Chapter: Pathology: Joint Pathology
Arthritis Related to Crystal Deposition
ARTHRITIS RELATED TO CRYSTAL DEPOSITION
In gout, hyperuricemia and the deposition of
monosodium urate crystals in joints will result in recurrent bouts of acute
arthritis. The hyperuricemia can be caused by overproduction or underexcretion
of uric acid.
•
Primary
gout (90%) is idiopathic, affects males more than females, and is typically seen in older men.
•
Secondary
gout (10%) is seen with excessive cell breakdown (chemotherapy), decreased renal excretion (drugs),
and Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
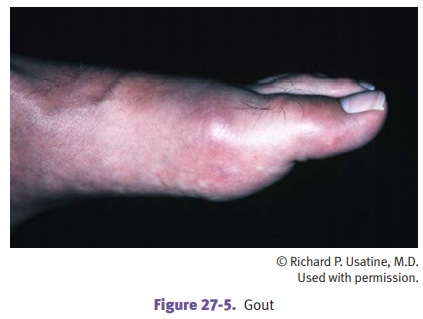
Gout affects the great toe
(podagra, characterized by an exquisitely painful, inflamed big toe), ankle,
heel, and wrist.
Joint aspiration shows
birefringent, needle-shaped uric acid crystals and numer-ous neutrophils. Tophi are deposits of crystals
surrounded by inflammation. Skin ulceration and destruction of adjacent joints
may occur. Complications include joint destruction and deformity, uric acid
renal calculi, and renal failure. Treatment is NSAIDs, colchicine, probenecid,
and allopurinol.
Pseudogout (chondrocalcinosis) is deposition of calcium
pyrophosphate crystals in joints, leading to
inflammation. Affected patients are usually age >50. The knee joint is most
commonly involved. Aspiration of the joint demonstrates positively birefringent
(weak), rhomboid-shaped crystals. Pseudogout is associated with many metabolic
diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypothyroidism, ochronosis), and it may mimic OA or
RA.
Related Topics