Meaning, Definition, Form, Contents, Types - Auditing - Audit Report | 12th Auditing : Chapter 10 : Company Audit
Chapter: 12th Auditing : Chapter 10 : Company Audit
Audit Report
Audit Report
Audit
report is the final stage of audit process. The results of the audit are
communicated through audit report. Audit report is the written opinion of an
auditor regarding companies financial statements. Audit report is a document
prepared by an auditor to certify the financial position and accounting records
of a firm.
Meaning of Audit Report
Audit
report is the statement included in the financial statements. It contains the
opinion of the auditor in financial statements. The auditor reports to the
shareholders who have appointed him. He has to provide his opinion on the truth
and fairness of financial statements. Thus, the auditor protects the interest
of shareholders through audit report.
Definition of Audit Report
Lancaster has defined a report as “a report is a statement of collected and
considered facts, so drawn up as to give clear and concise information to
persons who are not already in possession of the full facts of subject matter
of the report.”
According
to Cambridge Business English Dictionary, Audit report is defined as a formal
document that states an auditor’s judgment of a company’s accounts.
Under
Sec. 143(3), auditor of a company must report to its members.
(a) The
accounts examined by him;
(b) Balance
Sheet, Profit and Loss Account, and Cash Flow statement, which are laid in
general meeting of a company during his tenure of office; and
(c) The
document declared to be attached to the Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss
Account.
Form of Audit Report
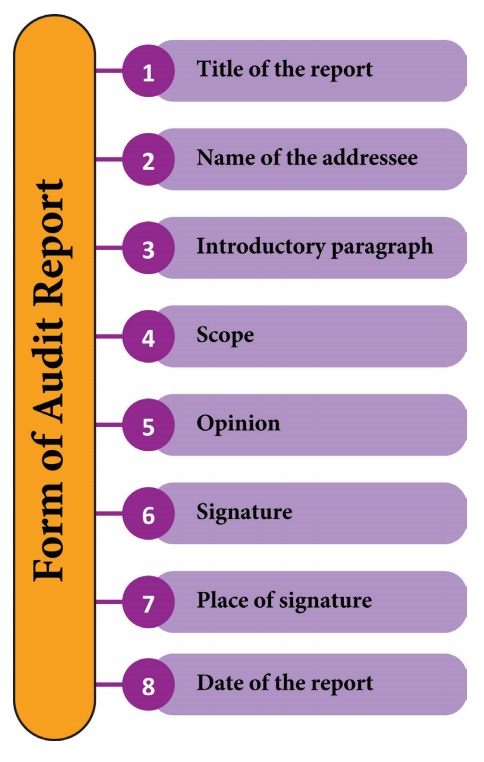
1. Title of the report
The
title of audit report should help the reader to identify the report. It should
disclose the name of the client. The title distinguishes the audit report from
other reports.
2. Name of the Addressee
The
addressee normally refers to the person who appoints the auditor. If a company
appoints the auditor, the addressee should be shareholders. As per law, the
complete address of the addressee is required. Addressee for the statutory
audit shall be shareholders and in case of Special Audit, it is Central
Government.
3. Introductory Paragraph
The
introductory paragraph should specify that it is the auditor’s opinion on
financial statements audited by him. The period covered by financial statements
should be stated with exact dates.
4. Scope
This
part should include the matter-of-fact relating to the manner in which audit
examination was made. The audit examination should cover company’s accounts,
Profit and Loss Account, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statements. The
examination should be as per the relevant law. The auditor should not curtail
or limit any examination task.
5. Opinion
The
auditor’s opinion on the books of account and financial statements examined by
him is based on the information and free from bias. The auditor has to give his
opinion as follows:
·
Whether the financial statements are
arithmetically correct and correspond to the figures recorded in the books of
accounts.
·
In case of unqualified opinion, whether the
financial statements represent a true and fair view of the state of affairs and
the results of operations.
·
In case of qualified opinion, if the Balance
Sheet and Profit and Loss account do not present a true and fair view, the
reasons for what and where is wrong.
6. Signature
The
signature part should include the manual signature of the auditor.The personal
name and signature of the auditor should be given. If the auditor is a firm,
the signature in the personal name and firm name should be given.
7. Place of Signature
This
should include the location of the auditor or the auditor firm, which is
ordinarily their city.
8. Date of the Report
The date
of completion of the audit work should be mentioned in this section.
Contents of Audit Report
As per
Sec. 143 of the Companies Act, the auditor’s report shall also state—
a. whether he has sought and
obtained all the information and
explanations which to the best of his knowledge and belief were necessary for
the purpose of his audit and if not, the details thereof and the effect of such
information on the financial statements;
b. whether, in his opinion,
proper books of account as required
by law have been kept by the company so far as appears from his examination of
those books and proper returns adequate for the purposes of his audit have been
received from branches not visited by him;
c. whether the report on the
accounts of any branch office of the
company audited under sub-section (8) by a person other than the company’s auditor
has been sent to him and the manner in which he has dealt with it in preparing
his report;
d. whether the company’s Balance
Sheet and Profit and Loss account
dealt with in the report are in agreement with the books of account and
returns;
e. whether, in his opinion, the
financial statements comply with the
Accounting Standards;
f. the observations or comments of the auditors on
financial transactions or matters which have any adverse effect on the
functioning of the company;
g. whether any director is disqualified from being appointed as a director
under sub-section (2) of section 164;
h. any
qualification, reservation or adverse remark relating to the maintenance of
accounts and other matters connected therewith;
i. whether
the company has adequate internal financial control system in place and the
operating effectiveness of such controls;
j. such
other matters as may be prescribed.
Types of Audit Report
The
audit report may be of the following types:
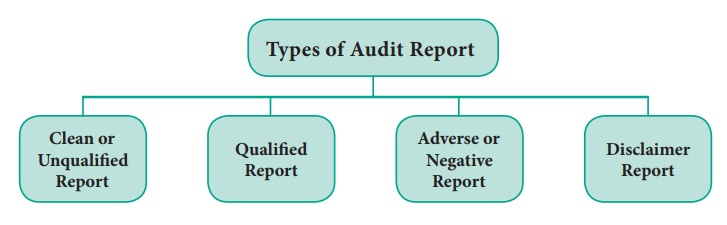
1. Clean or Unqualified Report
Clean or Unqualified report will be given by the auditor if the auditor is satisfied that the accounts, Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Account and Cash Flow statement do represent a true and fair view and they are prepared in conformity with the accounting principles and statutory requirements.
2. Qualified Report
In
qualified report the auditor believes that overall financial statements are not
fairly stated. The reasons for giving Qualified Report are be as follows:
i. The
books of accounts, Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet do not
represent the true and fair view of the state of affairs and results of the
operations, due to lack of conformity with the accounting principles and
statutory requirements,
ii. The
auditor is not able to verify the value and existence of certain assets,
iii. The
information requested by the auditor is not furnished,
iv. Proper
books of account are not maintained as required by law,
v. Part
of audit examination done by other auditors.
3. Adverse or Negative Report
When
there is sufficient basis for the auditor to form an opinion that the whole
accounts and financial statements, do not present a true and fair view of the
financial condition and results of operation, the adverse or negative opinion
will be given. The adverse or negative report will be given on the following
grounds:
·
When the auditor is not satisfied with the
truth and fairness of financial statements,
·
Non conformity with the Generally Accepted
Accounting Principles,
·
Mistakes, discrepancies and material
misstatement in the financial statements,
·
Omission of a material disclosure.
4. Disclaimer Report
![]() The auditor may disclaim or
refuse opinion on the accounts, Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet,
when he does not have sufficient information to base his opinion. In the scope
and opinion paragraph, the auditor should give disclaimer information. This may
happen on the following grounds:
The auditor may disclaim or
refuse opinion on the accounts, Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet,
when he does not have sufficient information to base his opinion. In the scope
and opinion paragraph, the auditor should give disclaimer information. This may
happen on the following grounds:
·
The auditor has not been able to obtain
sufficient information to form his opinion,
·
The audit examination is not adequate to form
an opinion,
·
There are some material un-determined item in
audit examination.
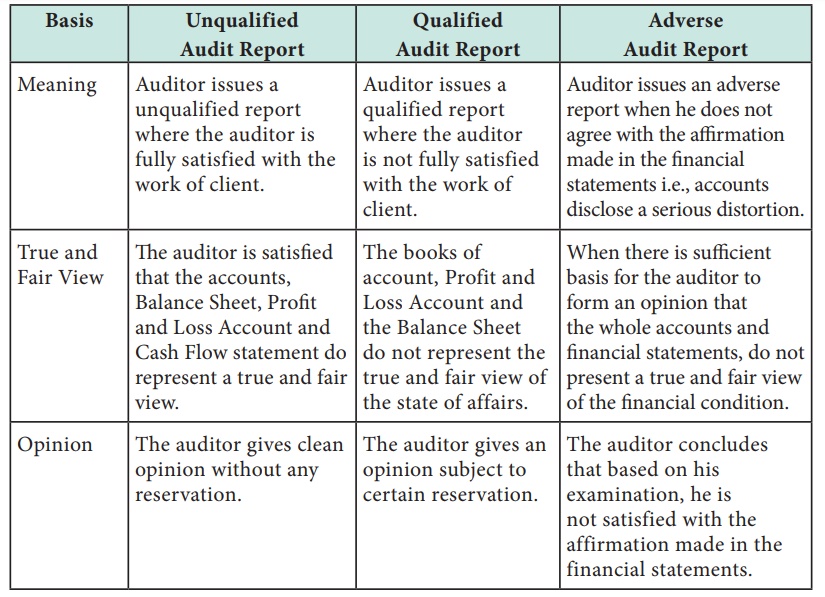
Differences between Unqualified, Qualified Differences between Unqualified, Qualified
Related Topics