Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: Chemistry
Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
CHEMISTRY
Aminoglycosides are
hydrophilic, polycationic, amine-containing carbohydrates that are usually
composed of three to five rings. Most aminoglycosides are either nat-ural
products or derivatives of soil actinomycetes. They are often secreted by these
actinomycetes as mixtures of closely related compounds. The polycationic
amino-glycoside chemical structure results in a binding both to the anionic
outer bacterial membrane and to anionic phospholipids in the cell membranes of
mammalian re-nal proximal tubular cells. The former contributes to the
bactericidal effects of these compounds, while the latter binding accounts for
their toxicity. Because of their hy-drophilicity, the transport of
aminoglycosides across the hydrophobic lipid bilayer of eukaryotic cell
membranes is impeded.
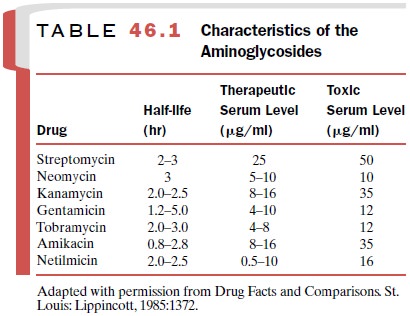
The major clinically
important aminoglycosides are amikacin (Amikin),
gentamicin (Garamycin), kanamycin (Kantrex), netilmicin (Netromycin), neomycin (Myci-fradin), streptomycin, and
tobramycin (Nebcin). Their pharmacokinetic characteristics are
shown in Table 46.1.
Related Topics