Chapter: Medical Electronics : Assist Devices and Bio-Telemetry
Bio Telemetry
BIO TELEMETRY
Telemetry is a technology that allows remote
measurement and reporting of information. The word is derived from Greek roots tele = remote, and metron = measure. Systems that need external instructions and data
to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand.
Although
the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g. using radio
or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media,
such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired
communications. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost
and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry
data.
·
Bio telemetry is the measurement of biological
parameters over long distance.
·
For conveying biological information from a living
organism and its environment to a different location where this can be
recorded.
·
This involves radio frequency signal as a carrier
for modulation, referred to as radio telemetry.
ELEMENTS OF BIOTELEMETRY
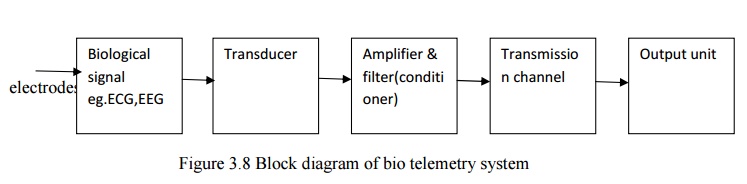
ECG,EEG,EMG-
Electrodes act as transducer
For
measuring temperatures-Thermisto is used as transducer
For
measuring blood pressure-strain gauge is
used as transducer
For
measuring stomach pH-glass electrode is used as transducer.
DESIGN OF BIO TELEMETRY
·
Telemetry system should be selected to transmit the
bio –electric Signal with maximum fidelity and simplicity.
·
The sysetem should not affect the living system by
any interference.
·
Smaller in size light in weight.
·
It should have more stability and reliability.
·
The power consumption at the transmitter and
receiver should be small.
·
It should reject common mode interference rejection.
·
Miniatured radio telemetry system should be used to reduce noise.
1. RADIO TELEMETRY SYSTEMS
·
Single channel telemetry system
·
Multi channel telemetry system
1.1. SINGLE CHANNEL TELEMETRY SYSTEM
·
For a single channel telemetry system, a miniature
battery operated radio transmitter is connected to the electrodes of the
patients.
·
The transmitter broadcasts the biopotential to a
remote place in which the receiver detects the radio signal and recovers signal
for further processing.
·
The receiving system can be located in a room
separately from the patients.
·
The only risk is shock to the patient.
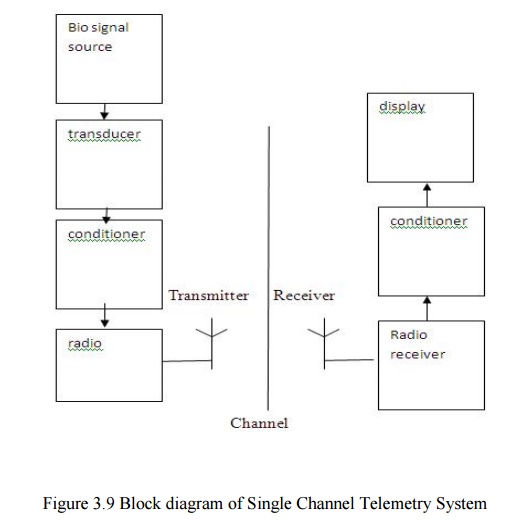
·
Biosignal from the patient is converted into
electrical signals by the transducer.
·
They are amplified and filtered at the conditioner.
Further they are frequency modulated or pulse modulated.Frequency modulation
provides the high noise interference rejection and high stability.
·
The biosignals are amplified to radio frequency
range of few hundred KHz to about 300 KHz and then they are transmitted by transmitter
antenna.s
·
At radio receiver the corresponding frequency are
received and then they are demodulated, amplified and displayed.
Transmission of bioelectric variables:
·
Active measurements
·
Passive measurements Tunnel diode FM transmitter
·
The tunnel diodes exhibit a specific
characteristics known as negative resistance. They have extremely low values of
inductance an capacitance.
·
It is used for the transmission of EMG,ECG,
respiration rates.
·
Tunnel diodes are used as active devices and this
circuit has higher fidelity and sensitivity.
·
Total weight is 1.44 gm with battery and the size
is small.
·
Varactor diode is basically a reverse biased PN
junction which utilizes the inherent capacitance of depletion layer.
·
Varactor diodes are voltage capacitors used for
frequency modulation.
·
The signal is transmitted through the inductor L of
the tank circuit of RF oscillator.
Advantages:
·
All the signal can be transmitted by using the
circuit.
·
No shielded room is needed.
·
Interference is much reduced.
Radio telemetry with sub carrier sytem:
Transmitter side:
·
When the position of transmitter to the body or
other conduction object change, the carrier frequency and amplitude will change
due to the loading change of the carrier frequency resonant circuit.
·
If the signal has a frequency different from the
loading effect ,they can be separated by filters. .Otherwise the real signal
will be distorted by loading effect.
·
To avoid this loading effect the sub carrier system
is needed. The signal is modulated on a sub carrier to convert the signal
frequency to the neighbourhood of the sub carrier frequency.
·
Then the RF carrier is modulated by this sub
carrier carrying the signal.
Ø The 20
KHz sub carrier signal is given to
amplitude modulator.
Ø The
signals are amplified and forwarded to
the transmitter.
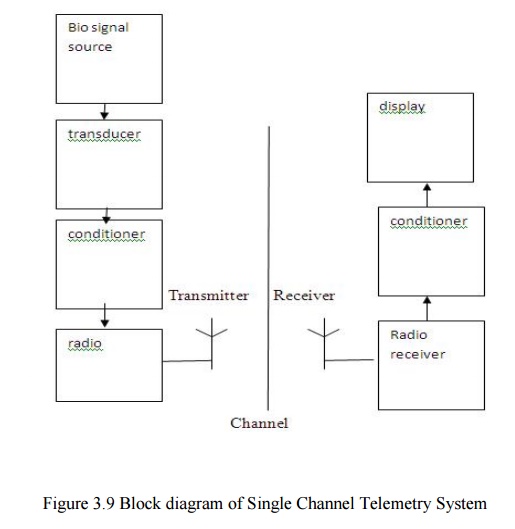
Receiver side:
·
At the receiver end the receiver detects the RF and
recovers the sub carrier carrying the signal.
·
At the receiver side, the signals are passed to
demodulator, demodulated signal is filtered, amplified by amplifier and then
they are given to additional demodulator. It is used to convert the signal from
the modulated sub carrier system an to get the original signal.
·
Finally the signal is displayed.
1.2 MULTI CHANNEL TELEMETRY SYSTEM:
·
For most biomedical applications, simultaneous
recording of Bio signals are required for correlation study.
·
Each signal is in need of one channel. When the
number of channels is more than the two or three, the simultaneous operation of
the several single channel is difficult. At that time multiple channel
telemetry system is adopted.
Two types of multiplexing:
1.
FDM
2.
TDM
Frequency division multiplex system
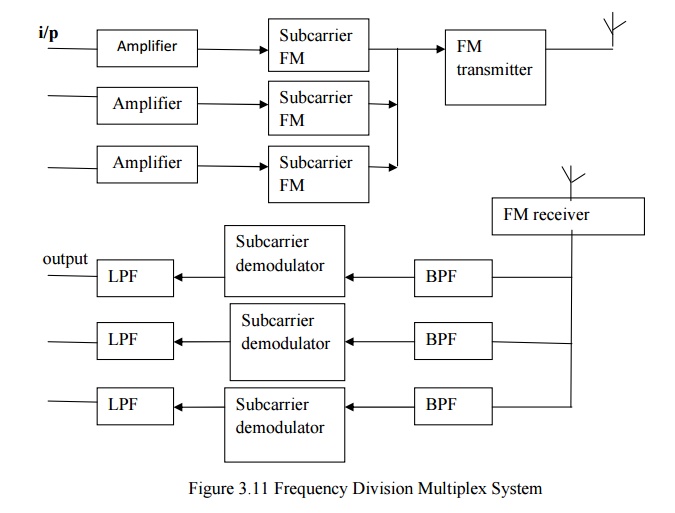
·
Each signal is frequency modulated on a sub carrier
frequency.
·
Modulated sub carrier frequencies are combined to
modulate the RF carrier.
·
At receiver the modulated sub carrier can be
separated by the proper band pass filter.
·
Then the each signals are demodulated by using
specified frequency.
·
Frequency of the sub carrier has to be carefully
selected to avoid interference.
·
The low pass filter are used to extract the signals
without any noise. Finally the output unit displays the original signal.
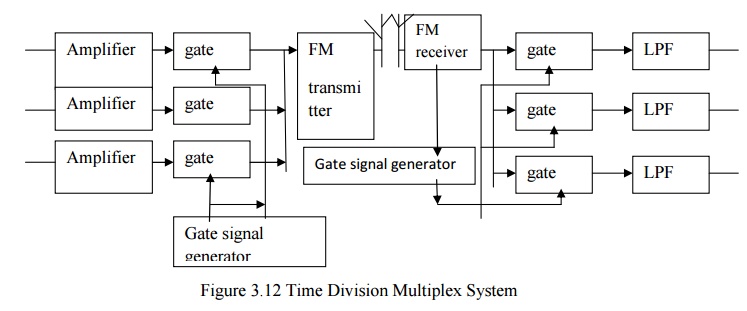
Time division multiplex telemetry system:
·
Most biomedical signals have low frequency
bandwidth requirement, we can use time division multiple system by time sharing
scheme.
· Transmission channel is connected to each signal channel input for a short time to sample and transmit that signal.
·
Transmitter is switched to the next input signal
channel in a definite sequence.
·
All the channels have been scanned once, a cycle is
completed and the next cycle will start. Scanning follows a order from signal 1
to signal 3.
·
At the receiver the process is reversed. The
sequentially arranged, signal pulses are given to the individual channels by
using gate signal generator.
·
If the number of scanning cycles per second is
large and if the transmitter and the receiver are synchronized, the signal in
each channel at the receiver side can be recovered. But the scanning frequency
has to satisfy the following condition.
fscan =
2fmax
The
maximum number of channels practically allowed is smaller than the calculated
value of n to avoid the interference between channels.
Advantages of
biotelemetry:
·
Used to record the biosignals over long periods.
·
Patient is not disturbed during recording
·
For future reference or to study the treatment
effect
·
Monitor the athletes running a race.
·
For monitoring the persons who are in action the
biotelemetry is an ideal one.
·
For recording on animals, particularly for research
, the biotelemetry is greatly used.
Applications
Motorracing
·
Telemetry is a key factor in modern motor racing,
allowing race engineers to interpret the vast amount of data collected during a
test or race, and use that to properly tune the car for optimum performance.
Systems used in some series, namely Formula One, have become advanced to the
point where the potential lap time of the car can be calculated and this is
what the driver is expected to meet. Some examples of useful measurements on a
race car include accelerations (G forces) in 3 axis, temperature readings,
wheel speed, and the displacement of the suspension. In Formula 1, the driver
inputs are also recorded so that the team can assess driver performance and, in
the case of an accident, the FIA can determine or rule out driver error as a
possible cause.
Later developments
saw two way telemetry, that
allowed the engineers
the ability to update calibrations on the car in real time, possibly
while it is out on the track. In Formula 1, two-way telemetry surfaced in the
early nineties from TAG electronics, and consisted of a message display on the
dashboard which the team could update. Its development continued until May
2001, at which point it was first allowed on the cars. By
·
2002 the teams were able to change engine mapping
and deactivate particular engine sensors from the pits while the car was on
track. For the 2003 season,
the FIA
banned two-way telemetry from Formula 1, however the technology still exists
and could eventually find its way into other forms of racing or road cars.
·
In addition to that telemetry has also been applied
to the use of Yacht racing. The technology was applied to the Oracle's USA-76.
Agriculture
·
Most activities related to healthy crops and good
yields depend on timely availability of weather and soil data. Therefore,
wireless weather stations play a major role in disease prevention and precision
irrigation. These stations transmit major parameters needed for good decisions
to a base station: air temperature and relative humidity, precipitation and
leaf wetness (for disease prediction models), solar radiation and wind speed
(to calculate evapotranspiration), water deficit stress (WDS) leaf sensors and
soil moisture, crucial to understand the progress of water into soil and roots
for irrigation decisions.
·
Because local micro-climates can vary
significantly, such data needs to come from right within the crop. Monitoring
stations usually transmit data back by terrestrial radio though occasionally
satellite systems are used. Solar power is often employed to make the station
independent from local infrastructure.
Water Management
·
Telemetry has become indispensable for water
management applications, including water quality and stream gauging functions.
Major applications include AMR (automatic meter reading), groundwater
monitoring, leak detection in distribution pipelines and equipment
surveillance. Having data available in almost real time allows quick reactions
to occurrences in the field.
Defense, space and resource exploration systems
· Telemetry
is an enabling technology for large complex systems such as missiles, RPVs,
spacecraft, oil rigs and chemical plants because it allows automatic
monitoring, alerting, and record-keeping necessary for safe, efficient
operations. Space agencies asNASA, ESA, and other agencies use
telemetry/telecommand systems to collect data from operating spacecraft and
satellites.
Telemetry
is vital in the development phase of missiles, satellites and aircraft because
the system might be destroyed after/during the test. Engineers need critical
system parameters to analyze (and improve) the performance of the system.
Without telemetry, these data would often be unavailable
Rocketry
·
In rocketry, telemetry equipment forms an integral
part of the rocket range assets used to monitor the progress of a rocket
launch. Some special problems are the extreme environment (temperature,
accelerations, vibrations...), the energy supply, the precise alignment of the
antenna and (at long distances, e.g. in spaceflight) the signal travel time.
Flight Test
·
Flight test programs typically telemeter data
collected from on-board flight test instrumentation over a PCM/RF link. This
data is analyzed in real-time for safety reasons and to provide feedback to the
test pilot. Particular challenges for telemetering this data includes fading,
multipath propagation and the Doppler effect. The bandwidth of the telemetry
link is often insufficient to transfer all the data acquired and therefore only
a limited set is sent to the ground for real-time processing while an on-board
recorder ensures the full dataset is available for post flight analysis.
Enemy Intelligence
·
Telemetry was a vital source of intelligence for
the US and UK when Soviet missiles were tested. For this purpose, the US
operated a listening post in Iran. Eventually, the Russians discovered this
kind of US intelligence gathering and encrypted their telemetry signals of
missile tests. Telemetry was a vital source for the Soviets who would operate
listening ships in Cardigan Bay to eavesdrop on the UK missile tests carried
out there.
ENERGY MONITORING
·
In factories, buildings, and houses, energy
consumption of systems such as HVAC are monitored at multiple locations,
together with the related parameters (e.g. temperature) via wireless telemetry
to one central location. The information is collected and processed enabling
intelligent decisions regarding the most efficient use of energy to be
implemented. Such systems also facilitate predictive maintenance.
Related Topics