Binomial Coefficients | Definition, Formula, Solved Example Problems, Exercise | Mathematics - Binomial Theorem | 11th Mathematics : UNIT 5 : Binomial Theorem, Sequences and Series
Chapter: 11th Mathematics : UNIT 5 : Binomial Theorem, Sequences and Series
Binomial Theorem
Binomial
Theorem
The prefix bi in the words bicycle, binocular, binary and
in many more words means two. The word binomial stands for expressions
having two terms. For examples (1
+ x), (x + y), (x2 + xy) and (2a + 3b) are some binomial
expressions.
1. Binomial Coefficients
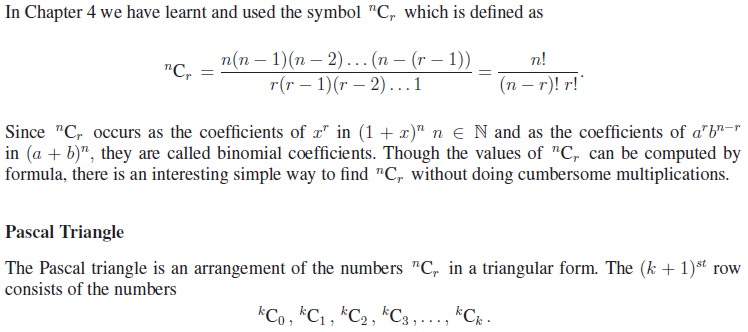
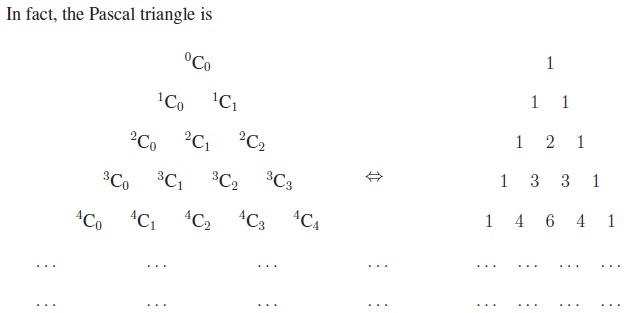

If we observe carefully the
Pascal triangle, we may notice that each row starts and ends with 1 and other
entries are the sum of the two numbers just above it. For example ‘3’ is the
sum of 1 and 2 above it; ‘10’ is the sum of 4 and 6 above it. We will prove in
a short while that
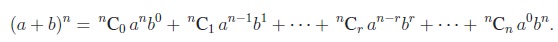
which is the binomial expansion of (a
+ b)n. The binomial expansion of (a + b)n for any n ∈ N can be written using
Pascal triangle. For example, from the fifth row we can write down the
expansion of (a + b)4
and from the sixth row
we can write down the expansion of (a + b)5 and so on. We know the terms (without coefficients) of (a
+ b)5 are
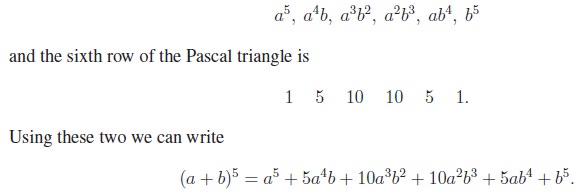
The Pascal triangle
can be constructed using addition alone, without using any multiplication or
division. So without multiplication we can write down the binomial expansion
for (a
+ b)n for any n ∈ N.
The above pattern
resembling a triangle, is credited in the name of the seventeenth century
French Mathematician Blaise Pascal, who studied mathematical properties of this
structure and used this concept effectively in Probability Theory.
2. Binomial theorem for positive integral index
Now we prove the most
celebrated theorem called Binomial Theorem.
Theorem 5.1 (Binomial theorem for positive integral index): If n is any positive integer, then
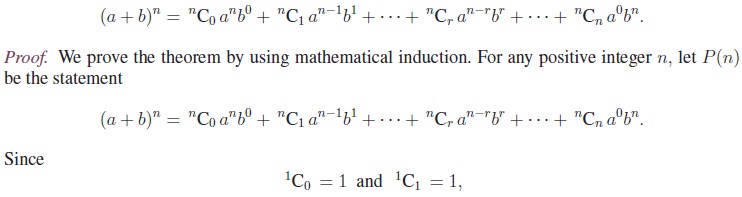


Related Topics