Carbon and its Compounds | Chemistry | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Chemistry : Carbon and its Compounds
Chapter: 9th Science : Chemistry : Carbon and its Compounds
Answer the following questions
CHEMISTRY
CARBON
AND ITS COMPOUNDS
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
IV. Answer briefly:
1. Differentiate graphite and
diamond.
Answer:

Graphite
•
Each carbon atom has three covalent bonds.
•
Soft, slippery to touch and opaque
•
It has planar layers of hexagon units.
•
It is conductor of heat and electricity.
Diamond
•
Each carbon atom has four covalent bonds.
•
Hard, heavy and transparent
•
It has tetrahedral units linked in three dimension
•
It is non-conductor of heat and electricity
2. Write all possible isomers of
C4 H10.
Answer:
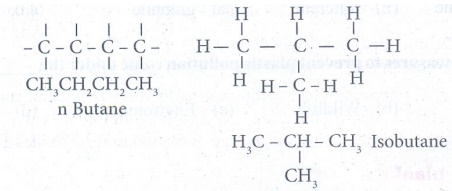
3. Carbon forms only covalent
compounds. Why?
Answer: Carbon
forms only covalent compounds because it has 4 electrons, in its.
4. Define Allotrophy.
Answer:
Allotrophy is a property by which are element can exist in more than one form
that are physically different and chemically similar.
5. Why are one-time use and
throwaway plastics harmful?
Answer: 1. Use
and throwaway plastics cause short and long-term environmental damage.
2.
Half of all the plastic made today is used for throwaway plastic items. These
block drains and pollute water bodies.
3.
One-time use plastic causes health problems for humans, plants and animals.
4.
Some examples are plastic carry bags, cups, plates, straws, water pouches,
cutlery and plastic sheets used for food wrapping.
V.Answer in detail:
1. What is catenation? How does
carbon form catenated compounds?
Answer:
Catenation is
binding of an element to itself or with other elements through covalent bonds
to form open chain or closed chain compounds.
(i)
Carbon is the most common element which undergoes catenation and forms long
chain compounds.
(ii)
Carbon atom links repeatedly to itself through covalent bond to form linear
chain, branched chain (or) ring structure.
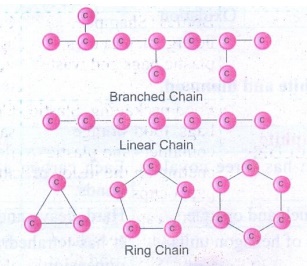
(iii) This property of carbon itself is the
reason for the presence of large number of organic carbon compounds.
(iv)
So organic chemistry essentially deals with catenated carbon compounds.
(v)
Example: Starch and cellulose contain chains of hundreds of carbon atoms.
2. What are the chemical
reactions of carbon?
Answer: Elemental
carbon undergoes no reaction at room temperature.
Oxidation: Carbon
combines with oxygen to form its oxides such as carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon
dioxide (CO2), with evolution of heat. Organic carbon compounds like
hydrocarbon also undergo oxidation to form oxides and steam with evolution of
heat and flame.
This
reaction is also called ‘Combustion’.
2C(S)
+ O2(g) → 2CO(g) + heat.
C(s)
+ O2(g) → CO2(g) + heat.
CH4(g)
+2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) +
heat.
Reaction with Steam: Carbon
reacts with steam to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen. This mixture is called
water gas.
C(S)
+H2O(g) → CO(g) + H 2(g)
Reaction with Sulphur: With
sulphur, carbon forms its disulphide at high temperature.
C(S)
+ 2S(g) → CS2(g)
Reaction with
Metals: At elevated temperatures, carbon reacts with some metals like
iron, tungsten, titanium, etc., to form their carbides.
Tungesten
+ Carbon → Tungesten carbide
W
+ C → WC.
3. Name the three safer resin
codes of plastics and describe their features.
Answer:

VI. Higher Order
Thinking Skills:
1. Why do carbon exist mostly in
combined state?
Answer: 1.Carbon
is found in free state as well as combined state in nature.
2.
Due to the following properties, carbon can form innumerable compounds.
1)
Catenation, 2) Tetravalency, 3) Multiple bonds, 4) Isomerism, 5) Allotropy.
2. When a carbon fuel burns in
less aerated room, it is dangerous to stay there. Why?
Answer:
1.
When a carbon fuel burns in less aerated room, the fuel may undergo incomplete combustion.
2.
It results in the formation of carbon monoxide.
3.
When exposed to carbon monoxide (CO) it enters human body, through breathing, affects
the function of haemoglobin.
4.
Sometimes, it will lead to death.
3. Explain how dioxins are
formed? Which plastic type they are linked to and why they are harmful to
humans?
Answer:
Dioxin formation:
1.
Dioxin compounds are not created intentionally, but are formed inadvertently by
a number of human and natural activities.
2.
These activities include combustion and incineration, forest fires, chlorine
bleaching of pulp and paper, certain types of chemical manufacturing and
processing, and other industrial processes.
3.
Cigarette smoke, some home-heating systems, and exhaust from vehicles using
leaded and unleaded petrol as well as diesel fuels also produce small amounts
of dioxins.
4.
Burning materials that may contain chlorine such as plastics, wood treated with
pentachlorophenol (PCP), pesticide-treated wastes, other chemicals such as
polychlorinated biphenols (PCBs), and even bleached paper can produce dioxins.
Their link with plastic:
1.
Dioxins are linked with PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride plastics).
2.
The most dangerous emissions can be caused by burning PVC, as it releases
dioxins.
Harmful effects of
Dioxins to humans:
1.
Dioxins are the most toxic to the human organisms.
2.
Dioxins can cause cancer, disrupt the endocrine system, alteration in pituitary
and thyroid gland functions, immune suppression, neurobehavioral effects and
cause reproductive and developmental effects.
3.
They are carcinogenic and a hormone disruptor and persistent, and they
accumulate in our body-fat and thus mothers give it directly to their babies
via the placenta.
4. Yugaa wants to buy a plastic
water bottle. She goes to the shop and sees four different kinds of plastic
bottles with resin codes 1,3,5 and 7. Which one should she buy? Why?
Answer: 1.Yugaa
should buy a plastic water bottle with Resin Code No.5, which is considered as
one of the safer plastics. It is light and hard.
Reasons to avoid
resin codes 1, 3, 7
1.
Bottle with Resin Code 1 is to be used only once. This plastic can release a
chemical additive called antimony, which is not good for health.
2.
Bottle with Resin Code 3 is most toxic plastic. It will have a smell of a new
shoe. It should be avoided.
3.
Bottle with Resin Code 7 has the plastic types PC and ABS which are unsafe and
toxic.
Intext activities
ACTIVITY - 1
With the help of your teacher,
try to classify the following as organic and inorganic compounds.
HCN, CO2, Propane,
PVC,CO Keroserie, LPG, Coconut oil, Wood , Perfume, Alcohol, Na2CO3,
CaCO3, MgO, Cotton, Petrol.
Solution:
Inorganic
CO2
CO
MgO
HCN
Na2CO3
PVC
Organic
Propane
Wood, kerosene,coconut oil
Perfume
Alcohol
Cotton
Petrol
LPG
ACTIVITY - 2
Take a football since it
resembles to Buckminster fullerene. Count how many hexagonal and pentagonal
panels are in it. Every corner is considered as one carbon. Compare your
observation with fullerene and discuss with your friends.
Aim:
To
compare the structure of fullerene with football
Materials required:
Foot
ball
Procedure:
1.
Take a foot ball.
2.
Count the hexagonal and pentagonal rings shapes in foot ball.
Observation:
Shapes Fullerene
(CAft) Foot ball

Conclusion:
The
structure of foot ball is compared with fullerene.
Related Topics