Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Arthropod-Borne and Other Zoonotic Viruses
Arthropod-Borne and Other Zoonotic Viruses
Arthropod-Borne and Other Zoonotic Viruses
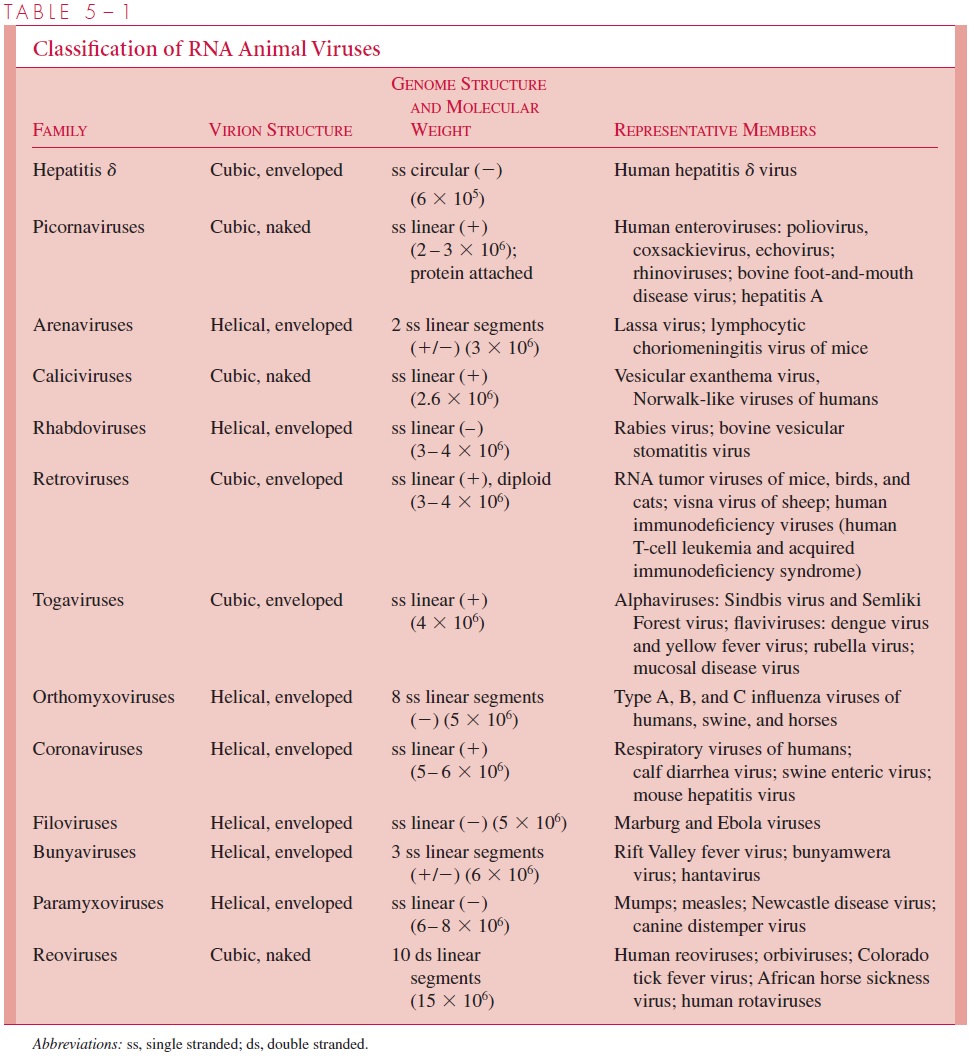
The zoonotic viruses comprise more than 400 agents, one or more of which occur inmost parts of the world. Members of the group have their ultimate reservoirs in lower ver-tebrates or insects. They are from diverse taxonomic families of RNA viruses that primar-ily include the togaviruses, bunyaviruses, reoviruses, arenaviruses, and filoviruses. Their major morphologic and genetic features are summarized in Table 5–1. Certain DNA viruses (poxviruses) are also transmissible from animals to humans.
The zoonotic viruses discussed here are divided into two groups. The arboviruses are transmitted to humans by infected bloodsucking insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, andPhlebotomus flies (sandflies). The other zoonotic RNA viruses are generally believed tobe transmitted by inhalation of infected animal excretions, by the conjunctival route, or occasionally by direct contact with infected animals. Rabies virus, which is commonly transmitted by animal bites.
VIROLOGY
In most cases, the zoonotic viruses were first named after the place of initial isolation (eg, St. Louis encephalitis) or after the disease produced (eg, yellow fever). More recent studies have assigned the majority to families and genera on the basis of properties indi- cated in Table 5–1. The major characteristics of these families are summarized below.
TOGAVIRUSES AND FLAVIVIRUSES
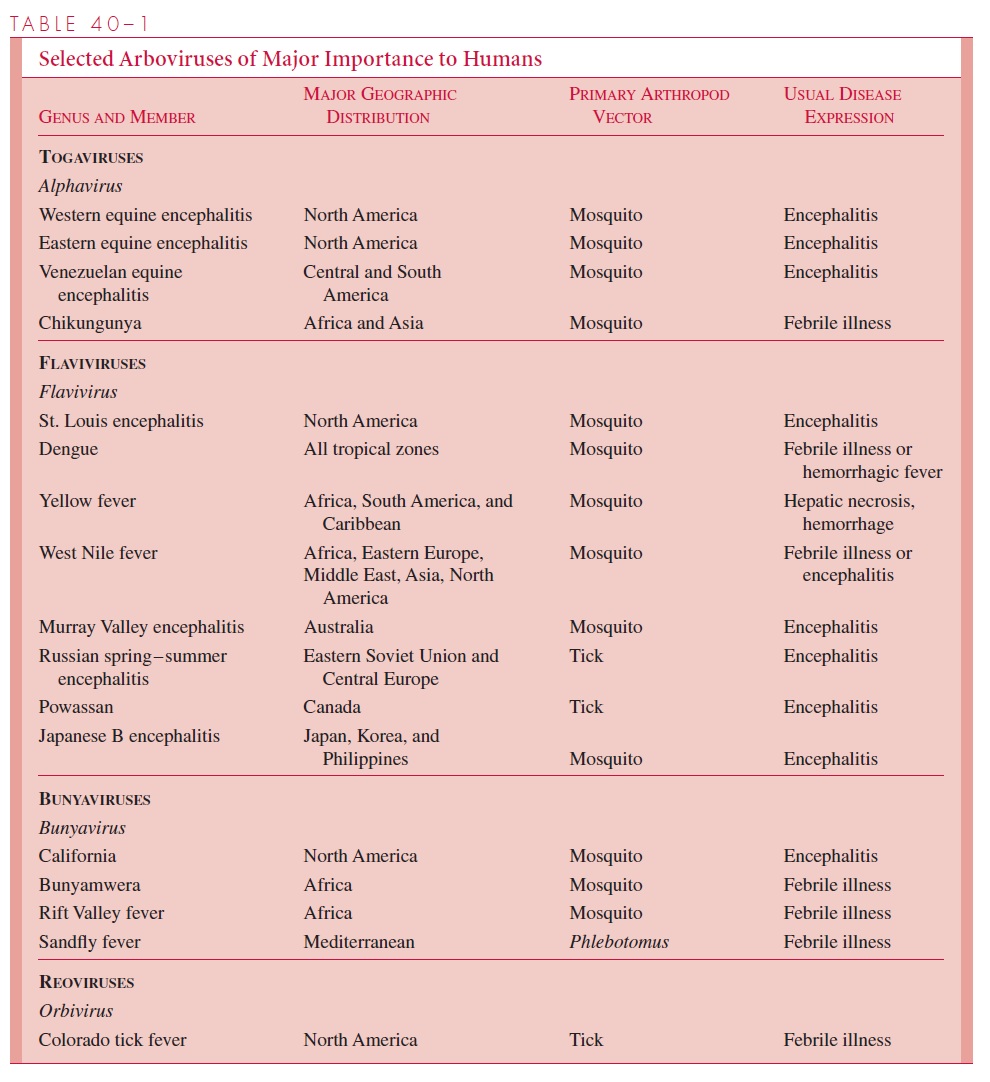
Togaviruses and flaviviruses are enveloped virions containing single-stranded, positive-sense RNA measuring 40 to 70 nm in external diameter. The envelope contains a hemag-glutinin and lipoproteins. Virions mature by budding from cellular membranes. Replication can occur in cells of infected arthropods and vertebrate hosts. TheAlphavirus and Flavivirus genera within these families include most arthropod-borne viruses. Each genuspossesses its own unique primary structure of the RNA genome. Viruses within these genera are frequently serologically related to one another but not to others. Representa-tives are listed in Table 40–1.
BUNYAVIRUSES
Bunyaviruses are spherical, enveloped, single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses approx-imately 90 to 100 nm in external diameter. They mature by budding into smooth-surfaced vesicles in or near the Golgi region of the infected cell. The major disease-causing bunyaviruses in North America are California virus and hantavirus.
REOVIRUSES
Reoviruses are spherical, unenveloped, double-stranded RNA viruses that measure about 80 nm in diameter with a segmented genome. The most important North American arbovirus of this family, which is a member of the genus Coltivirus, causes Colorado tick fever.
ARENAVIRUSES
The arenaviruses are enveloped, spherical or pleomorphic viruses containing singlestranded,negative-sense RNA in several segments and measuring 50 to 300 nm in diameter. They mature by budding from host cell cytoplasmic membranes and contain host cell ribosomes in their interior. These ribosomes confer a granular appearance to the viruses, hence their name (from the Latin arenosus for “sandy”). The most significant arenavirus infections in humans are the hemorrhagic fevers, including Lassa fever. The virus of lymphatic choriomeningitis is occasionally transmitted to humans from infected mice and other rodents.
FILOVIRUSES
Filoviruses are enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses. They are filamentous and highly pleomorphic, averaging 80 nm in diameter and 300 to 14,000 nm in length as they bud from the cell membrane. They are the cause of Marburg and Ebola fevers, two highly fatal hemorrhagic fevers.
Related Topics