Chapter: Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing : Process Planning and Concurrent Engineering
Advanced Manufacturing Planning
ADVANCED MANUFACTURING
PLANNING
Advanced manufacturing
planning emphasizes planning for the future. It is a corporate level activity
that to distinct from process planning because it is concerned with products
being contemplated in the company's long-term plans (210year future), rather
than products currently being designed and released. Advanced manufacturing planning involves working with sates,
marketing, and design engineering to forecast the new products that will be
introduced and to determine what production resources will be needed to make
those future products. Future products may require manufacturing technologies
and facilities not currently available within the firm. In advanced
manufacturing planning, the current equipment and facilities are compared with
the processing needs created by future planned products to determine what new
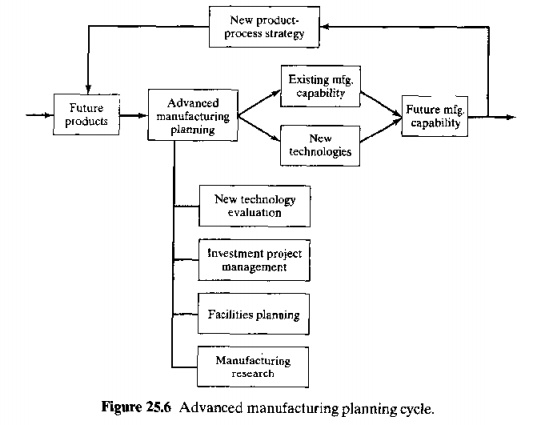
facilities should be installed. The general planning cycle is portrayed in
Figure 25.6. Activities in advanced manufacturing planning include: (1) new
technology evaluation, (2) investment project management, (3) facilities
planning. And (4) manufacturing research
New
Technology Evaluation. Certainly one of the reasons why a company may consider installing
new technologies is because future product lines require processing methods not
currently used by the company. To introduce the new products. the company must
either implement new processing technologies in-house or purchase the
components made by the new technologies from vendors. For strategic reasons, it
may be in the company's interest to install a new technology internally and
develop staff expertise in that technology as a distinctive competitive
advantage for the company. These issues must be analyzed, and the processing
technology itself must be evaluated to assess its merits and demerits.
A good
example of the need for technology evaluation has occurred in the
microelectronics industry, whose history spans only the past several decades.
The technology of microelectronics has progressed very rapidly, driven by the
need to include ever-greater numbers of devices into smaller and smaller
packages. As each new generation has evolved, alternative technologies have
been developed both in the products themselves and the required processes to
fabricate them. It has been necessary for the companies in this industry. as
wel! as companies that use their products, to evaluate the alternative
technologies and decide which should be adopted
There an:
other reasons why a company may need to introduce new technologies: (1) quality improvement. (2) productivity
improvement, (3) cost reduction, (4) lead time reduction, and (5) modernization
and replacement of worm-out facilities with new equipment. A good example of
the introduction of a new technology is the CAD/CAM systems that were installed by
many companies during the t 980s. Initially, CAD/CAM was introduced to
modernize and increase productivity in the drafting function in product design.
As CADlCAM
technology itself evolved and its capabilities expanded to include three dimensional
geometric modeling, design engineers began developing their product designs on
these more powerful systems. Engineering analysis programs were written to perform
finite-element calculations for complex heat transfer and stress problems. The
usc of CAD had the effect of increasing design productivity, improving the
quality of the design, improving communications, and creating a data base for
manufacturing. In addition, CAM software was introduced to implement process
planning functions such as numerical control part programming (Section 6.5) and
CAPP, thus reducing transition time from design to production
Investment
Project Management. Investments in new technologies or new equipment
are generally made one project at a time. The duration of each project may be
several months to several years. The management of the project requires a
collaboration between the finance department that oversees the disbursements, manufacturing
engineering that provides technical expertise in the production technology, and
other functional areas that may be related to the project. For each project,
the following sequence of steps must usually be accomplished: (1) Proposal to
justify the investment is prepared.
(2)
Management approvals are granted for the investment. (3) Vendor quotations are
solicited. (4) Order is placed to the winning vendor. (5) Vendor progress in
building the equipment is monitored. (6) Any special tooling and supplies are
ordered. (7) The equipment is installed and debugged. (8) Training of
operators. (9) Responsibility for running the equipment is turned over to the
operating department.
Facilities
Planning. When new equipment is installed in an existing plant, an alteration of
the facility is required. Fluor space must be allocated to the equipment, other
equipment may need to be relocated or removed, utilities (power, heat, light,
air, etc.] must be connected, safety systems must be installed if needed, and various
other activities must be accomplished to complete the installation. In extreme
cases, an entire new plant may need to be designed to produce a new product line
or expand production of an existing line. The planning work required to
renovate an existing facility or design a new one is carried out by the plant
engineering department (or similar title) and is called facilities planning. In
the design or redesign of a production facility. manufacturing engineering and
plant engineering must work closely to achieve a successful installation.
Facilities planning is
concerned with the planning and design of the fixed assets (e.g land. buildings, and equipment) of an
organization. Facilities planning can be divided into two types of problems:
(1) facilities location and (2) facilities design. Facilities location deals with the problem of determining the optimum geographical location for a
new facility. Factors that must be considered in selecting the best location
include: location relative to customers and suppliers. Labor availability skills of labor pool, transportation, cost of living. quality of life. energy costs,
construction (;OSIS. and tax and other incentives that may be offered by the 10l:alor state government. The choices i:l facilities location include
international a~ well as national alternatives. Once the general location of
the facility has been decided (i.e.,state and region within the state). the
local site must be selected.
Facilities design consists
of the design of the plant, which includes plant layout, material handling.
building, and related issues. The plant
layout is the physical arrangement of equipment and space in the building.
Objectives in designing a plant layout include logical work flow. minimum material movement. convenience
of those using the facility. safety, expandability, and flexibility in case
rearrangement is necessary. Material
handling is concerned with the efficient. movement 01 work in the factory.
This is usually accomplished by means of equipment such as powered forklift
trucks. conveyors of various types. automatic guided vehicles. cranes, and
hoists (Chapter 10). Material
handling and plant layout arc closely related design issues. Building design deals with the
architectural and structural design of the plant and includes not only brick,
and mortar but also utilities and communications lines
Manufacturing Research
and Development. To develop the required manufacturing technologies, the
company may find it necessary to undertake a program of manufacturing research
and development (R&D). Some of this research is done internally, whereas in
other cases projects are contracted to university and commercial research
laboratories specializing in the associated technologies. Manufacturing
research can take various forms. including:
Development
of new processing technologies - This R&D activity involves the
development of new processes that have never been used before. Some of the
processing technologies developed for integrated circuits fabrication represent
this category Other recent examples include rapid prototyping techniques
(Section 24.1.2).
Adaptation
of existing processing technologies A manufacturing process may exist that has never been used on the type of
products made by the company yet it is perceived that there is a potential for
application. In this case, the company must engage in applied research to
customize the process to its needs.
Process
fine. tuning This involves research on processes used by the
company. The objectives of a given
study can be any of the following; (J) improve operating efficiency, (2)
improve product quality, (3) develop a process model, (41 learn how to better
control the process. (5) determine optimum operating conditions, and so forth.
Software
systems development - These are projects involving
development of customized manufacturing related software for the company.
Possible software development projects might include: cost estimating software,
parts classification and coding systems. CAPP, customized CAD/CAM application
software, production planning and control systems, work-in-process tracking
systems. and similar projects. Successful development of a good software
package may give the company a competitive advantage
Automation
systems development - These projects are similar to the
preceding except they deal with hardware or hardware/software combinations.
Studies related to
applications
of industrial robots (Chapter 7) in the company are examples of this kind of
research .
Operations
research and simulation Operations research
involves the development of
mathematical models to analyze operational problems. The techniques include
linear programming, inventory models, queuing theory, and stochastic processes.
In many problems, the mathematical models are sufficiently complex that they
cannot be solved in closed form. In these cases, discrete event simulation can
be used to study the operations. A number of commercial simulation packages are
available for this purpose.
Manufacturing
R&D is applied research. The objective is to develop or adapt a technology or technique
that will result in higher profits and a distinctive competitive advantage for
the company.
Related Topics