Chapter: Business Science : Managerial Behavior and Effectiveness : Concept of Managerial Effectiveness
Concept of Managerial Effectiveness
CONCEPT OF MANAGERIAL EFFECTIVENESS
1 Concept of Managerial Effectiveness
2 Measuring managerial effectiveness
3 Methods of Measuring Managerial Effectiveness
4 Current Industrial and Government Practices in
the Management of Managerial Effectiveness
5 Effective Manager as an Optimizer
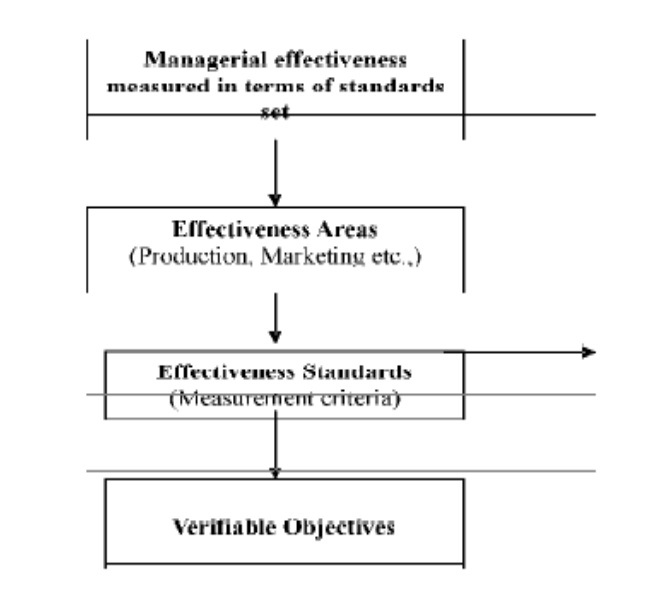
1 Concept of Managerial Effectiveness
Definition
:Managerial effectiveness is made measurable, verifiable, operational and more
specific with the help of effectiveness areas, standards and objectives
Describing
managerial effectiveness is in terms of effectiveness areas, effectiveness
standards and objectives.
Effectiveness
areas indicate general output requirements of managerial position.
The idea
of effectiveness is based on the view that all managerial positions are best
seen in terms of the output associated with it.
For e.g.,
the areas could be in terms of sales level, production level, inventory
control, best utilization of resources etc., the effectiveness areas emanate
from the strategy of the firm to make its organizational structure operational.
The
effectiveness areas are divided into sub-division
Effectiveness
areas can be broken down into effectiveness standards.
When
effectiveness standards are made more specific, they are called objectives.
Objectives
have time limits and numerical values are attached to them
2 Measuring managerial effectiveness
Managerial
effectiveness is measured through comparing the actual standard set with the achieved
standard.
Both the
standards will match perfectly provided the managers prove to be an effective
delegator, frank and fearless, well-defined, award subordinates for good job,
pro-active, innovative, energetic and adaptive in approach.
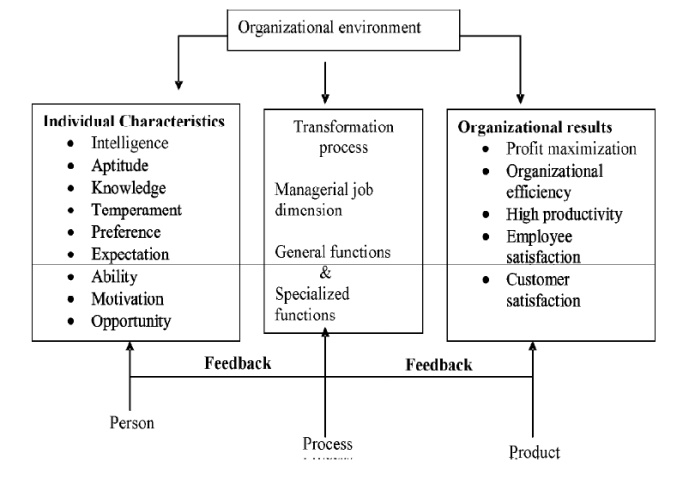
3 Methods of Measuring Managerial Effectiveness
1.The
Person, Process, Product Approaches – Bridging the gap
2.Managerial Grid
A graphic
presentation of a two dimensional view of leadership style has been developed
by Blake and Mouton
They
proposed a Managerial Grid based on the styles of ‘concern for people’ and ‘concern for production’
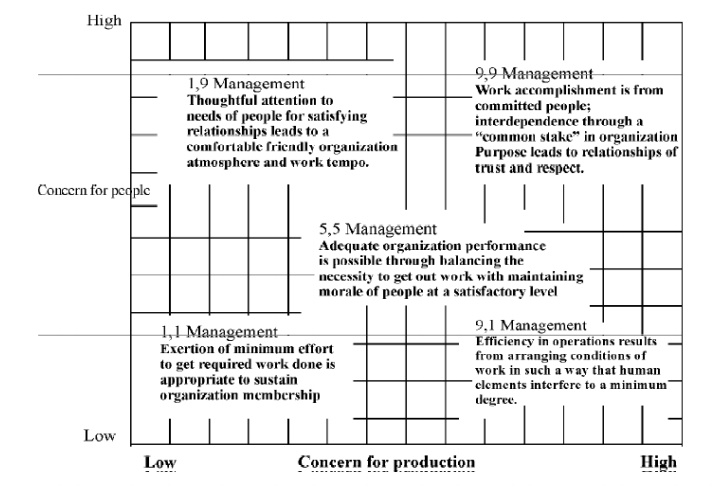
The grid identified five basic styles of
leadership.
The 9,1
(task management) leader is primarily concerned with production and has little
concern of people. This person believes in getting work done at all costs.
The 1,9
(country club management) leader is primarily concerned with people.
The 5,5
(middle of the road management) leader represents a moderate concern for both.
The 9,9
(team management) style demonstrates high concern for both production and
people and is therefore the ideal approach to leadership.
The 1,1 (
impoverished management) has minimum concern for people and production.
The model
is useful to managers in as much as it helps them identify their current styles and develop the most desirable style.
It seems
unlikely that the 9,9 management style is appropriate for organizations
experiencing different growth rates,
labour relations, competition, and a host of other differentiating problems
GLOBAL MEASURES OF MANAGERIAL EFFECTIVENESS
Managerial Effectiveness an also be measured
through
Supervisory
rankings
Salary
Hierarchical
position
Strengths of such a measurement
Period of
assessment is long, so it is fairly stable.
It can be
used for validation.
Close
monitoring by supervisor is there.
Peer
rankings form a basis of comparison.
Weaknesses-It suffers from deficiency
Measures
only a small portion of variance caused by behaviour
Variations
are dependent on many other factors
Some
factors are not controllable by managers.
Subjective
criteria need to be relied on.
Example : In General Electric Company the evaluator
evaluates effectiveness based on
Absence
rate
Separation
rate
Medical
leave
Disciplinary
actions
Suggestion
submitted
Grievance
Certain other Industries
Use
observations.
Use
tests.
Use
correlation measurements.
Personality
inventories.- emotional stability, sociability, general activity
Leadership
ability test
4 Current Industrial and Government Practices in
the Management of Managerial Effectiveness
The
government and industries have adopted certain practices to ensure the
effectiveness of managers which involves
completion
of work on time
effective
and efficient output
management
of knowledge and information
careful
preparations of meetings and
presentations
and follow-up with deviations and corrections to ensure that agreements and
commitments have been fulfilled.
1. Sets up
procedures to ensure high quality of work (e.g., review meetings).
2. Arrange
for training and executive development programs
3. Involvement
in career development program of its employees.
4. Monitor
the quality of work through performance appraisal.
5. Verification
of information through feedback.
6. Checking
the accuracy of one‘s own and others‘ work.
7. Developing
and using systems to organize and keep track of information or work progress.
8. Carefully
preparing for meetings and presentations.
9. Organizing
information or materials for others.
10.
Carefully reviewing and checking the accuracy of
information in work reports (e.g., production, sales, financial performance)
provided by management, management information systems, or other individuals
and groups.`
Some
other areas, which require attention of both the government and the industries
in the management of managerial effectiveness
1. Developing Initiative
Drive : High motivation for work and also
encourage others to work towards a common goal.
Energy : Enthusiastic in work place.
Self-starter : Does jobs proactively and seizes
the opportunities.
2.Encouraging self management approach
Team player : Works in a team, supports and
encourages team members.
Leader : Defines goals and standards of
performance, delegates and allocates work according to abilities.
Develops subordinates : Identifies,
train and involves people in all activities.
Individual / Disciplined :
Maintains decorum of the workplace, has respect for seniors and juniors
3.Facilitating appropriate Communication
Articulate / expressive: Can
communicate (verbal & written) in a fashion, which is understood and appreciated by people.
Persuasive/ winning : Sticks to
a problem until it is resolved.
Supportive : Supports subordinates in their
work.
Confident : Has confidence in his values and
action
The
skills and competencies of their managers would help them perform better in
certain core areas like:
Ability to plan : Formulate,
plans and business goals.
Organize : Divide jobs into logical
entities.
Execute : Works according to plans.
Meet Deadlines : Follow a strict schedule and
completes a job.
Adoption of Skills by Managers for Effective
Management of Corporate
Certain
skills should be practiced and developed by the managers in order to
efficiently perform their responsibilities in a competitive driven business environment.
1. Problem solving:
Identifies
the specific information needed to clarify a situation or to make a decision.
Gets more
complete and accurate information by checking the multiple sources.
Probes
skilfully to get at the facts, when others are reluctant/unwilling to provide
full, detailed information.
Routinely
walks around to see how people are doing and to hear about any problems they
are encountering.
Questions
others to assess whether they have thought through a plan of action.
Questions
others to assess their confidence in solving a problem or tackling a situation.
Asks
questions to clarify a situation.
Seeks the
perspective of everyone involved in a situation.
Seeks out
knowledgeable people to obtain information or clarify a problem.
2. Analytical thinking: The
ability to tackle a problem by using a logical, systematic, sequential approach.
Makes a
systematic comparison of two or more alternatives.
Notices
discrepancies and inconsistencies in available information.
Identifies
a set of features, parameters or considerations to take into account, in
analyzing a situation or making a decision.
Approaches
a complex task or problem by breaking it down into its component parts and
considering each part in detail.
Weigh the
costs, benefits, risks and chances for success, in making a decision.
Identifies
many possible causes for a problem.
Carefully
weighs the priority of things to be done.
3. Forward thinking: The
ability to anticipate the implications and consequences of situations and take appropriate action to be prepared
for possible contingencies.
Anticipates
possible problems and develops contingency plans in advance.
Notices
trends in the industry or market place and develops plans to prepare for
opportunities or problems.
Anticipates
the consequences of situations and plans accordingly.
Anticipates
how individuals and groups will react to situations and information and plans
accordingly.
4. Conceptual thinking: The
ability to find effective solutions by taking a holistic, abstract, for theoretical perspective.
Notices
similarities between different unrelated situations.
Quickly
identifies the central or underlying issues in a complex situation.
Creates a
graphic diagram showing a systems view of a situation.
Develops
analogies or metaphors/ descriptions to explain a situation.
Applies a
theoretical framework to understand a specific situation.
Adjusts
behavior, strategies according to changing environment and circumstances.
Goes
beyond conventional thinking and produces imaginative or unique response to a
problem
5. Strategic thinking: The
ability to analyze the organization‘s competitive position by considering market and industry trends, existing
and potential customers (internal and external), and strengths and weaknesses
as compared to competitors.
Understands
the organization‘s strengths and weaknesses as compared to competitors.
Understands
the industry and market trends affecting the organization‘s competitiveness.
Has an
in-depth understanding of competitive products and services available within
the marketplace.
Develops
and proposes a long term (3-5 year) strategy for the organization based on an
analysis of the industry and marketplace and the organization‘s current and
potential capabilities to other competitors.
6. Technical expertise: The
ability to demonstrate depth of knowledge and skill in a technical area.
Effectively
applies technical knowledge to solve a range of problems.
Possesses
an in-depth knowledge and skill in a technical area.
Develops
technical solutions to new or highly complex problems that cannot be solved
using existing methods or approaches.
Is sought
out as an expert to provide advice or solutions in his/her technical
specialization
Keeps
informed about cutting-edge technology in his/her technical area.
7. Entrepreneurial orientation: The
ability to look for and seize profitable business opportunities; willingness to take calculated risks
to achieve business goals.
Notices
and seizes profitable business opportunities.
Stays
abreast of business, industry and market information that may reveal many
business opportunities.
Demonstrates
willingness to take calculated risks to achieve business goals.
Proposes
innovative business deals to potential customers, suppliers and business
partners.
Encourages
and supports entrepreneurial behavior in others
8. Fostering innovation: The
ability to develop, sponsors, or support the introduction of new and improved method, products, procedures,
or technologies.
Personally
develops a new product or service, process or approach, methods and
technologies.
Supports
the development of new products, services, methods or procedures.
Develops
better, faster, or less expensive ways to do things.
Works
cooperatively with others to produce innovative solutions.
9. Results Orientation: The
ability to focus on the desired result of one‘s own or one‘s unit‘s work‘s setting challenging goals, focusing
effort on the goals and meeting or exceeding them.
Develops
challenging but achievable goals.
Develops
clear goals for meetings and projects.
Maintains
commitment to goals in the face of obstacles and frustrations.
Finds or
creates ways to measure performance against set goals.
Exerts
unusual effort over time to achieve a goal.
Has a
strong sense of urgency about solving problems and getting work done.
10.
Decisiveness:
The
ability to make difficult decisions in a timely manner.
Is
willing to make decisions in difficult or ambiguous situations, when time is
critical.
Takes
charge of a group when it is necessary to facilitate change, overcome an
impasse, face issues, or ensure that decisions are made.
Makes
tough decisions (e.g., closing a facility, reducing staff, accepting or
rejecting a high-stakes deal).
11.Self Confidence: Faith in
one‘s ideas and capability to be successful; willingness to take an independent position in the face of
any opposition.
Is
confident of own ability to accomplish goals.
Presents
oneself impressively
Is
willing to speak up to the right person or group at the right time, when he/she
disagrees with a decision or strategy.
Approaches
challenging tasks with a ―can-do‖ attitude.
12. Stress Management: The
ability to keep functioning effectively when under pressure and maintain self control in the face of
hostility or provocation/ frustration.
Remains
calm under stress.
Can
effectively handle several problems or tasks at once.
Controls
his/her response when criticized, attacked or provoked.
Maintains
a sense of humor under difficult circumstances.
Manages
own behaviour to prevent or reduce feelings of stress.
13.
Personality
Credibility: Demonstrated concern that one be perceived as
responsible, reliable and trustworthy.
Does what
he/she commits to doing.
Respects
the confidentiality of information or concerns shared by others.
Is honest
and forthright/direct with people.
Carries
his/her fair share of the workload.
Takes
responsibility for own mistakes; does not blame others.
Conveys a
command of the relevant facts and information.
14.
Flexibility:
Openness
to different and new ways of doing things; willingness to modify one‘s preferred way of doing things.
Is able
to see the merits of perspectives other than his/her own.
Demonstrates
openness to new organizational structure, procedures and technology.
Switches
to a different strategy when an initially selected one is unsuccessful.
Demonstrates
a willingness to modify a strongly held position in the face of contrary
evidence.
5 Effective Manager as an Optimizer
Effective
manager focuses on what he is doing and efficiency deals with how well he does
with minimum wastage of resources.
Since
managers deal with input resource that is scarce such as money, people,
equipment, and time, they should be more concerned about its efficient utility,
minimizing resource cost and optimizing the output.
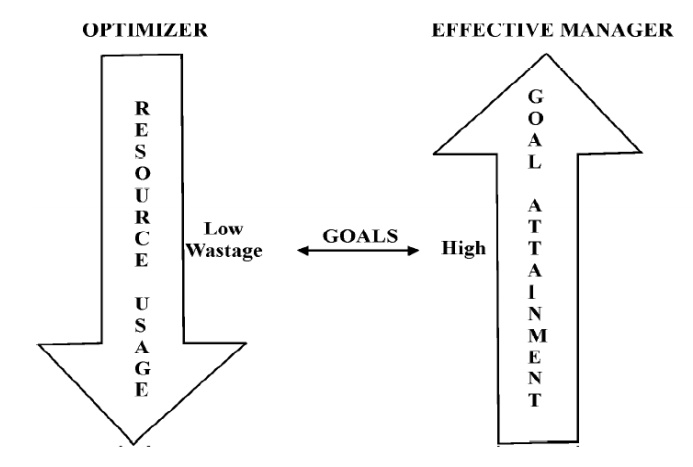
According
to Campbell, in his behavioural approach, effective manager is said to be an
optimizer in utilizing all available and potential resources.
Effective
managerial job behaviour talks about as "any set of managerial actions
believed to be optimal for identifying, assimilating/ incorporating and
utilizing both internal and external resources towards the functioning of the
organizational unit and sustaining in the long run, for which a manager has
high degree of responsibility‖.
Therefore
effective manager is expected to work as an optimizer by focusing on low waste
and high goal attainment
Effective
managers do differently from their less-effective counterparts.
Have high
concern for people and productivity
Effective
managers are able to communicate
Spend
Time in Managing
Using
General Style
Allow
Employees to Influence them
Have
influence upward
Minimize
Status Differences
Spend
Time Managing
The effective manager spend most of their time manager . That is they
spend most of their time identifying opportunity for improvement, locating
problems, training subordinates , developing contacts with other in the
organization, working through inter- unit differences .
Manager
as a Optimizer
The
actions he is to take will arise from the answers a manager gives to these
questions.
§ What is
my potential contribution?
§ What are
my objectives?
§ What does
it take to be effective here?
§ What
needs changing?
§ What is
organization‘s philosophy
§ What can
I do now?
Related Topics