Exploring Continents | Chapter 7 | Geography | 8th Social Science - Africa | 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 7 : Exploring Continents: Africa, Australia and Antarctica
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 7 : Exploring Continents: Africa, Australia and Antarctica
Africa
Africa
Location and size
Africa is the second largest and
second most populous continent after Asia. It stretches from 37°21'North
latitude to 34° 51' South latitude and from 17°33' West longitude to 51°27'
East longitude. It spreads over an area of about 30.36 million square
kilometres (20.2% of the world’s land area). The equator passes through the
middle of Africa and cuts into two equal halves. It is the only continent
through which the major latitudes such as Tropic of Cancer, Equator and Tropic
of Capricorn pass. Its north -south extent is 7623 km and east-west extent is
7260 km. The Prime Meridian passes near Accra the capital of Ghana in the West
of this continent. Africa is located in all the four hemispheres.
The great explorers David Living
Stone and H.M. Stanley were the first to explore the interior parts of this
continent. The sources reveal that the early human ancestors have lived in
Africa for more than 5 million years. Africa is nicknamed as the "Mother Continent" as it was the
oldest inhabited continent on Earth. The diverse geographical condition of the
Continent is the main reason for heterogeneous culture and home of several
ethnic groups in Africa.
Africa is called a Dark
Continent. In the beginning the interior of Africa was largely unknown to them.
The European explorer Henry M. Stanley was the first to use the term the “Dark Continent” (1878).
Political Divisions
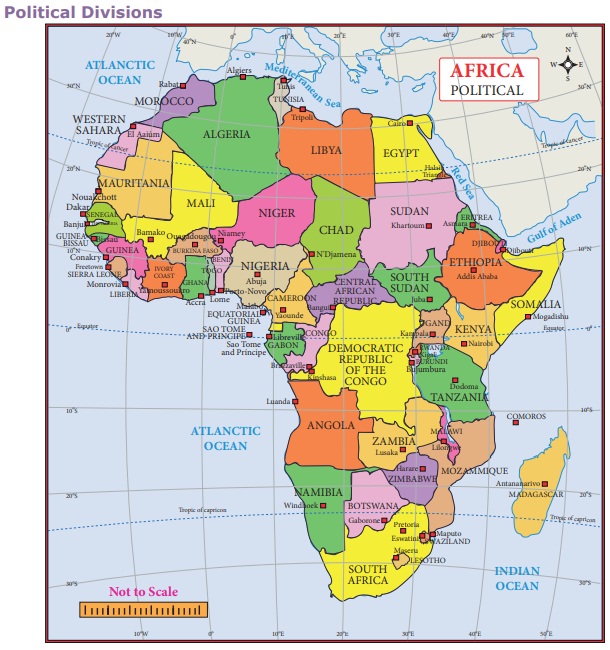
The continent of Africa consists of
54 countries. On the basis of their geographical location, the countries are
grouped as
a)West Africa b) North Africa c)
Central Africa d) Eastern Africa e) Southern Africa.
The north-western African
countries of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, Mauritania and Tunisia are collectively
called ‘Maghreb’ which means west in
Arabic language.
Physiographic Divisions
Africa consists of mixture of land
forms such as mountains, plateaus and plains.
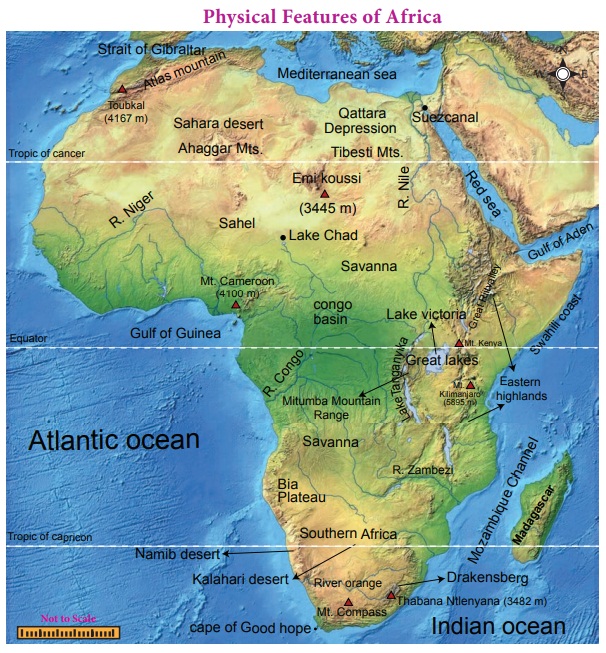
The following are the 8 major
physical divisions of Africa. Madagaskar is the major island of Africa.
1. Sahara
The world-famous Sahara Desert is located in the northern part of Africa. It is one of the largest hot deserts in the world. It has an area of 9.2 million sq km. The Sahara is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, the Red Sea in the east, the Mediterranean Sea in the north and Sahel in the south. This desert covers the areas of 11 countries: Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan and Tunisia.
It consists of many topographical
features such as mountains, plateaus, ergs, oases, sand-and gravel-covered
plains, salt flats, basins and depressions. Mount Koussi, an extinct volcano in
Chad, is the highest point in the Sahara with 3,445 m and the Qattara
Depression in Egypt is the Sahara’s deepest point (133 m below sea level). Nile
and Niger rivers run through the desert.
Atlas Mountain lies in the north-
west of Africa. It is a young fold mountain. It separates the Mediterranean sea
and Atlantic ocean. The highest point is Mount Toubkal (4167m).
2. Sahel
Sahel means border or margin. Sahel
is a semi-arid tropical Savanna region lies between the Sahara Desert in the
north and Savanna grassland in the south. It stretches east-west for a distance
of 4000 km and covers an area of 3.0 million sq km. It is largely a semi-arid
belt of barren, sandy and rocky land. This region marks the physical and
cultural transition between the more fertile tropical regions in the south and
desert in the north.
3. Savanna
Tropical dry grasslands with
scattered trees are known as ‘Savanna’.
It is located near the equator and covers almost half of the area of Africa.
This grassland is found in the regions just north and south of the rainforests
that lie along the equator. Trees are the main features of the landscape in
some parts of the savanna, while tall grass covers the other areas. Animals of
many species graze in this zone. The Serengeti Plain is one of the largest
plains in Savanna. This is called the ‘Open
Air Zoo’.
4. The Great Rift Valley and the Great Lakes of Africa
A rift valley is a large crack in
the earth’s surface formed by the shifting of tectonic plates. One of the major
geographical and geological features of Africa is the Great Rift Valley. It
stretches from northern Syria in Asia to central Mozambique in Africa for a
distance of 6400 kilometers. It runs through the eastern Africa and contains
many lakes.
ACTIVITY :
Find out-the Great
Rift Valley and the lakes connected with it from the atlas and mention them on
the map of Africa.
The African Great Lakes are a series
of lakes found in the rift valley. The water in the Great lakes of Africa
constitutes about 25% of the planet's unfrozen surface fresh water. There are
seven major lakes in this region.
Lake Victoria of this region is the
largest fresh water body in Africa and second largest in the world, next to
Lake Superior in USA. It is the source of river Nile. The other lake in the
valley is Tanganyika which is the longest and deepest fresh water lake in the
world. Lake Albert, Lake Edward, Lake Kivu, Lake Malawi, and Lake Turkana are
the other important lakes in Africa.
The glaciers on the top
of Kilimanjaro have been disappearing since 20th centuries. If this trend continues,
Kilimanjaro summit will be ice –free by 2025.
5. East African Highlands
Most African mountains are found in these
high lands. It stretches from Ethiopia to Cape of Good Hope. Mt. Kilimanjaro
(5895m) is the highest peak located in these highlands. Mt. Kenya and Mt.
Ruwenzori are the major mountains located in these high lands. This region is
sparsely populated and covered with rich grassland, forests, streams and
waterfalls of natural scenic beauty. It enjoys misty mornings and fresh
mountain breezes which attract large number of tourists from other parts of the
World.
6. Swahili Coast
Swahili coast is located along the
shores of East Africa. It stretches about 1,610 kilometers along the Indian
Ocean from Somalia to Mozambique. It was a region where the Africans and Arabs
mixed to create a unique culture referred to as Swahili Culture. People of this
coast are also called 'Swahili'.
7. The Congo Basin or Zaire Basin
Congo Basin lies on the both sides
of the the equator in west Central Africa. It comprises an area of more than
3.4 million square kilometres and covered with dense evergreen forest. It
provides food, shelter, medicine, water, and materials for over 7.5 million
people. It is the world’s second largest river basin next to Amazon.
8. Southern Africa
Most part of the Southern Africa is
a plateau region. Drakensberg Mountain
is found in the eastern portion of the escarpment. It extends from north east
to south west for 1125 km. Its highest peak is Thabana Ntlenyana (3482m). This
region is covered with grasslands known as ‘Veld’. Kalahari Desert lies in the south and Namib Desert is along
the south -west shore of Africa. Kalahari Desert in this region is not actually
a desert, but a bushy scrubland situated between the Orange and Zambezi Rivers.
Sheep rearing in semi
–arid region of South Africa is called 'Karoos'.
Drainage of Africa
1. River Nile
The Nile is the longest river in the
world with a length of 6650 km. It has two main tributaries. They are the White
Nile, which originates from Burundi, and the Blue Nile, which originates from
Ethiopia. These two join and form the Nile River at Khartoum, in Sudan. It
flows towards northward and drains into the Mediterranean-sea. Nile is known as
the “Father of African Rivers”.
The country Egypt is
called the “Gift of the Nile” as it is
the lifeline of the Egypt. Without Nile the Egypt would have been a desert.
ACTIVITY : On the outline map of Africa draw the courses of main rivers and name them.
2. River Congo or Zaire
Congo is the second largest river of
Africa after Nile. Its length is about 4700km. Congo rises in the highlands of
North Eastern Zambia between lakes Tanganyika and Nyasa. It flows through West
Central Africa and drains into the Atlantic Ocean.
3. River Niger
Niger is one of the major rivers in
West Africa and rises from the highlands of Guinea. It flows for about 4184 km
and finally drains into the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean.
4. River Zambezi
The Zambezi River is the fourth
longest in Africa. It rises in the north western Zambia. It is about 2574 km
long and drains into the Indian ocean.The world famous waterfall ‘Victoria’ is
formed by this river at the height of 108 meters. It is called the Southern
Africa’s “River of Life”.
River Limpopo and river Orange are
the other important rivers of Africa.
Climate
Africa is divided into six major
climatic zones. They are:
1. Arid and semi-arid climate: Northern Africa and Southern Africa have this climate. Rainfall is scanty
in this part.
2. Tropical savanna climate: It is found from 100-200 latitudes on either side of the equator. It is a
tropical wet and dry climate.
3. Equatorial climate: It is found in the equatorial
region covering the Congo River basin and east African highlands. Temperature
and rainfall are high all the year round in this region
4. Temperate climate: It prevails in southern
tip of South Africa. Since this part is located on the coast, the climate
of this region is equable.
5. Mediterranean climate: It is found in the north-western
and south western tips of Africa. These regions get rainfall in winters while
in summers it is hot and dry.
6. Tropical Monsoon climate: It is found in the eastern shore of Africa. Summers are hot with monsoon winds
bringing good rainfall while winters are cool and dry.
FACT
Tropical deserts are
located between 20° and 30° north and south of the equator on the western
margin of the continents. The deserts lie in the belt of the trade winds which
blow from northeast in the northern hemisphere and southeast in the southern
hemisphere. Therefore, the general direction of the trade winds is from east to
west. These winds shed their moisture on the eastern margins of the continents
and by the time they reach the west, they lose their moisture.
Flora and Fauna
African vegetation develops in
direct response to the interacting effects of rainfall, temperature, topography
and type of soil. Forests cover about 20% of the total land area of the
continent.The flora and fauna currently found in Africa are descended from plant
and animal species that were present in the continent when it was separated
from other land masses during the break up of Gondwanaland.
Baobab, Fever tree and Sausage are
the major trees of Africa. There are over one million species of animals in
Africa, including both the heaviest (elephants) and the tallest (giraffes) land
animals on the earth. White Rhinoceros, Western Green Mamba, Zebra, African
Elephants, chimpanzee, gorilla, Wildebeest, Hippopotamus, and Giraffe are the
major animals of Africa. Bonobo, Wild Dogs, hyena and Lemur are the typical
animals of Africa.

A hot and dry dusty
local wind blowing from the Sahara desert to Guinea coast is called 'Harmattan'.
* A hot local wind blowing from Sahara to Mediterranean Sea is
called 'Sirocco'.
* Tropical rain forest
is called the 'Jewel of the earth' and the World’s largest pharmacy.



Agriculture
Agriculture is a major economic
activity of the African continent. Wheat is grown in the temperate grasslands,
Mediterranean region and the Nile valley. Rice is cultivated in Guinea coast,
Mozambique, Madagascar and Nile valley. Maize and millets are grown all over
the plateau regions. Cotton is the chief cash crop of Africa. Egypt and Sudan
cultivate the best quality long staple cotton in the world. Coffee is grown in
Ethiopia. Ghana is the chief producer of cocoa. Oil palm is cultivated in West
African countries. Sugarcane, rubber, sisal and tobacco are the other major
crops and are mostly grown in East African countries.
Minerals
Africa is rich in few mineral
deposits. The region at the south of Sahara and the plateaus of Africa are the
major mineral regions of the continent. Diamonds are found in South Africa,
Congo, Botswana, Sierra Leone and Angola. Kimberly in South Africa is the
important producer of diamond. Angola, Nigeria, Gabon and Congo have more oil
reserves. Gold is found in South Africa, Namibia, West Africa and Ghana.
Chromium, cobalt, copper, iron ore, manganese. Zinc and nickel are scattered across
the continent.
Transport
Transports play an important role in
the economic development of a region. The physical features and slow economic
growth hinder the transport system in many African countries.
1. Land ways
Roadways and Railways in Africa are
poorly developed due to the presence of many barriers. It is very difficult to
lay the roads and rails across the deserts and the dense forests. South Africa,
Kenya, Egypt, Libya, Morocco and Nigeria have roadways and railways to some
extent.
2. Waterways
Africa has trade routes between Asia
and Australia in the east, Europe in the north and America in the west. The
major sea ports of Africa are Durban, Dar es Salaam and Mogadishu on the Indian
Ocean, Port Said, and Alexandria, on the Mediterranean Sea, Cape Town, Algiers
and Abidjan on the Atlantic Ocean.
3. Airways
They connect the capital cities of
Africa and the other parts of the world. The major international airports of
the continent are Cairo, Johannesburg, Nairobi, Dakar, Addis- Ababa,
Casablanca, Durban, Douala and Logos.
Population
Africa is the world’s second most
populous continent. The United Nations estimated the population of Africa as
131 crores in 2019. The population is unevenly distributed due to physical
barriers. The population density in Africa is 45 persons per sq km. 41% of the
population lives in urban and 59% in rural areas. Nile delta region and South
Africa are the densely populated regions of Africa. Nigeria is the most
populous country of Africa followed by Ethiopia.
The major tribes of
the world are called the first indigenous people. These people have a strong
sense of their own identity as unique with their own lands, languages and
cultures. Afar, Fatwa, Bushmen, Dinka, Masai, Pygmies, Zulu, Tswan, and Efe are
the major tribes of Africa.
Related Topics