Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Complexometric Analysis
Complexometric Analysis: Assay Methods
ASSAY METHODS
The complexometric titrations involving various inorganic
pharmaceutical substances may be catego-rized into three broad heads, namely :
(i) Direct
titration methods,
(ii) Masking
and demasking agents, and
(iii) Residual
titration methods.
1. DIRECT TITRATION METHODS
In direct titration, usually an appropriate buffer
solution and a suitable indicator are added to the M2+ (metal-ion)
solution and subsequently the resulting solution is titrated with previously
standardized disodium-EDTA until the indicator just changes colour. Sometimes,
a simultaneous blank determination is also recommended to have a check for the
presence of traces of metallic impurities in the reagents.
1.1. Preparation of 0.05 M Disodium Ethylenediamine Tetracetate Solution (Disodium Edetate 0.05 M)
Materials Required : Disodium
ethylenediaminetetracetate : 18.6 g.
Procedure : Weigh accurately 18.6 g of
disodium ethylenediaminetetracetae, dissolve in sufficient DW in a 1 litre volumetric flask and make up the volume upto the
mark.
Calculations :
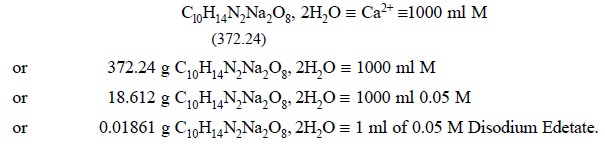
1.2. Standardization of 0.05 M Disodium Edetate Solution
Materials Required : Granulated zinc : 0.8 g ;
dilute HCl (10% w/v of HCl) : 12.0 ml ; bromine water (3 ml Br2 in
100 ml H2O) : 5 ml ; sodium hydroxide (2 N) : 20.0 ml ; ammonia
buffer (pH 10.0) (dissolve 5.4 g of NH4Cl in 70 ml of 5 N ammonia
and dilute with water to 100 ml) : 100 ml ; Mordant Black II mixture (mixture
of 0.2 part Mordant Black II with 100 parts of NaCl) : 50 mg ; disodium edetate
: 0.05 M.
Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.8 g
of granulated zinc, dissolve by gentle warming in 12 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid and 5 drops of bromine water. Boil to
remove excess bromine, cool and add sufficient DW to produce 200 ml in a
volumetric flask. Pipette 20 ml of the resulting solution into a flask and
neutralize carefully with 2 N sodium hydroxide. Dilute to about 150 ml with DW,
add to it sufficient ammonia buffer (pH 10.0) to dissolve the precipitate and
add a further 5 ml quantity in excess. Finally add 50 mg of Mordant Black II
mixture and titrate with the disodium edetate solution until the solution turns
green. Each 0.003269 g of granulated zinc is equivalent to 1 ml of 0.05 M
disodium ethylenediaminetetracetate.
Calculations :
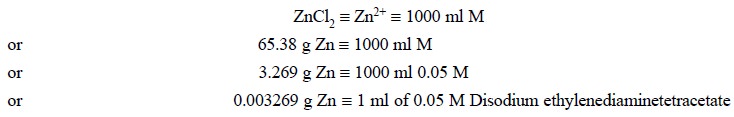
1.3. Calcium Chloride
Materials Required : Calcium chloride dihydrate :
0.15 g ; dilute hydrochloric acid (10% w/w of HCl) : 3.0 ml ; 0.05 M disodium
edetate ; sodium hydroxide solution (20% w/v in water) ; calcon mixture (a
mixture of 1 part of calcon with 99 parts of freshly ignited anhydrous Na2SO4)
: 0.1 g.
Equations :

Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.15 g
of calcium chloride dihydrate and dissolve it in 50 ml of DW. Titrate with 0.05 M disodium ethylenediamine tetracetate to
within a few ml of the expected end point, add 8.0 ml of sodium hydroxide
solution and 0.1 g of calcon mixture and continue the titration until the
colour of the solution changes from pink to a full blue colour. Each ml of 0.05
M disodium ethylene disodium tetracetate is equivalent to 0.007351 g of CaCl2
. 2H2O.
1.4. Magnesium Sulphate
Materials Required : Magnesium sulphate
heptahydrate : 0.3 g ; strong ammonia-ammonium chloride solution (6.75 g NH4Cl in 74.0 ml strong
ammonia solution add water q.s. to produce to 100 ml) ; 0.05 M disodium edetate
; Mordant Black II mixture (mixture of 0.2 part mordant black II with 100 parts
of NaCl) : 0.1 g.
Equations :
The assay of MgSO4.7H2O is based
upon the reactions designated by the following equations :

Procedure : Weigh accurately about 0.3 g
of magnesium sulphate heptahydrate and dissolve in 50 ml of DW. Add to it 10 ml of strong ammonia-ammonium chloride
solution, and titrate with 0.05 M disodium ethylenediaminetetracetate employing
0.1 g of mordant black II mixture as indicator, until the pink colour is
discharged from the blue. Each ml of 0.05 M disodium ethylenediaminetetracetate
is equivalent to 0.00602 g of MgSO4.
1.5. Cognate Assays
A number of pharmaceutical inorganic substances may be
assayed by the direct titration method using disodium ethylenediaminetetracetate.
A few typical examples are cited in the following Table 9.2.
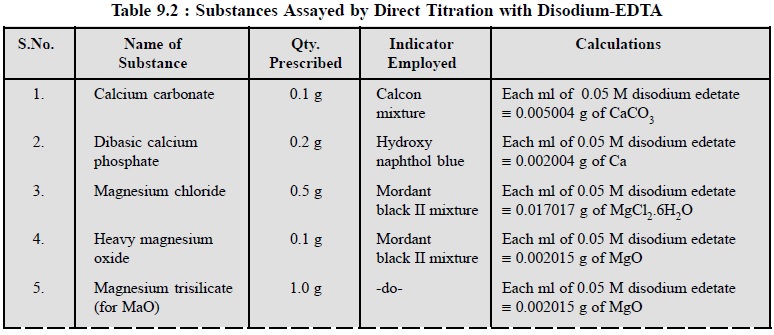
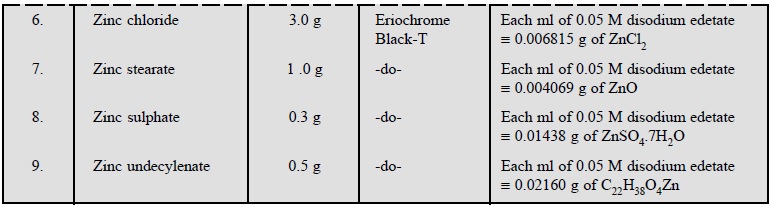
2. MASKING AND DEMASKING AGENTS
The disodium ethylenediaminetetracetate usually complexes
with a wide spectrum of cations, which ultimately renders the selectivity of
the titration procedure adversely, thereby providing enough scope for the
accompanying metal impurities to be titrated along with the ion it is aimed at
for actual estimation. Therefore, in a situation where one or two ions present
in a mixture of cations is specifically required to be determined with a view
to eliminate completely the possible effects of unwanted impurities that may
enhance the titre value, a third substance is added, which is known as the
Masking Agent. These agents must fulfil the follow-ing three requirements, namely :
(a) should act
by precipitation,
(b) should form
complexes that are definitely more stable than the interfering ion-edetate
complex, and
(c) colour
developed by either precipitates or auxiliary complexes should not obscure the
end-point.
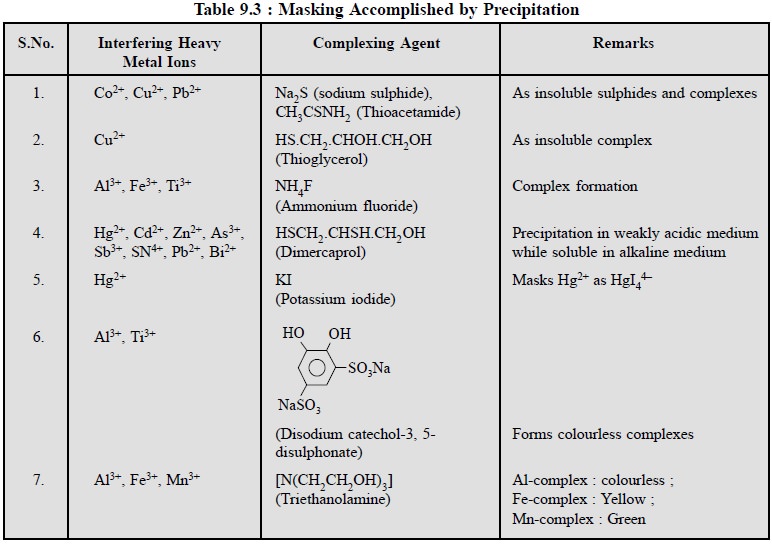
A few typical examples are cited below in Table 9.3 where
masking has been accomplished by precipitation.
3. RESIDUAL TITRATION METHODS
Direct titration method offers a serious limitation for
the assay of aluminium and bismuth containing pharmaceutical inorganic
substances because of the precipitation of the metal as their corresponding
hydroxides in alkaline media thereby introducing undesirable errors.
In actual practice, an excess of the standard solution of
disodium edetate is added to the sample, pH is adequately adjusted for the
residual titration with a metal-ion solution e.g., ZnSO4 and employing an appropriate indicator which
is sensitive enough to the respective titrant. However, the metal ion under
estimation remains firmly complexed with the EDTA and offers little
interference with the Zn-EDTA complex formed. It has been established
experimentally that bismuth readily yields a highly stable complex which may be
titrated conveniently between pH 1 and 2. Bismuth forms a stable complex by
reacting with EDTA quantitatively at pH 4.0 and, therefore, dithizone is
employed as an indicator to detect the end-point for it has a transition state
of colour at pH 4.6.
3.1. Potassium Alum, KAl(SO4)2, 12H2O
Materials Required : Potassium alum : 1.7 g ; 0.05
M disodium edetate : 30.0 ml ; hexamine : 1.0 g ; 0.05 M lead nitrate ; xylenol
orange solution (0.1% w/v in water) : 0.4 ml.
Theory : The solution of potassium alum
is heated with an excess of disodium edetate to ensure complete formation of aluminium-edetate complex. Hexamine serves
as a buffer thereby stabilizing the pH between 5 and 6, the ideal pH for the
titration of the disodium edetate not required by the Al with 0.05 M lead
nitrate employing xylenol orange as indicator. The various reactions involved
may be represented by the following equations :
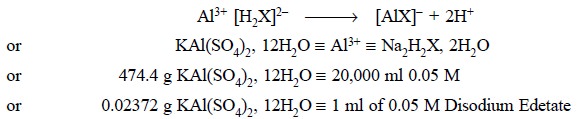
Procedure : Weigh accurately 1.7 g of
potassium alum and dissolve it in suffcient DW in a flask. Heat the contents of flask over a water-bath
for 10 minutes to allow completion of complexation and cool to ambient
temperature. Now, add 1 g hexamine to act as buffer and titrate with 0.05 M
lead nitrate employing 0.4 ml of xylenol orange solution as an indicator. The
colour shall change from that of the indicator (yellow at the pH of the
titration) to the corresponding reddish purple, the colour of the lead complex
of the indicator. Each ml of 0.05 M disodium edetate is equivalent to 0.02372 g
of KAl(SO4)2, 12H2O.
3.2. Glycobiarsol [Bismethyl-N-glycolyl-arsanilate]
Materials Required : Glycobiarsol : 0.2 g ; 0.05 M
disodium edetate : 10.0 ml ; acetic acid-ammo-nium acetate buffer (mix 13.6 g
of sodium acetate and 7.7 g of ammonium acetate in water to make 100 ml. Add
25.0 ml of glacial acetic acid and mix) : 10.0 ml ; alcohol : 25.0 ml :
dithizone solution (0.05% w/v in chloroform) : 2.0 ml ; 0.025 M ZnSO4
solution.
Procedure : Weigh accurately 0.20 g of
glycobiarsol into a 250-ml conical flask and add 10.0 ml of 0.05 M disodium edetate. Warm the contents of the flask over a
water-bath until glycobiarsol gets dissolved completely and then cool the
contents to the room temperature (25°C). Add to it 10.0 ml of acetic
acid-ammonium acetate buffer, 25.00 ml of alcohol and 2 ml of dithizone solution
as an indicator. Titrate the excess of disodium edetate with 0.025 M zinc
sulphate until the resulting solution turns rose pink in colour. Each
millilitre of 0.05 M disodium edetate consumed is equivalent to 10.45 mg of Bi.
Note : The content of Bi, calculated
on dried basis, lies between 38 to 42.5%.
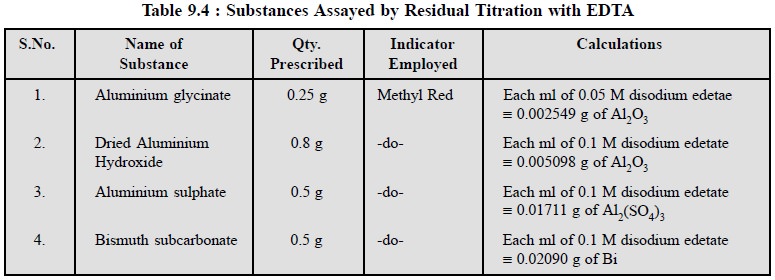
3.3. Cognate Assays
A number of inorganic pharmaceutical substances may be
assayed by adopting the residual titration method as depicted in Table 9.4.
Related Topics