony morphology can be
identified.
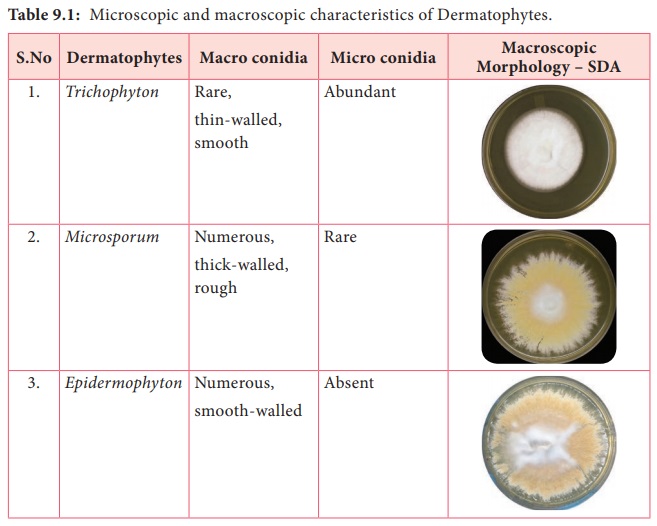
The three
genera of dermatophytes are Trichophyton,
Microsporum and Epidermophyton (Table 9.1). They are identified based on morphology of the macro conidia, micro
conidia, their shape, position on the spore bearing hyphae such as spiral
hypha, racquet hypha, nodular pectinate body.
ii. Special Techniques
1. Wood’s Lamp Examination
Clinical
samples are exposed to Wood’s lamp. Wood’s glass consists of Barium silicate
containing 9% Nickel oxide. It transmits long wave ultra violet light with a
peak of 365nm that shows a characteristic fluorescence produced by the samples.
The patterns of fluorescence are bright green, golden yellow and coral red. Microsporum species and Trichophyton species are differentiated using this technique.
2. Hair brush sampling Technique
It involves brushing the scalp with a sterile plastic hair brush, which is then inoculated into an appropriate culture medium by plates, is incubated at 25°C–35°C. The colony morphology can be identified.
Dermatophyte infections, also known as tinea, are the most common fungal infections of
the skin, hair, and nails.The term “dermatophyte” refers to fungal species that
infect keratinized tissue, and includes members of the Trichophyton,
Microsporum, and Epidermophyton genera
3. Hair perforation Test
It is
used to differentiate T. mentagrophytes
and T. rubrum. Wedge-shaped
perforations in the hair shaft are
observed in hair infected with T.
mentagrophytes.
4. Urease Test
It is used to differentiate between
mentagrophytes and T.
rubrum. T. mentagrophytes hydrolyzes
urea and becomes deep red, showing
positive result
iii. Treatment
Whitfield’s
ointment is used for all Tinea infections. Oral griseofulvin is the drug of
choice for nails and scalp infections. Itraconazole and terbinafine may be
given as pulse therapy.
Related Topics