Accountancy - Classification of errors | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Rectification of Errors
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Rectification of Errors
Classification of errors
Classification of errors
The errors can be classified into
four types as follows:
1. Error of omission
The failure of the accountant to record a transaction or an item in the
books of accounts is known as an error of omission. It can be complete omission
or partial omission.
(i) Error of complete omission
It means the failure to record a transaction in the journal or subsidiary
book or failure to post both the aspects in ledger. This error affects two or
more accounts.
Examples

(ii) Error of partial omission
When the accountant has failed to record a part of the transaction, it is known as error of partial omission. This error usually occurs in posting. This error affects only one account.
Examples


2. Error of commission
When a transaction is incorrectly recorded, it is known as error of
commission. It usually occurs due to lack of concentration or carelessness of
the accountant.
The following are the
possibilities of error of commission:
i. Entering a wrong amount in a correct subsidiary book
Examples

ii. Entering a correct amount in a wrong subsidiary book
Examples

iii. Entering a wrong amount in a wrong subsidiary book
Examples

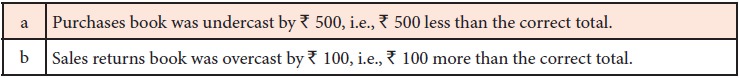
iv. Over-casting or under-casting in a subsidiary book
Examples
v. Posting a correct amount to the wrong side of an account in the Ledger
Examples

vi. Posting a wrong amount to the correct side of an account
Examples
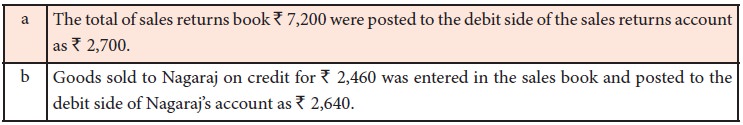
vii. Posting a wrong amount to the wrong side of an account
Examples

viii. Posting a correct amount to a wrong account
Examples

ix. Posting a wrong amount to a wrong account
Examples

x. Double posting in an account
Example

xi. Entering a transaction twice in the journal
Examples

xii. Errors arising in carrying forward from one page to the next page of an account
While carrying forward the total of one page of a ledger account to the
next page, the wrong amount may be recorded

(xiii) Error arising in the balancing of an account
Sometimes, at the time of balancing a ledger account, the wrong balance
may be written.
3. Error of principle
It means the mistake committed in the application of fundamental
accounting principles in recording a transaction in the books of accounts.
The following are the
possibilities of error of principle:
i. Entering the purchase of an asset in the purchases book
Example

ii. Entering the sale of
an asset in the sales book
Example

iii. Treating a capital expenditure as a revenue expenditure
Examples

iv. Treating a revenue expenditure as a capital expenditure
Example

4. Compensating errors
The errors that make up for each other or neutralise each other are
known as compensating errors. These errors may occur in related or unrelated
accounts. Thus, excess debit or credit in one account may be compensated by
excess credit or debit in some other account. These are also known as
offsetting errors.
Examples

Related Topics