Organ Systems in Animals | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Organ Systems in Animals
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Organ Systems in Animals
Answer the following questions
ORGAN
SYSTEMS IN ANIMALS
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
V. Differentiate the
following :
a. Excretion and Secretion
b. Absorption and Assimilation
c. Ingestion and Egestion
d. Diphyodont and Heterodont
e. Incisors and Canines
Answer:
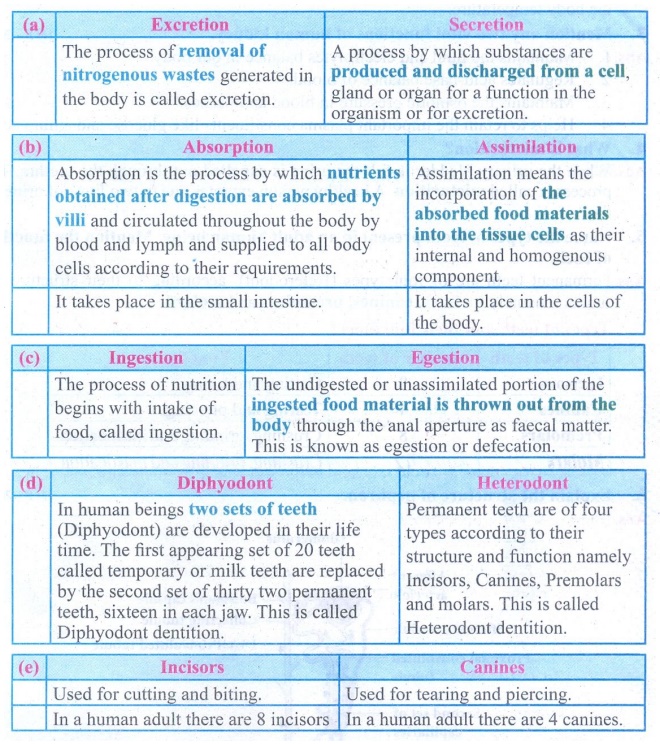
(a)
Excretion
The
process of removal of nitrogenous wastes generated in the body is called
excretion.
Secretion
A
process by which substances are produced and discharged from a cell, gland or
organ for a function in the organism or for excretion.
(b)
Absorption
Absorption
is the process by which nutrients obtained after digestion are absorbed by
villi and circulated throughout the body by blood and lymph and supplied to all
body cells according to their requirements.
It
takes place in the small intestine.
Assimilation
Assimilation
means the incorporation of the absorbed food materials into the tissue cells as
their internal and homogenous component.
It
takes place in the cells of the body.
(C)
Ingestion
The
process of nutrition begins with intake of food, called ingestion.
Egestion
The
undigested or unassimilated portion of the ingested food material is thrown out
from the body through the anal aperture as faecal matter. This is known as
egestion or defecation.
(d)
Diphyodont
In
human beings two sets of teeth (Diphyodont) are developed in their life time.
The first appearing set of 20 teeth called temporary or milk teeth are replaced
by the second set of thirty two permanent teeth, sixteen in each jaw. This is
called Diphyodont dentition.
Heterodont
Permanent
teeth are of four types according to their structure and function namely Incisors,
Canines, Premolars and molars. This is called Heterodont dentition.
(e)
Incisors
Used
for cutting and biting.
In
a human adult there are 8 incisors.
Canines
Used
for tearing and piercing.
In
a human adult there are 4 canines.
VI. Answer briefly:
1. How is the small intestine
designed to absorb digested food?
Answer: Heum is
the longest part of the small intestine. It contains minute finger like projections
called villi (one millimeter in length) where absorption of food
takes place. They are approximately 4 million in number. Internally, each
villus contains fine blood capillaries and lacteal tubes. The small intestine
serves both for digestion and absorption.
2. Why do we sweat?
Answer: The human
body functions normally at a temperature of about 37°C. When it gets hot sweat
glands start secreting sweat, which contains water with small amounts of other
chemicals like ammonia, urea, lactic acid and salts (mainly sodium chloride).
The sweat passes through the pores in the skin and gets evaporated, which
reduces the body temperature.
3. Mention any two vital
functions of human kidney.
Answer:
1.
Maintains the fluid and electrolytes balance in our body.
2.
Regulates acid-base balance of blood.
3.
Maintains the osmotic pressure in blood and tissues.
4.
Helps to retain the important plasma constituents like glucose and amino acids.
4. What is micturition?
Answer: When the
urinary bladder is full the urine is expelled out through the urethra. This
process is called micturition. A healthy person excretes one to
two litres of urine per day.
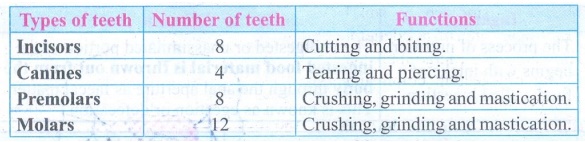
5. Name the types of teeth
present in an adult human being. Mention the functions of each.
Answer: Permanent
teeth are of four types (Heterodont), according to their structure and function
namely incisors,
canines, premolars and molars.
Tpes of teeth and
their functions:
6. Explain the structure of
nephron.
Answer:
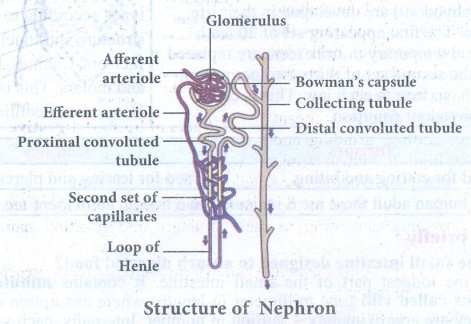
Structure of Nephron
(i)
Each kidney consists of more than one million nephrons. Nephrons or uriniferous tubules are structural and functional units of the kidneys.
(ii)
Each nephron consists of Renal corpuscle or Malphlgian corpuscle and renal tubule.
(iii)
The renal corpuscle consists of a cup-shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule containing a bunch of capillaries
called glomerulus.
(iv)
Blood enters the glomerular capillaries through afferent arterioles and leaves
out through efferent arterioles.
(v)
The Bowman’s capsule continues as the renal tubule which consists of three regions proximal convoluted tubule, U-shaped hair
pin loop, the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted tubule.
(vi)
The distal convoluted tubule which opens into the collecting tubule. The
nitrogenous wastes are drained into renal pelvis of kidney which leads to
ureters and stored in the urinary bladder.
(viii)
Urine is expelled out through the urethra.
VII. Answer in detail:
1. Describe the alimentary canal
of man.
Answer:
Alimentary
canal is a muscular coiled, tubular structure. It consists of mouth, buccal
cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (consisting of duodenum,
jejunum and ileum), large intestine (consisting of caecum, colon and rectum)
and anus.
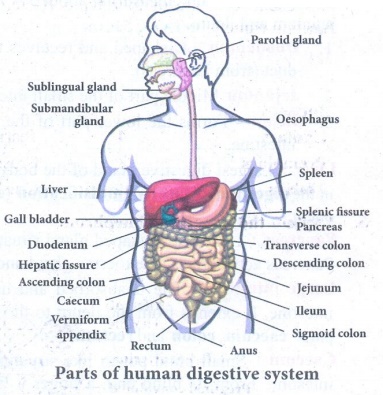
Mouth: Leads into the buccal cavity. It is
bound 2 soft movable upper and lower lips. The buccal cavity is a large space bound above
by the palate (which separates the wind pipe and food tube), below by the
throat and on the sides by the jaws. The jaws bear teeth.
Teeth: Hard
structures meant for holding, cutting, grinding and crushing the food. In human
beings two sets of teeth (Diphyodont) are developed in their life time. Each
tooth has a root fitted in the gum (Theocodont). Permanent teeth are of four
types (Heterodont), according to their structure and function namely incisors, canines, premolars and molars.
Dental formula represents
the number of different type of teeth present in each half of a jaw (upper and
lower jaw).
For
Permanent teeth in each half of upper and lower jaw:
2,1,2,3 / 2,1,2,3 = 16×2 = 32
Salivary glands: There
are 3 pairs :
(i) Parotid glands Largest
salivary glands, which lie in the cheeks in front of the ears.
(ii) Sublingual
glands Smallest lands and lie beneath the tongue.
(iii) Submaxillary or Submandibular-glands-lie
at the angles of the lower jaw.
Tongue: Muscular,
sensory organ - Helps in mixing the food with the saliva.
Pharynx: It is a
membrane lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the
oesophagus. Serves as a pathway for the movement of food from mouth to
oesophagus.
Oesophagus:
Muscular-membranous canal about 22 cm in length. It conducts food from pharynx
to the stomach by peristalsis (wave-like movement) produced by the rhythmic
contraction and relaxation of the muscular walls of alimentary canal.
Stomach: Wide
J-shaped muscular organ located.
Location: Between
oesophagus and the small intestine.
Small intestine: The
small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal, which is a long
coiled tube measuring about 5 - 7 m. It comprises three parts- duodenum,
jejunum and ileum.
1. Duodenum -
C-shaped and receives the bile duct (from liver) and pancreatic duct (from
Pancreas).
2. Jejunum - Middle part of the small
intestine.Short region of the small intestine
3. Ileum - Forms
the lower part of the small intestine and opens into the large intestine.
Liver: Largest
digestive gland of the body, reddish brown in colour. Bile salts help in the digestion of
fats by emulsification (conversion of large fat droplets into small
ones).
Pancreas: Lobed,
leaf shaped gland situated between the stomach and duodenum. Pancreas acts both
as an exocrine gland and as an endocrine gland.
Large intestine: The
unabsorbed and undigested food is passed into the large intestine. It extends
from the ileum to the anus. About 1.5 meters in length. Has 3 parts-caecum, colon and rectum.
Caecum: Small
blind pouch like structure at the junction of the small and large intestine.
From its blind end, a finger - like structure called vermiform appendix arises.
It is a vestigial (functionless) organ in human beings.
Colon: Much
broader than ileum. Passes up the abdomen on the right ascending colon, crosses
to the left just below the stomach (transverse colon) and down on the left side
(descending colon).
Rectum: Last
part which opens into the anus muscles called anal sphincter which opens when passing
stools.
2. Explain the structure of
kidney and the steps involved in the formation of urine.
Answer:
STRUCTURE OF
KIDNEYS:
(i)
Kidneys are bean-shaped reddish brown in colour.
(ii)
The kidneys lie on either side of the vertebral column in the abdominal cavity
attached to the dorsal body wall.
(iii)
The right kidney is placed lower than the left kidney as the liver takes up
much space, on the right side.
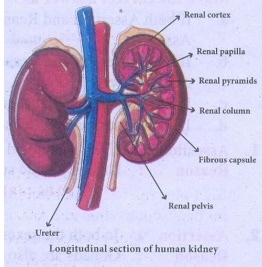
(iv)
Each kidney is about 11 cm long, 5 cm wide and 3 cm thick.
(v)
Internally the kidney consists of:
(a)
An outer dark region the cortex.
(b)
Inner lighter region the medulla.
Both
of these regions contain uriniferous tubules or nephrons.
(vi)
The medulla consists of multitubular conical masses called the medullary
pyramids or renal pyramids whose bases are adjacent to
cortex.
(vii) On the inner concave side of each kidney, a notch called hilum is present through which blood vessels and nerves enter in and the urine leaves through the Ureter.
STEPS INVOLVED IN
URINE FORMATION:
There
are three stages.
(i)
Glomerular filtration
(ii)
Tubular reabsorption and
(iii)
Tubular secretion
Glomerular
filtration: Urine formation begins with the filtration of
blood through epithelial walls of the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. The filtrate is
called as the glomerular filtrate. Both essential and non-essential
substances present in the blood are filtered.
Tubular
reabsorption: The filtrate in the proximal tubule consists of
essential substances such as glucose, amino acids, vitamins, sodium, potassium,
bicarbonates and water that are reabsorbed into the blood by a process of
selective reabsorption.
Tubular secretion:
Substances such as H+ or K+ ions are secreted into the
tubule. This tubular filtrate is finally known as urine, which is hypertonic in man.
Finally the urine passes into collecting ducts to the pelvis and through the
ureter into the urinary bladder. When the urinary bladder is full the urine is
expelled out through the urethra. This process is called micturition. The
healthy person excretes 1-2 litres of urine/day.
VIII. Assertion and
reason type questions:
Mark the correct
answer as:
a.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion.
b.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation
of Assertion.
c.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
1. Assertion: Urea is
excreted out through the kidneys.
Reason: Urea is a
toxic substance.
[Answer:(a) Both
Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion)
2. Assertion: In both
the sexes gonads perform dual function.
Reason: Gonads
are also called primary sex organs.
(Ans: (a) Both
Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of
Assertion]
IX. Higher Order
Thinking Skills:
1. If pepsin is lacking in
gastric juice, then which event in the stomach will be affected?
a. digestion of starch into
sugars.
b. breaking of proteins into
peptides.
c. digestion of nucleic acids.
d. breaking of fats into glycerol
and fatty acids.
Answer: b. breaking
of proteins into peptides
2. Name the blood vessel that (a)
enter malphigian capsule and (b) leaves malphigian capsule
Answer:
(a)
Afferent arteriole.
(b)
Efferent arteriole.
3. Why do you think that urine
analysis is an important part of medical diagnosis?
Answer:
Analysis
of urine helps to detect
(i)
diabetes,
(ii)
kidney malfunctions
(iii)
liver diseases and
(iv)
Urinary tract functions.
Similarly
in case of back pain, blood in the urine or painful urination also, required
the urine analysis. Thus urine analysis is an important part of medical
diagnosis.
4. Why your doctor advises you to
drink plenty of water?
Answer: Drinking
water helps
1.
Maintain the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body.
2.
When muscle cells don't get enough water it results in muscle fatigue.
3.
Functioning of kidneys also requires lot of water.
4.
Staying hydrated is necessary for good health.
5. Can you guess why there are sweat
glands on the palm of our hands and the soles of our feet?
Answer: Sweating
on the palm of our hands and soles of our feet is more related to mental and
emotional status of an individual and not by heat. This also acts to prevent
slippage while performing delicate tasks using fingers.
X. Match the parts of
the given figure with the correct option:
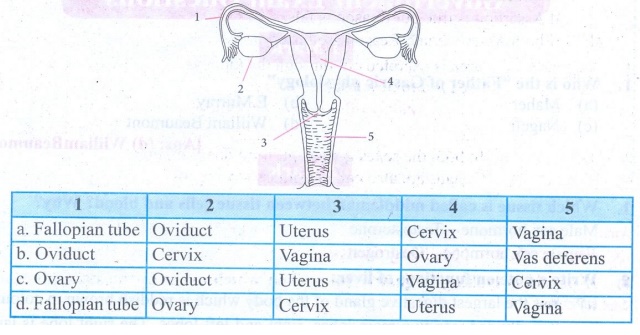
Answer:
d. 1. Fallopian tube 2. Ovary 3. Cervix 4. Uterus 5. Vagina
lntext Activities
ACTIVITY – 1
Look at the pictures given below
and answer the questions that follow.

1. Are the teeth of animals
similar to ours?
2. How is the shape of their
teeth related to their food habit?
Answer: There
are many differences between human teeth and animal teeth.
(i)
Humans have at most 32 teeth, but many animals have more than we do.
(ii)
Human use their for breaking down food but animals need this teeth for breaking
down of food and also for survival such as hunting, attacking and defending
themselves.
Lion Teeth: They are
Carnivore Teeth: Teeth are
very sharp and scissor - like. Their front teeth are used to bite and hold onto
prey while their long canine teeth are used for tearing flesh and meat. Their
molars are also sharp - and used for slicing rather than chewing because they
mainly swallow their food in whole chunks.
Bison or buffalo
teeth: They are
Herbivore teeth: An herbivore is an animal that gets energy from eating plants. Herbivors have more molars than we do. They use these flat teeth for grinding branches, grasses and seeds. Since their food doesn't try to escape, they use their front teeth like pruning shears to clip leaves and stems.
Related Topics