Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 29 : Elements of Contract
Classification/Types of Contract
Classification/Types of Contract
TYPES OF CONTRACTS
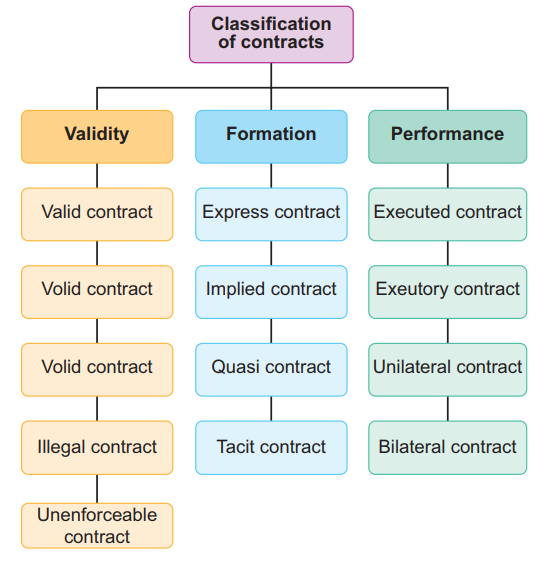
I. On the Basis of the validity
1. Valid Contract
An agreement which fulfils all the essentials prescribed by law on the basis of its creation. For example S offers to sell his car for Rs.2,00,000 to T. T agrees to buy it. It is a Valid Contract.
2. Void Contract (2(j))
A contract which ceases to be
enforceable by law. A contract which does not satisfy any of the essential
elements of a valid contract is said to be Void. For example A contract between
drug dealers to buy and sell drugs is a void contract.
3. Voidable Contract 2(i)
An agreement which is enforceable by law
at the option of one or more parties but not at the option of the other or
others is a voidable contract. This is the result of coercion, undue influence,
fraud and misrepresentation.
4. Illegal Contract
It is a contract which is forbidden by
law. All illegal agreements are Void but all void agreements or contracts are
not necessarily illegal. Contract that is immoral or opposed to public policy
are illegal in nature.
·
Unlike illegal agreements there is no
punishment to the parties to a void agreement.
·
Illegal agreements are void from the
very beginning but sometimes valid contracts may subsequently become void.
5. Unenforceable Contract
Where a contract is unenforceable
because of some technical defect i.e. absence in writing barred by imitation
etc. If the parties perform the contract it will be valid, but the court will
not compel them if they do not
II. On the Basis of the Formation
1. Express Contract
A contract made by word spoken or
written. According to Section. 9, in so for as the proposal or acceptance of
any promise is made in words, the promise is said to be express. For example P
says to Q ‘will you buy my bicycle for Rs.1,000?” Q says to P “Yes”.
2. Implied Contract
The implied contract is one, which is
not expressly written but understood by the conduct of parties. Where the
proposal or acceptance of any promise is made otherwise than in words, the
promise is said to be implied. For example A gets into a public bus, there is
an implied contract that he will pay the bus fare.
3. Quasi Contract
It is a contract created by law.
Actually, there is no contract. It is based on the principle that “a person
shall not be allowed to enrich himself unjustly at the expense of the other”.
In other words it is an obligation of one party to another imposed by law
independent of an agreement between the parties.
4. Tacit Contract
A contract is said to be tacit when it
has to be inferred from the conduct of the parties. For example obtaining cash
through automatic teller machine, sale by fall of hammer of an auction sale.
III. On the Basis of Performance
1. Executed Contract
A contract in which both the
parties have fulfilled their
obligations under the contract. For example X contracts to buy a car from Y by paying cash, Y instantly
delivers his car.
2. Executory Contract
A contract in which both the parties are
yet to fulfil their obligations, it is said to be an executory contract. For
example A agrees to buy B’s cycle by promising to pay cash on 15th June. B
agrees to deliver the cycle on 20th June.
3. Unilateral Contract
A unilateral contract is a one sided
contract in which only one party has performed his promise or obligation, the
other party has to perform his promise or obligation.
For example X promises to pay Y a sum of
Rs.10,000 for the goods to be delivered by Y. X paid the money and Y is yet to
deliver the goods.
4. Bilateral Contract
A contract in which both the parties
commit to perform their respective promises is called a bilateral contract. For
example R offers to sell his fiat car to S for Rs.10,00,000 on acceptance of
R’s offer by S, there is a promise by R to Sell the car and there is a promise
by S to purchase the car, there are two promises.
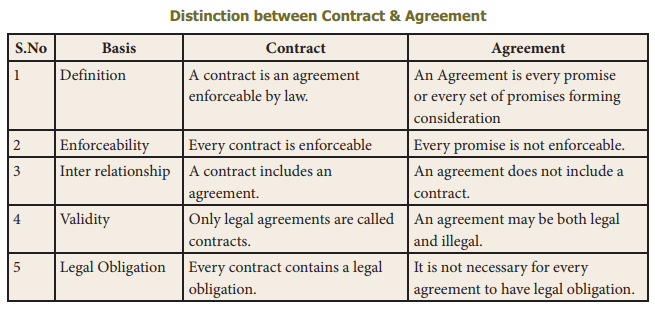
Related Topics