Chapter: Fiber optics and Laser instruments : Optical Fiber and Their Properties
Construction of optical fiber cable
Construction of optical fiber
cable
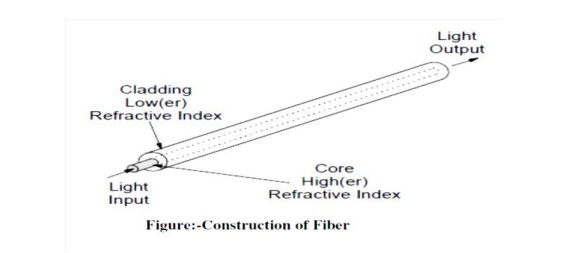
An
optical fiber is a very thin strand of silica glass in geometry quite like a
human hair. In reality it is a very narrow, very long glass cylinder with
special characteristics. When light enters one end of the fiber it travels
until it leaves the fiber at the other end. An optical fiber consists of two
parts: the core and the cladding. The core is a narrow cylindrical strand of
glass and the cladding is a tubular jacket surrounding it. The core has a
(slightly) higher refractive index than the cladding. Light travelling along
the core is confined by the mirror to stay within it even when the fiber bends
around a corner.
A fiber
optic cable has an additional coating around the cladding called the jacket.
The jacket usually consists of one or more layers of polymer. Its role is to
protect the core and cladding from shocks that might affect their optical or
physical properties. It acts as a shock 14
absorber.
The jacket also provides protection from abrasions, solvents and other
contaminants. The jacket does not have any optical properties that might affect
the propagation of light within the fiber optic cable.
1.Guiding mechanism in optical
fiber
Light ray
is injected into the fiber optic cable on the right. If the light ray is
injected and strikes the core-to-cladding interface at an angle greater than an
entity called the critical angle then it is reflected back into the core. Since
the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection the reflected
light will again be reflected. The light ray will then continue this bouncing
path down the length of the fiber optic cable. If the light ray strikes the
core-to-cladding interface at an angle less than the critical angle then it
passes into the cladding where it is attenuated very rapidly with propagation
distance. Light can be guided down the fiber optic cable if it enters at less
than the critical angle. This angle is fixed by the indices of refraction of
the core and cladding and is given by the formula
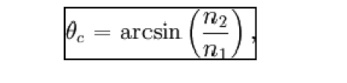
The
critical angle is measured from the cylindrical axis of the core. By way of
example, if n1 = 1.446 and n2 = 1.430 then a quick computation will show that
the critical angle is 8.53 degrees, a fairly small angle.
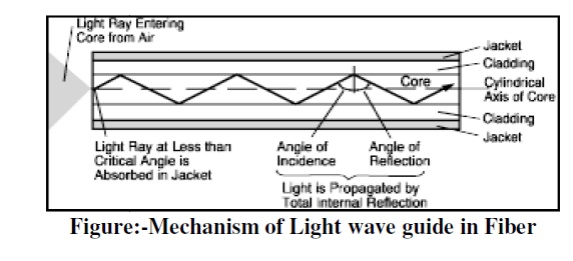
Of
course, it be noted that a light ray enters the core from the air outside, to
the left of Figure. The refractive index of the air must be taken into account
in order to assure that a light ray in the core will be at an angle less than
the critical angle. This can be done fairly simply. Suppose a
light ray
enters the core from the air at an angle less than an entity called the
external acceptance angle It will be guided down the core.
2. Basic component of optical
fiber communication
1
Transmitters - Fiber optic transmitters are devices
that include an LED or laser source, and signal conditioning electronics, to
inject a signal into fiber. The modulated light may be turned on or off, or may
be linearly varied in intensity between two predetermined levels.
2
Fiber – It is the medium to guide the light from
the transmitter to receiver.
3
Receivers – Fiber optic receivers are instruments
that convert light into electrical signals. They contain a photodiode
semiconductor, signal conditioning circuitry, and an amplifier at the receiver
end.
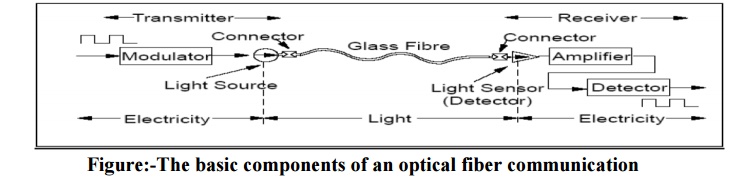
Process
of Optical Fiber Communication –
A serial
bit stream in electrical form is presented to a modulator, which encodes the
data appropriately for fiber transmission.
A light
source (laser or Light Emitting Diode - LED) is driven by the modulator and the
light focused into the fiber.
The light
travels down the fiber (during which time it may experience dispersion and loss
of strength).
At the
receiver end the light is fed to a detector and converted to electrical form.
The
signal is then amplified and fed to another detector, which isolates the
individual state changes and their timing. It then decodes the sequence of
state changes and reconstructs the original bit stream.
The timed
bit stream so received may then be fed to a using device
Related Topics