Accountancy - Book-keeping: An introduction | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 2 : Conceptual Framework of Accounting
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 2 : Conceptual Framework of Accounting
Book-keeping: An introduction
Book-keeping-An introduction
The first
step in the accounting process is identifying and recording of transactions in
the books of accounts. This is necessary for any business as the transactions
happening in a business entity must be recorded so that the information is
available for further analysis.
Book-keeping
forms the base for the preparation of financial statements and interpretation
which are the important functions of accounting. In a broad sense, accounting
includes book-keeping also. In a small business, the entire accounting work may
be performed by a single accountant. In a large firm, there may be a separate
person or department for book-keeping work.
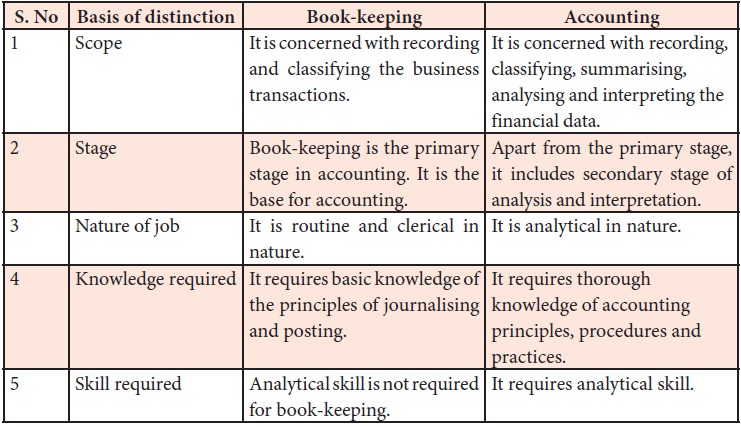
Meaning of book-keeping
Book-keeping
is the process of recording financial transactions in the books of accounts. It
is the primary stage in the accounting process. It includes recording the
transactions and classifying the same under proper heads. Book-keeping work is
of routine nature. Transactions may be recorded in the accounting note books
and ledgers or may be recorded in a computer.
Definition of book-keeping
“Book-keeping is an art of recording business
dealings in a set of books”. - J.R.Batliboi.
“Book-keeping is the science and art of recording correctly in the books of account all those business transactions of money or money’s worth”. -R.N.Carter.
Features of book-keeping
Following are
the features of book-keeping:
i.
It is the
process of recording transactions in the books of accounts.
ii.
Monetary
transactions only are recorded in the accounts.
iii.
Book-keeping
is the primary stage in the accounting process.
iv.
Book-keeping
includes journalising and ledger processing.
Objectives of book-keeping
Following are the objectives of book-keeping:
i.
To have a
complete and permanent record of all business transactions in chronological
order and under appropriate headings.
ii.
To
facilitate ascertainment of the profit or loss of the business during a
specific period.
iii.
To
facilitate ascertainment of financial position.
iv.
To know
the progress of the business.
v.
To find
out the tax liabilities.
vi.
To fulfil
the legal requirements.
Advantages of Book-keeping
Book-keeping has the following advantages:
i.
Transactions
are recorded systematically in chronological order in the book of accounts.
Thus, book-keeping provides a permanent and reliable record for all business
transactions.
ii.
Book-keeping
is useful to get the financial information.
iii.
It helps
to have control over various business activities.
iv.
Records
provided by business serve as a legal evidence in case of any dispute.
v.
Comparison
of financial information over the years is possible. Also comparison of
financial information of different business units is facilitated.
vi.
Book-keeping
is useful to find out the tax liability.
Limitations of book-keeping
Book-keeping has the following limitations:
i.
Only
monetary transactions are recorded in the books of accounts.
ii.
Effects
of price level changes are not considered.
iii. Financial data recorded are historical in nature, i.e., only past data are recorded.
Related Topics