Nursing Communication Skills - Barriers of Communication | 12th Nursing : Chapter 10 : Communication Skills
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 10 : Communication Skills
Barriers of Communication
BARRIERS OF
COMMUNICATION
Barriers to effective
communication can retard or distort the message or intention of the message
being conveyed. This may result in failure of the communication process or
cause an effect that is undesirable.

Types of Barriers
Physical Barriers: Physical Barriers are often due to the nature
of the environment like noise, invisibility, etc.
Organisational Barriers: It refers to the problem with the
structures or systems in
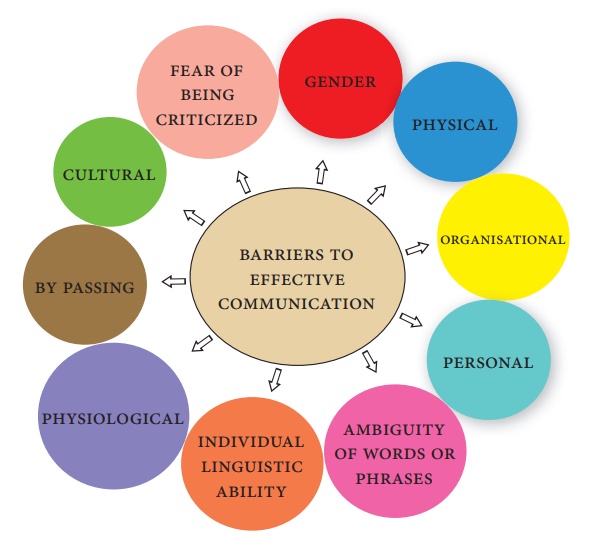
PersonalBarriers: It is due to
psychological problems of individuals. E.g., lack of motivation or
dissatisfaction in work.
Ambiguity of
words/Phrases: Words sounding the same but having different meaning can
convey a different meaning altogether. Hence the communicator must ensure that
the receiver receives the same meaning.
Individual linguistic
ability: The
use of jargon, difficult or inappropriate words in communication can
prevent the recipients from understanding the message.
Physiological Barriers: These may result from
individual’s personal discomfort, caused by ill health, poor eyesight or
hearing difficulties.
Bypassing: These happens when the
communicators (sender and the receiver) do not attach the same symbolic
meanings to their words.
Cultural Barriers: Strong beliefs, customs,
attitudes, religious, sentiments, illiteracy may influence communication.
Fear of being
criticized: This is a major factor that prevents good communication.
Gender Barriers: Most communicators show
a difference in thought, often have a set of agenda. This is noticeable among
the different genders.
How to Overcome the Barriers of Communication

Clarify the idea – The communicator must
be clear about what he wants to communicate.
Completeness of the
message: The
message should be relevant to the nature and purpose of communication.
Understand the receiver:
The communicator
should be aware of the total physical and human setting.
Use appropriate
channels: The
channels should be appropriate to the message.
Consistency in
communication: The message should be consistent with objective.
Feedback: It involves effective
participation and improves mutual understanding.
Simplified structure: The communication can
be strengthened by simple procedure and regulating the information flow.
Improve listening: The sender and receiver
must listen with attention, patience and empathy.
Mutual trust and
confidence: It improves the effectiveness of communication.
Related Topics