Chapter: Mechanical Engineering : Air Conditioning
Air Conditioning
Air Conditioning
1 Classification Of Air Conditioning
2 Window Type Air Conditioner
AIR CONDITIONING:
Air Conditioning is the process of conditioning
the air according to the human comfort, irrespective of external conditions.
Applications of Air Conditioning
Used in offices, hotels, buses, cars, etc.
Used in industries having tool room machines. Used in textile
industries to control moisture. Used in printing press.
Used in Food industries, Chemical plants.
CLASSIFICATION OF AIR
CONDITIONING:
Air
conditioning systems are classified as
1) According
to the purpose
·
Comfort Air conditioning.
·
Industrial Air conditioning. 2) According to
Season of the year
·
Summer Air conditioning.
·
Winter Air conditioning.
·
Year round Air conditioning.
Types of Air conditioners
·
Room Air conditioners
·
Winter Air conditioners
·
Central Air conditioners
Functions
of Air conditioners
·
Cleaning air.
·
Controlling the temp of air.
·
Controlling the moisture content.
·
Circulating the air.
BASIC CONCEPTS:
·
Dry air: The atmospheric air which no water vapour
is called dry air.
·
Psychometry: Psychometry is the study of the
properties of atmospheric air.
· 3)
Temperature: The degree of hotness (or)
Coldness is called the temperature.
·
Moisture: Moisture is the water vapour present in
the air.
·
Relative humidity: Relative humidity is the ratio
of actual mass of water vapour in a given volume to the mass of water vapour.
·
Dry bulb temperature: The temperature of air
measured by the ordinary thermometer is called dry bulb temperature:
·
Wet bulb Temperature: The temperature of air
measured by the thermometer when it is covered by the wet cloth is known as wet
bulb Temperature.
·
Dew point Temperature: The temperature at which
the water vapour starts condensing is called dew point Temperature
WINDOW TYPE AIR CONDITIONER:
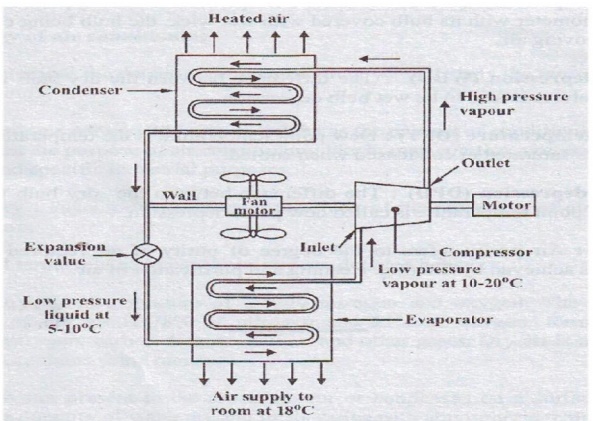
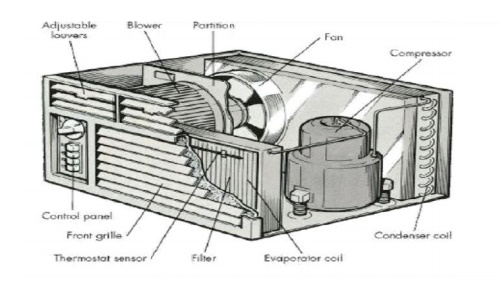
Construction:
This is
also called room air conditioner.
This unit
consists of the following.
·
A cooling system to cool and dehumidify the air
involves a condenser, a compressor and a refrigerant coil.
·
A filter to any impurities in the air. The filter
is made of mesh, glass wool or fibre.
·
A fan and adjustable grills to circulate the air.
·
Controls to regulate the equipment operation.
·
The low pressure refrigerant vapour is drawn from
the evaporator to the hermetic compressor through suction pipe.
·
It is compressed from low pressure to the high
pressure and supplied to the condenser.
·
It is condensed in the condenser by passing the
outdoor air over the condenser coil by a fan.
·
The liquid refrigerant is passed through the
capillary into the evaporator.
·
. In the evaporator the liquid refrigerant picks
up the heat from the refrigerator surface and gets vaporized.
·
A motor driven fan draws air from the room through
the air filter and this air is cooled by losing its heat to the low temperature
refrigerant and cold air is circulated back into the room.
·
The vapour refrigerant from the evaporator goes to
the compressor from evaporator and the cycle is repeated.
·
Thus the room is air conditioned
·
The quantity of air circulated can be controlled
by the dampers.
·
The moisture in the air passing over the
evaporator coil is dehumidified and drips into the trays.
·
This water evaporator to certain extent and thus
helps in cooling the compressor and condenser.
·
The unit automatically stops when the required
temperature is reached in the room. This is accomplished by the thermostat and
control panel.
Merits and Demerits of Window type air
conditioner:
Merits :
A separate temperature control is provided in each room. Ducts
are not required for distribution.
Cost is less.
Skilled technician is required for installation.
Demerits:
It makes noise.
Large hole is made in the external wall or a large opening to
be created in the window panel. This leads to insecurity to inmates.
Split Type Air Conditioner - Layout
In split air type air conditioner noise making components like
compressor and condenser are mounted outside or away from room.
·
Split type air conditioning system has two
main components.
·
The indoor unit consists of power cables,
refrigerant tube and an evaporator mounted inside the room.
Working:
·
Compressor is used to compress the
refrigerant.
·
The refrigerant moves between the evaporator
and condenser through the circuit of tubing and fins in the coils.
·
The evaporator and condenser are usually made
of coil of copper tubes and surrounded by aluminium fins.
·
The liquid refrigerant coming from the
condenser evaporates in the indoor evaporator coil.
·
During this process the heat is removed from
the indoor unit air and thus, the room is cooled.
·
Air return grid takes in the indoor air.
·
Water is dehumidified out of air is drained
through the drain pipe.
·
The hot refrigerant vapour is passed to the
compressor and then to
·
the condenser where it becomes liquid. Thus
the cycle is repeated.
·
A thermostat is used to keep the room at a
constant, comfortable temperature avoiding the frequent turning on off.
Merits and Demerits of Split type air conditioner:
Merits
It is compact
Upto four indoor AHU’s may be connected to
It is energy and money saving. Duct is not used.
Easier to install.
It is noiseless, because rotary air compressor used is, kept
outside. It is more efficient and powerful.
It has the flexibility for zoning.
DeMerits
:
• Initial cost is
higher than window air conditioner
• Skilled
technician is required for installation.
• Each zone or
room requires thermostat to control the air cooling.
Applications
of air conditioning:
• Used in houses,
hospitals, offices, computer centres, theatres, departmental stores etc.,
• Air-conditioning
of transport media such as buses, cars trains, aeroplanes and ships.
• Wide application
in food processing, printing, chemical, pharmaceutical and machine tool, etc.,
Related Topics