Declaration, Syntax, Initialization, Accessing, Example Program - C++: Two-dimensional array | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 12 : Arrays and Structures
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 12 : Arrays and Structures
C++: Two-dimensional array
Two-dimensional
array
Two-dimensional
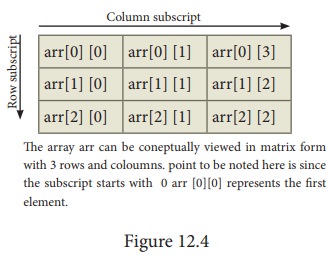
(2D) arrays are collection of similar elements where the elements are stored in
certain number of rows and columns. An example m × n matrix where m denotes the
number of rows and n denotes the number of columns is shown in Figure12.4
int arr[3][3];
Declaration of 2-D array
The
declaration of a 2-D array is
data-type
array_name[row-size][col-size];
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() In the above declaration, data-type refers to any valid C++
data-type, array_name refers to the name of the 2-D array, row-size refers to
the number of rows and col-size refers to the number of columns in the 2-D
array.
In the above declaration, data-type refers to any valid C++
data-type, array_name refers to the name of the 2-D array, row-size refers to
the number of rows and col-size refers to the number of columns in the 2-D
array.
For example
int A[3][4];
In
the above example, A is a 2-D array, 3 denotes the number of rows and 4 denotes
the number of columns. This array can hold a maximum of 12 elements.
Array size must be an unsigned integer value which is greater
than 0. In arrays, column size is compulsory but row size is optional.
Other
examples of 2-D array are:
int A[3][3];
float x[2][3];
char name[5][20];
Initialization of Two-Dimensional array
The
array can be initialized in more than one way at the time of 2-D array
declaration. For example
int matrix[4][3]={
{10,20,30},// Initializes row 0
{40,50,60},// Initializes row 1
{70,80,90},// Initializes row 2
{100,110,120}// Initializes row 3
};
int matrix[4][3]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120};
Array’s
row size is optional but column size is compulsory.
For example
int matrix[][3]={
{10,20,30},// row 0
{40,50,60},// row 1
{70,80,90},// row 2
{100,110,120}// row 3
};
Accessing the two-dimensional array
Two-dimensional
array uses two index values to access a particular element in it, where the
first index specifies the row value and second index specifies the column
value.
matrix[0][0]=10;// Assign 10 to the first element of the first
row
matrix[0][1]=20;// Assign 20 to the second element of the first
row
matrix[1][2]=60;// Assign 60 to the third element of the second
row
matrix[3][0]=100;// Assign 100 to the first element of the
fourth row
Write a program to perform addition of two matrices
#include<iostream>
#include<conio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int row, col,
m1[10][10], m2[10][10], sum[10][10];
cout<<"Enter
the number of rows : ";
cin>>row;
cout<<"Enter
the number of columns : ";
cin>>col;
cout<<
"Enter the elements of first matrix: "<<endl;
for (int i =
0;i<row;i++ )
for (int j = 0;j
<col;j++ )
cin>>m1[i][j];
cout<<
"Enter the elements of second matrix: "<<endl;
for (int i =
0;i<row;i++ )
for (int j =
0;j<col;j++ )
cin>>m2[i][j];
cout<<"Output:
"<<endl;
for (int i =
0;i<row;i++ )
for (int j =
0;j<col;j++ )
{
sum[i][j]=m1[i][j]+m2[i][j];
cout<<sum[i][j]<<"
";
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
getch();
return 0;
}

Memory representation of 2-D array
Normally,
the two-dimensional array can be viewed as a matrix. The conceptual view of a
2-D array is shown below:
int A[4][3];
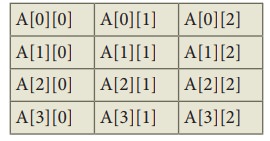
In
the above example, the 2-D array name A has 4 rows and 3 columns.
Like one-dimensional, the 2-D array elements are stored in continuous memory.
There are two types of 2-D array memory representations.
They are:
•
Row-Major order
•
Column-Major order
For example
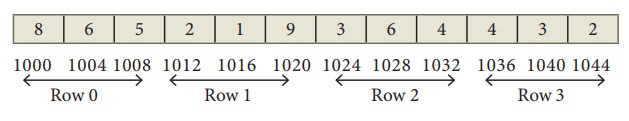
int A[4][3]={
{ 8,6,5}, { 2,1,9}, {3,6,4}, {4,3,2},
Row Major order
In
row-major order, all the elements are stored row by row in continuous memory
locations, that is, all the elements in first row, then in the second row and
so on. The memory representation of row major order is as shown below;
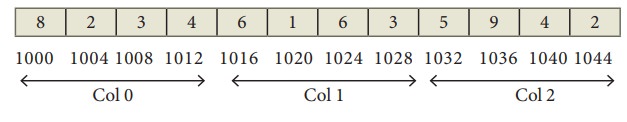
Column Major order
Related Topics