Introduction to Computers | Computer Science - Answer the following questions | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Computers
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Computers
Answer the following questions
Introduction to Computers
SECTION-B
Short Answers
1. What is a computer?
Answer: (i) A computer is an electronic device that manipulates
information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data.
(ii) Computer works faster than human being and given the values
more accuracy and reliable
2. Distinguish between data and information.
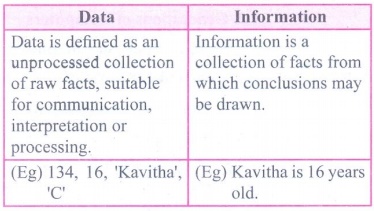
Data
• Data is defined as an unprocessed collection of raw facts,
suitable for communication, interpretation or processing.
• (Eg) 134, 16, 'Kavitha', 'C'
Information
• Information is a collection of facts from which conclusions
may be drawn.
• (Eg) Kavitha is 16 years old.
3. What are the components of a CPU?
Answer: The CPU has three components which are Control unit, Arithmetic
and logic unit (ALU) and Memory unit.
4. What is the function of an ALU?
Answer: (i) The ALU performs arithmetic operations.
(ii) The result of an operation is stored in internal memory of
CPU.
(iii) The logical operations of ALU promote the decision making
ability of a computer.
5. Write the functions of control unit.
Answer: The control unit controls the flow of data between the CPU,
memory and I/O devices. It also controls the entire operation of a computer.
6. What is the function of memory?
Answer: The primary memory is used to temporarily store the programs and
data when the instructions are ready to execute. The secondary memory is used
to store the data permanently.
7. Differentiate Input and output unit.
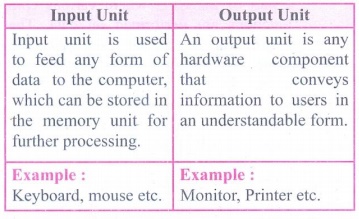
Input Unit
• Input unit is used to feed any form of data to the computer, which
can be stored in the memory unit for further processing.
• Example : Keyboard, mouse etc.
Output Unit
• An output unit is any hardware component that conveys
information to users in an understandable form.
• Example : Monitor, Printer etc.
8. Distinguish Primary and Secondary memory.
Answer:
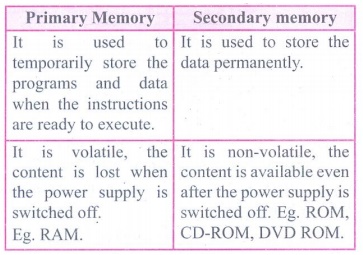
Primary Memory
• It is used to temporarily store the programs and data when the
instructions are ready to execute. .
• It is volatile, the content is lost when the power supply is
switched off. Eg. RAM.
Secondary memory
• It is used to store the data permanently.
• It is non-volatile, the content is available even after the
power supply is switched off. Eg. ROM, CD-ROM, DVD ROM.
SECTION-C
Explain in Brief
1. What are the characteristics of a computer?
1. What are the characteristics of a computer?
Answer: (i) Computer is the powerful machine.
(ii) It can perform large number of tasks.
(iii) The main capacities of computer are work length, speed
accuracy, diligence, versatility memory and automation and lots of more tasks.
2. Write the applications of computer.
Answer: The various applications of computers are,
(i) Business
(ii) Education
(iii) Marketing
(iv) Banking
(v) Insurance
(vi) Communication
(vii) Health care
(viii) Engineering - Robotics, Nano technology, Bio Engineering
3. What is an input device? Give two examples.
Answer: Input device is used to feed any form of data to the computer,
which can be stored in the memory unit for further processing.
Example: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Fingerprint scanner, Track Ball,
Retinal Scanner, Light pen etc.
4. Name any three output devices.
Answer:
(i) Monitor
(ii) Printer
(iii) Plotter
(iv) Speaker
(v) Multimedia projectors are the output devices.
5. Differentiate optical and Laser mouse
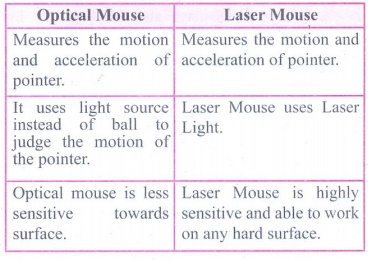
Optical Mouse
• Measures the motion and acceleration of pointer.
• It uses light source instead of ball to judge the motion of
the pointer.
• Optical mouse is less sensitive towards surface.
Laser Mouse
• Measures the motion and acceleration of pointer.
• Laser Mouse uses Laser Light.
• Laser Mouse is highly sensitive and able to work on any hard
surface.
6. Write shortnote on impact printer
Answer:
Impact printers :
(i) These printers print with striking of hammers or pins on
ribbon. These printers can print on multi-part (using carbon papers) by using
mechanical pressure. For example, Dot Matrix printers and Line matrix printers
are impact printers.
(ii) A Dot matrix printer that prints using a fixed number of
pins or wires.
(iii) Line matrix printers use a fixed print head for printing.
7. Write the characteristics of sixth generation.
Answer: (i) In the Sixth Generation, computers could be defined as the
era of intelligent computers based on Artificial Neural Networks.
(ii) One of the most dramatic changes in the sixth generation
will be the explosive growth of Wide Area Networking.
(iii) Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a component of
Artificial Intelligence (Al).
(iv) It provides the ability to develop the computer program to
understand human language.
8. Write the significant features of monitor.
Answer:
Monitor:
(i) Monitor is the most commonly used output device to display
the information. It looks like a TV.
(ii) Pictures on a monitor are formed with picture elements
called PIXELS.
(iii) Monitors may either be Monochrome which display text or
images in Black and White or can be color, which display results in multiple
colors.
(iv) There are many types of monitors available such as CRT
(Cathode Ray Tube), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and LED (Light Emitting Diodes).
(v) The video graphics card helps the keyboard to communicate
with the screen.
(vi) It acts as an interface between the computer and display
monitor.
SECTION - D
Explain in detail
1. Explain the basic components of a computer with a neat diagram.
Answer:
Components of a
Computer :
The computer is the combination of hardware and software.
Hardware is the physical component of a computer like motherboard, memory
devices, monitor, keyboard etc., while software is the set of programs or
instructions. Both hardware and software together make the computer system to
function. Every task given to a computer follows an Input- process - output
cycle (IPO cycle).

(i) Input unit: Input unit is used to feed any form of data to the computer,
which can be stored in the memory unit for further processing.
Example : keyboard, mouse etc.
(ii) Central
Processing Unit : CPU is the major component which
interprets and executes software instructions. It also control the operation of
all other components such as memory, input and output units.
(iii) Arithmetic
and Logic Unit : The ALU is a part of the CPU where
various computing functions are performed on data. The ALU performs arithmetic
operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and logical
operations.
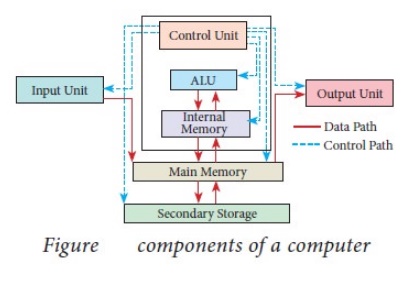
(iv) Control Unit : The control unit controls the flow of data between the CPU,
memory and I/O devices. It also controls the entire operation of a computer.
(v) Output Unit : An output unit is any hardware component that conveys
information to users in an understandable form. Example : Monitor, Printer etc.
(vi) Memory Unit : The Memory Unit is of two types which are primary memory and secondary memory. The primary memory is used to temporarily store the programs and data when the instructions are ready to execute. The secondary memory is used to store the data permanently. The Primary Memory is volatile, that is, the content is lost when the power supply is switched off. The Random Access Memory (RAM) is an example of a main memory. The Secondary memory is non volatile, that is, the content is available even after the power supply is switched off. Hard disk, CD-ROM and DVD ROM are examples of secondary memory.
2. Discuss the various generations of computers.
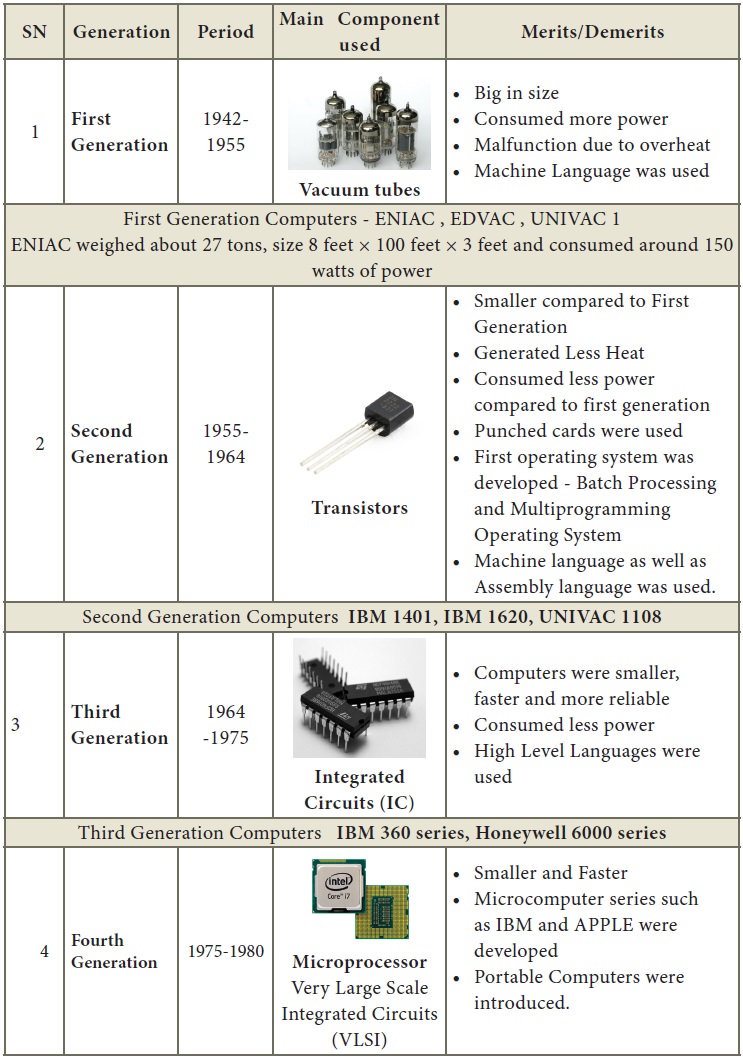
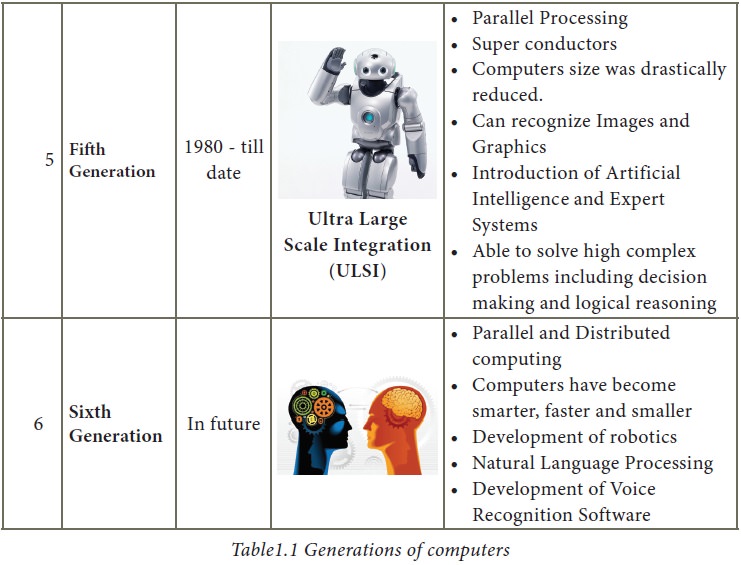
3. Explain the following
a. Inkjet Printer b. Multimedia projector c. Bar code / QR code Reader
Answer:
a. Inkjet Printers:
(i) Inkjet Printers use colour cartridges which combined
Magenta, Yellow and Cyan inks to create color tones. A black cartridge is also
used for monochrome output. Inkjet printers work by spraying ionised ink at a
sheet of paper.
(ii) They use the technology of firing ink by heating it so that
it explodes towards the paper in bubbles or by using piezoelectricity in which
tiny electric currents controlled by electronic circuits are used inside the
printer to spread ink in jet speed.
(iii) An Inkjet printer can spread millions of dots of ink at
the paper every single second.

b. Multimedia
Projectors:
(i) Multimedia projectors are used to produce computer output on
a big screen.
(ii) These are used to display presentations in meeting halls or
in classrooms.

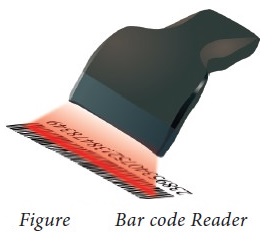
c. Bar Code / QR Code
Reader:
(i) A Bar code is a pattern printed in lines of different
thickness. The Bar code reader scans the information on the bar codes transmits
to the Computer for further processing.
(ii) The system gives fast and error free entry of information
into the computer.
QR (Quick response)
Code:
The QR code is the two dimension bar code which can be read by a camera and processed to interpret the image.
Related Topics