Nutrition and Health | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Nutrition and Health
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Nutrition and Health
Answer the following questions
NUTRITION
AND HEALTH
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
IX. Answer briefly:
1. Differentiate
a) Kwashiorkar from Marasmus
b) Macronutrients from
Micronutrients
Answer:
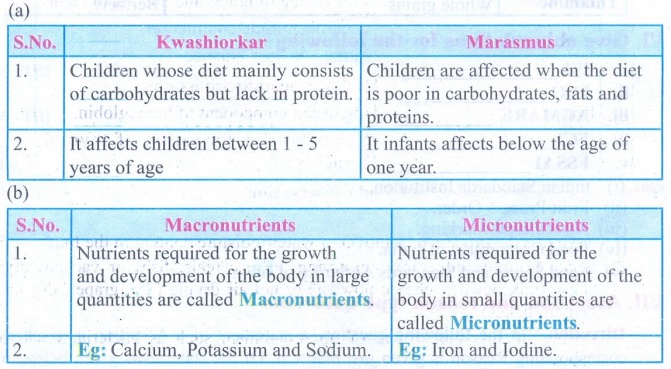
(a)
Kwashiorkar
1.
Children whose diet mainly consists of carbohydrates but lack in protein.
2.
It affects children between 1 - 5 years of age
Marasmus
1.
Children arc affected when the diet is poor in carbohydrates, fats and
proteins.
2.
It infants affects below the age of one year.
b)
Macronutrients
1.
Nutrients required for the growth and development of the body in large
quantities are called Macronutrients.
2. Eg:
Calcium, Potassium and Sodium.
Micronutrients
1.
Nutrients required for the growth and development of the body in small
quantities are called Micronutrients.
2.
Eg: Iron
and Iodine.
2. Why salt is used as
preservative in food?
Answer: (i)
Addition of salt removes the moisture content in the food by the process of
osmosis. This prevents the growth of bacteria and reduces the activity of microbial
enzymes.
(ii)
Meat, fish, gooseberry, lemon and raw mangoes are preserved by salting.
(iii)
Salt is also used as a preservative in pickles, canned foods, etc.
3. What is an adulterant?
Answer:
Adulteration is defined as “the addition or
subtraction of any substance to or from
food, so that the natural composition and
the quality of food substance is affected.” The adulterant is any material
which is used for the purpose of adulteration.
4. Name any two naturally
occuring toxic substances in food.
Answer:
(1)
Prussic acid in the seeds of apple.
(2)
Marine toxins in fishes.
5. What factors are required for
the absorption of Vitamin D from the food by the body?
Answer: (i) Human
skin can synthesize Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight (especially early
morning).
(ii)
When the sun rays falls on the skin dehydro cholesterol is converted into
Vitamin D. Hence, Vitamin D is called as “Sunshine vitamin”.
6. Write any one function of the
following minerals
a) Calcium
b) Sodium
c) Iron
d) Iodine
Answer:

Minerals
a. Calcium
Function
:
1. Constituent of bones and enamel of teeth. 2. Controls muscle contraction.
b. Sodium
Function
:
1. Maintains fluid balance. 2. Helps in neurotransmission.
c. Iron
Function
:
1. Important component of hemoglobin.
d. Iodine
Function
:
1. Necessary for formation of thyroid hormone.
7. Explain any two methods of
food preservation.
Answer:
Drying:
(i)
Drying is the process of removal of water/moisture content in the food.
(ii)
It can be done either by sun-drying, (Eg: cereals, fish) or vacuum drying
(Eg:
milk powder, cheese powder) or hot air drying (Eg: grapes, dry fruits, potato
flakes).
(iii)
Drying inhibits the growth of microorganism such as bacteria, yeasts and moulds.
Smoking:
(i)
In this process, food products like meat and fish are exposed to smoke.
(ii)
The drying action of the smoke tends to preserve the food.
8. What are the effects of
consuming adulterated food?
Answer: Consumption
of these adulterated foods may lead to serious health issues like fever,
diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal disorders, asthma, allergy,
neurological disorder, skin allergies, immune suppression, kidney and liver
failure, colon cancer and even birth defects.
X. Answer in detail:
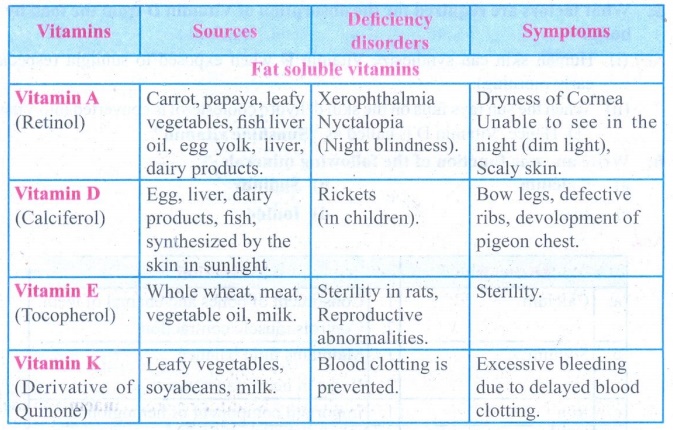
1. How are vitamins useful to us?
Tabulate the sources, deficiency diseases and symptoms of fat soluble vitamins.
Answer: Vitamins
are the vital nutrients, required in minute quantities to perform physiological
and biochemical functions.
2. Explain the role of food
control agencies in India.
Answer:
Food quality
control agencies:
ISI,
AGMARK, FPO, FCI and other health departments enforce minimum standards for the
consumer products. FCI (Food Corporation of India) was set up in the year 1965
with the following objectives:
(i)
Effective price support operations for safeguarding the interest of farmers.
(ii)
Distributing food grains throughout the country.
(iii)
Maintaining satisfactory levels of operational and buffer stock of food grains
to ensure national security.
(iv) Regulate the market price to provide food grains to consumers at reliable price.
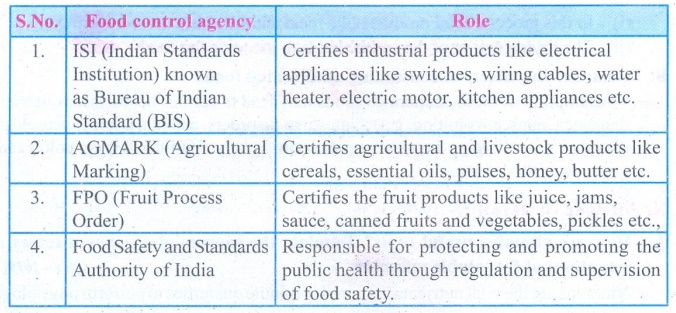
Food control agency
: Role
1. ISI (Indian Standards
Institution) known as Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS) : Certifies
industrial products like electrical appliances like switches, wiring cables,
water heater, electric motor, kitchen appliances etc.
2. AGMARK (Agricultural Marking) :
Certifies
agricultural and livestock products like cereals, essential oils, pulses,
honey, butter etc.
3. FPO (Fruit Process Order) : Certifies
the fruit products like juice, jams,
sauce, canned fruits and vegetables, pickles etc.
4. Food Safety and Standards
Authority of India : Responsible for protecting and promoting the
public health through regulation and supervision of food safety.
XI Higher Order
Thinking Skils:
1. Look at the picture and answer
the question that follows.
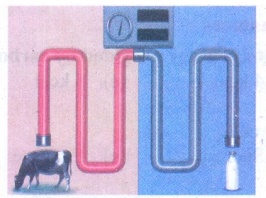
a) Name the process involved in
the given picture.
b) Which diary food is preserved
by this process?
c) What is the temperature
required for the above process?
Answer:
(a)
Pasteurization.
(b)
Milk.
(c)
63°C for 30 minutes followed by sudden cooling
2. The doctor advices an
adolescent girl who is suffering from anaemia to include more of leafy
vegetables and dates in her diet. Why so?
Answer: Anaemia
is a condition resulting from deficiency of haemoglobin in the blood. Iron is
necessary for the formation of a haemoglobin.Therefore the doctor advices the
girl to include leafy vegetables and dates in her diet since they are rich in
iron content.
3. Sanjana wants to buy a jam
bottle in a grocery shop. What are the things she should observe on the label
before purchasing it?
Answer: She must
look for the following details on the label of the jam bottle.
(i)
Date of manufacture and date of expiry. She must make sure that the contents of
the bottle must be conserved before the date of expiry.
(ii)
She must look for the FPO certification to ensure that the product has been certified
by the quality agency and is safe for consumption.
IX. Answer briefly:
1. Give an account of
classification of bacteria based on the shape.
Answer: Based on
the shapes, bacteria are grouped into 3 types:
1.
Spherical shaped bacteria as cocci (or coccus for a single cell).
2.
Rod shaped bacteria called as bacilli (or bacillus for a single cell).
3. Spiral
shaped bacteria called as spirilla (or spirillum for single cell).
2. Describe the role of microbes
in agriculture and industries.
Answer: Microbes in
Agriculture:
Microbes
play an important role in agriculture as biocontrol agents and biofertilizers.
(i) Biocontrol
agents:
Microorganisms
used for controlling harmful or pathogenic organisms and pests of plants are
called as biocontrol agents Biopesticides.
(E.g)Bacillus Thuringiensis. (Bt) is a
species of bacteria that produces a protein called as 'cry’ protein.
(ii) Biofertilizers:
1.
Microorganisms which enrich the soil with nutrients are called as biofertilizers.
2.
Bacteria, cyanobacteria and fungi are the main sources of biofertilizers.
3.
Atomspheric nitrogen has to be converted to available form of nitrogen.
Example:
Azotobacter Nitrosomonas Nostoc (free living), Symbiotic microbes
like Rhizobium, Frankia.
Microbes in
Industries
Microorganisms
play an important role in the production of wide variety of valuable products
for the welfare of human beings.
Production of
fermented beverages: Beverages like wine are produced by fermentation
of grape fruits by Saccharomyces
cerevisiae.
Curing of coffee
beans, tea leaves and tobacco leaves : Beans of coffee and cocoa, leaves
of tea and tobacco are fermented by the bacteria Bacillus megaterium. This gives the special aroma.
Production of curd:
Lactobacillus sp. converts milk to curd.
Production of organic
acids, enzymes and vitamins: Oxalic acid, acetic acid and
citric acid are produced by fungus Aspergillus
niger. Enzymes like lipases, invertase, proteases, and glucose oxidase are
derived from microbes. Yeasts are rich source of vitamin-B complex.
3. Explain the various types of
viruses with examples.
Answer:
Viruses are
categorised as:
1. Plant virus: Virus
that infect plants.
E.g.
Tobacco mosaic virus, Potato virus, Cauliflower mosaic virus.
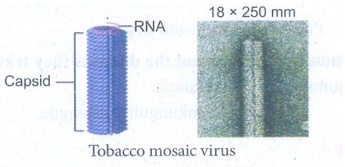
2. Animal virus: Virus
that infect animals.
E.g.
Adenovirus Retrovirus (HIV), influenza virus, polio virus.

3. Bacteriophages: Virus
that infect bacterial cells.
E.g.T4 bacteriophage.
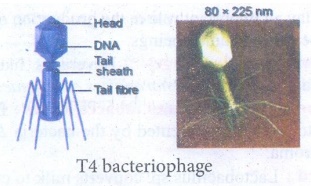
4. Suggest the immunization
schedule for a new born baby till 12 months of age. Why it is necessary to
follow the schedule?
Answer:
Immunization is a process of developing resistance to infections by
administration of antigens or antibodies. Inoculation of vaccines into the body
to prevent diseases is called as vaccination.
Immunization Schedule for Children
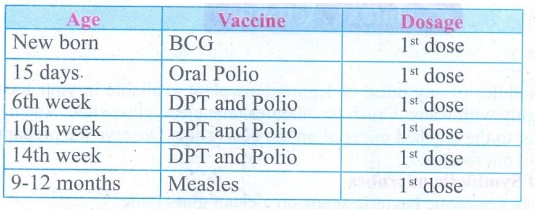
X. Assertion and reason
type questions:
Mark the correct
statement as.
(a)
If both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
(b)
If both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c)
If A is true but R is false.
(d)
If both A and R are false.
1. Assertion: Chicken pox is a disease indicated
by scars and marks in the body.
Reason: Chicken
pox causes rashes on face and further spreads throughout the body.
[Ans: (a) Both A
and R are true and R is correct explanation of A]
2. Assertion:
Dengue can be treated by intake of antibiotics.
Reason: Antibiotics
blocks the multiplication of viruses.
[Ans: (d) Both A
and R are false]
XI. Higher Order
Thinking Skills:
1. Suggest precautionary measures
you can take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious disease.
Answer:
1.
Clean and hygienic environment should be maintained inside and outside the
school.
2.
Enough first aid medicines should be kept in the school.
3.
Proper awareness about healthy diet and health instructions should be
instructed to the students.
4.
If a student is identified with disease, it must be properly communicated to
the students and nearby health authorities.
5.
The infected student / person must be kept away from other students in order to
avoid the spread of infection.
2. Tej as suffered from typhoid
while, Sachin suffered from tuberculosis. Which disease could have caused more
damage and why?
Answer:
Tuberculosis is more dangerous than typhoid.
Reason:
Tuberculosis (TB) primarily affects lungs and also affect intestines, bones,
and joints and other tissues of body. Severe cases may lead to death.
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY - 1
Take the root nodules of any
pulse or leguminous plant available in your locality. Wash it thoroughly with
water. Crush the nodules on a clean glass slide. Add a drop of distilled water
to the crushed material on the glass slide. Observe the preparation under
compound microscope.
Observation of
Symbiotic microbes
Aim: To
observe symbiotic bacteria shape on a clean glass plate.
Materials Required:
1.
Root nodules of leguminous plant, Clean glass slides, Water, Distilled water.
Procedure:
1.
Take the root nodules of the leguminous plant.
2.
Wash it throughly with water.
3.
Crush the nodules on a clean glass slide.
4.
Add a drop of distilled water to the crushed material on the glass slide.
Observation;
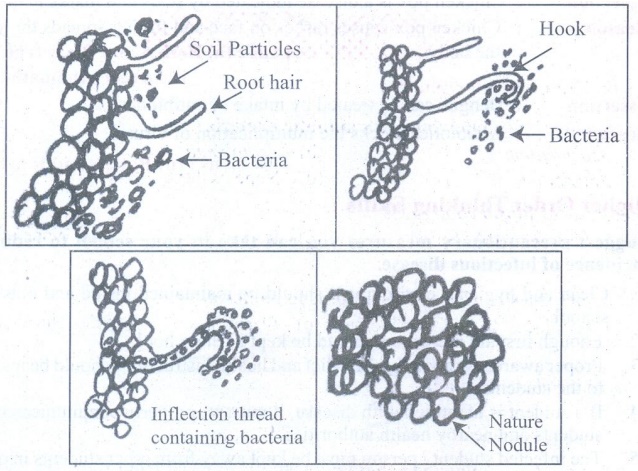
Conclusion:
The
structure of symbiotic bacteria is observed in a clean glass plate.
ACTIVITY – 2
Observe the mosquitoes that are
active during the day time. Catch them using an insect net and observe their
body and legs. What do you observe? Why are cases of Dengue reported in large
numbers during post-monsoon season?
Observation:
Body arid legs of Aedes aegypti:
We
can find black and white stripes on the bodies and leg.
The
white marking in the leg is in the form of a lyre.
High Dengue cases
during post - monsoon
1.
Due to the rainy season, conditions like stagnant water favours the mosquitoes
to grow in large number.
2. Thus, a sharp rise in dengue cases are reported.
Related Topics