Chapter: Power System Analysis : Symmetrical Components And Unbalanced Fault Analysis
Important Short Questions and Answers: Symmetrical Components And Unbalanced Fault Analysis
1. What
is meant by a fault?
A fault
in a circuit is any failure which interferes with the normal flow of current.
The faults are associated with abnormal change in current, voltage and
frequency of the power system.
2. Why
fault occur in a power system?
The
faults occur in a power system due to insulation failure of
equipments,flashover of lines initiated by a lightning stroke, due to permanent
damage to conductors and towers or due to accidental faulty operations.
3. List the various types of shunt and series faults. The various types
of shunt faults are:
(i)Line to Ground fault
(ii) Line to Line fault
(iii)Double line to Ground fault
(iv) Three phase fault
The
various types of series faults are:
(i)One open conductor fault
(ii)
Two open conductor fault
4. What
is symmetrical unsymmetrical fault?
The fault
is called symmetrical fault if the fault current is equal in all the phases.The
fault is called unsymmetrical fault if the fault current is not equal in all
the phases.
5. Name any two methods of reducing short –circuit current.
(i)By providing neutral reactance.
(ii)By
introducing a large value of shunt reactance between buses.
6.
What is meant by fault calculations?
The fault
condition of a power system can be divided into subtransient, transient and
steady state periods. The currents in the various parts of the system and in
the fault are different in these periods. The estimation of these currents for
various types of faults at various locations in the system are commonly
referred to as fault calculations.
7. What
is the need for short circuit studies or fault analysis?
The short
circuit studies are essential in order to design or develop the protective
schemes for various parts of the system. The protective schemes consists of
current and voltage sensing devices , protective relays and circuit breakers.
The selection of these devices mainly depends on various currents that may flow
in the fault conditions.
8. What
is synchronous reactance?
The
synchronous reactance is the ratio of induced emf and the steady rms current.
It is the sum of leakage reactance and the reactance representing armature
reaction.
9. Define
subtransient reactance.
The
subtransient reactance is the ratio of induced emf on no load and the subtransient
symmetrical
rms current.
10.
Define transient reactance.
The
subtransient reactance is the ratio of induced emf on no load and the transient
symmetrical rms current.
11. Name
the fault in which positive, negative and zero sequence component currents are
equal.
In Single line to ground fault positive, negative and zero sequence component currents are equal.
12. Name
the fault in which positive and negative sequence component currents together
is equal to zero sequence current in magnitude.
Double
line to ground fault.
13.
Define positive sequence impedance.
The
positive sequence impedance of an equipment is the impedance offered by the
equipment to the flow of positive sequence currents.
14.
Define negative sequence impedance.
The
negative sequence impedance of an equipment is the impedance offered by the
equipment to the flow of negative sequence currents.
15. Write the boundary condition in single line to ground fault.
Va = 0 ; Ib
= Ic = 0
16. What
are the boundary conditions in line to line fault?
Ia
= 0 ; Ib + Ic = 0 ; Vb = Vc
17. Write
down the boundary condition in double line to ground fault. Ia = 0 ;
Vb = 0 ; Vc= 0
18. Give
the boundary condition for 3-phase fault.
Ia
+ Ib = Ic = 0 ; Va = Vb = Vc=
0
Part-B
1.A
balanced delta connected load is connected to a three phase system and supplied
to it is a current of 15 amps. If the fuse is one of the lines melts, compute
the symmetrical components of line currents
2. 2.Draw
zero sequence network of the power system as shown in fig.
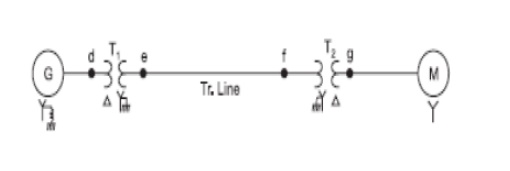
3.A
50MVA, 11KV, synchronous generator has a sub transient reactance of 20%.The
generator supplies two motors over a transmission line with transformers at
both ends as shown in fig. The motors have rated inputs of 30 and 15 MVA, both
10KV, with 25% sub transient reactance. The three phase transformers are both
rated 60MVA, 10.8/121KV, with leakage reactance of 10% each. Assume zero
sequence reactance for the generator and motors of 6% each. Current limiting
reactors of 2.5 ohms each are connected in the neutral of the generator and
motor number 2. The zero sequence reactance of the transmission line is 300
ohms. The series reactance of the line is 100 ohms. Draw the positive, negative
and zero sequence networks.
4.A 30
MVA, 13.2KV synchronous generator has a solidly grounded neutral. Its positive,
negative and zero sequence impedances are 0.30, 0.40 and 0.05 p.u respectively.
Determine the following:
i. What
value of reactance must be placed in the generator neutral so that the fault
current for a line to ground fault of zero fault impedance shall not exceed the
rated line current?
ii. What
value of resistance in the neutral will serve the same purpose?
iii.
What value of reactance must be placed in the
neutral of the generator to restrict the fault current to ground to rated line
current for a double line to ground fault?
iv.
What will be the magnitudes of the line currents
when the ground current is restricted as above?
v.
j) As the reactance in the neutral is indefinitely
increased, what are the limiting values of the line currents?
Related Topics