Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 10 : Secondary Growth
Cambial variants (Anomalous Secondary Growth)
Cambial variants (Anomalous
Secondary Growth)
Cambial
variants (previously known as anomalous
secondary growth) is a deviation from normal secondary growth and
production of secondary vascular and non- vascular tissues. A normal cambium
with abnormal activity, accessory (additional) cambia or abnormally situated
cambia with normal activity can produce anomalous secondary growth. The
anomalies may be listed as follows,
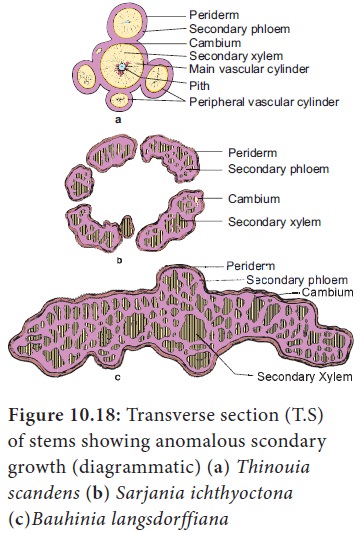
1. Anomalous position of vascular cambium
Unusual
shapes in stems are formed by the unusual position of cambium. Example: Thinonia scandens, Serjania ichthyoctona and Bauhinia
langsdorffiana.
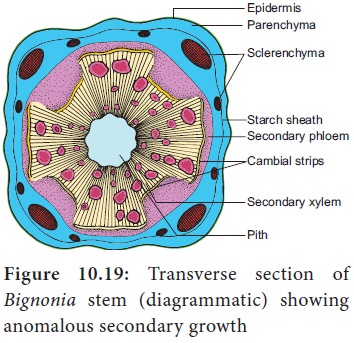
2. Abnormal behavior of normal cambium
Certain
segments of cambia cease to produce secondary xylem. But at the same time, it
produces secondary phloem only on the outer side. The remaining cambial
segments do the normal activity; As a result, ridged and furrowed steles are
formed. Example: Bignonia.
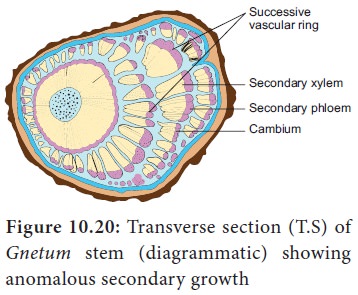
3. Successive cambium
In plants
like Aviccenia, Cycas, Gnetum a number of
cambial rings arise in succession and produce concentric rings of secondary
tissues.
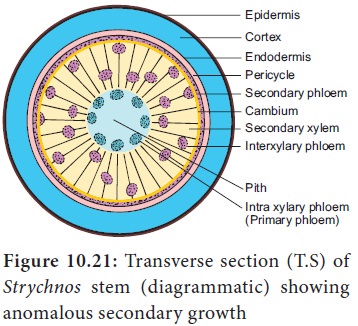
4. Interxylary or Included Phloem
The
secondary phloem found in the form of strands (islands) embedded in the
secondary xylem is called interxylary
or included phloem.
Example: Strychnos, Combretum and Salvadora.
5. Presence of medullary bundles along with normal cambial activity
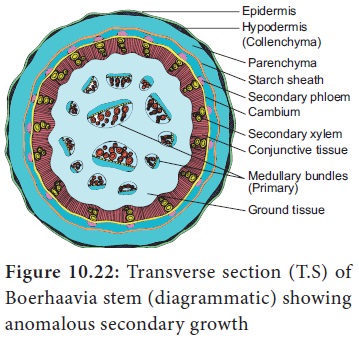
In this
type, the normal vascular bundles are arranged in a ring from which a normal cambial ring is formed. In addition, vascular
bundles are scattered or found in a ring in the pith or medullary region.
These are
called medullary vascular bundles. Example: Boerhaavia.
![]()
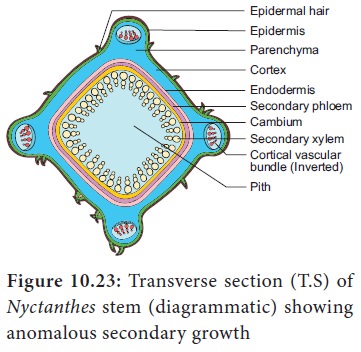
6. Presence of cortical bundles along with normal cambial activity
In this
type, a ring of vascular bundles are found, from which a normal cambial ring is
formed. In addition, in the cortical region additional vascular bundles are
found. Example: Nyctanthes.
7. Intraxylary or Internal Phloem
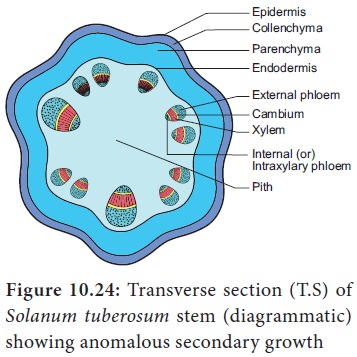
The
cambium usually forms primary phloem on the outer side. In some plants,it forms
the primary phloem on the inner side along with xylem towards pith. This is
called intraxylary or internal Phloem. Example: Solanum tuberosum
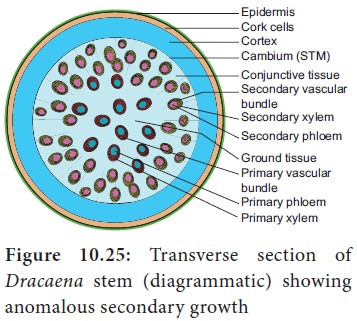
8. Secondary Growth in Monocot
In some
monocotyledons, the stems exhibit secondary growth. Example: Dracaena. Here, a secondary thickening meristems (STM) originate from the
ground tissue outside of the vascular bundles. STM cuts off cells on the inside
from additional vascular bundles are formed along with parenchyma cells in
between the vascular bundles. The STM consists of only one type of cells unlike
normal vascular cambium. STM does not produce continuous xylem on the inside
but only vascular bundle with xylem and phloem. Also no phloem is formed on the
outer side.
9. Anomalous primary growth
I) Absence of vessels in the xylem.
Usually,
vessels are found in the xylem of angiosperms, whereas some plants are lacking
vessels in the xylem. Example: Hydrilla,
Winteraceae family members.
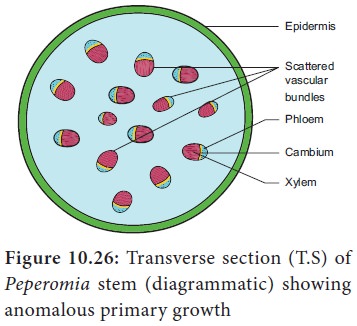
II) Scattered
Vascular bundles along with cambial activity in dicots.
In dicot
stem, normally the vascular bundles are arranged in a ring, whereas some dicot
stems possess scattered vascular bundles in the cortex like monocot stems.
Example: Piper, Peperomia.
Related Topics