Chapter: Power System Analysis : Stability Analysis
Classification of Power System Stability - Angle and Voltage Stability
Importance Of Stability Analysis In Power System Planning And Operation
Power system stability
The stability of an interconnected power system means is the ability of the power system is to return or regain to normal or stable operating condition after having been subjected to some form of disturbance.
Classification Of Power System Stability - Angle And Voltage Stability
Power system stability is classified
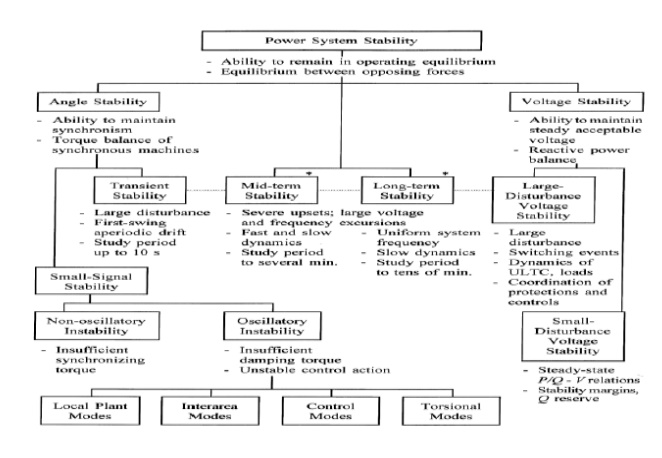
ANGLE AND VOLTAGE STABILITY
Rotor angle stability
Rotor angle stability is the ability of interconnected synchronous machines of a power system to remain in synchronism.
Steady state stability
Steady state stability is defined as the ability of the power system to bring it to a stable condition or remain in synchronism after a small disturbance.
Steady state stability limit
The steady sate stability limit is the maximum power that can be transferred by a machine to receiving system without loss of synchronism
Transient stability
Transient stability is defined as the ability of the power system to bring it to a stable condition or remain in synchronism after a large disturbance.
Transient stability limit
The transient stability limit is the maximum power that can be transferred by a machine to a fault or a receiving system during a transient state without loss of synchronism.Transient stability limit is always less than steady state stability limit
Dynamic stability
It is the ability of a power system to remain in synchronism after the initial swing (transient stability period) until the system has settled down to the new steady state equilibrium condition
Voltage stability
It is the ability of a power system to maintain steady acceptable voltages at all buses in the system under normal operating conditions and after being subjected to a disturbance.
Causes of voltage instability
A system enters a state of voltage instability when a disturbance, increase in load demand, or change in system condition causes a progressive and uncontrollable drop in voltage. The main factor causing instability is the inability of the power system to meet the demand for reactive power.
Related Topics