Chapter: Mechanical : Mechatronics : Actuation System
Actuation System: DC Servo Motor
DC SERVO MOTOR
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATING
A DC motor is used in a control system where an appreciable
amount of shaft power is required. The DC motors are either a rmature -
controlled with fixed field, or field - controlled with fixed armature current.
DC motor s used in instrument employ a fixed permanent - magnet field, and the
control signal is applied to the armature terminals.
In addition to the torque when conductor moves in magnetic
field, voltag e is generated across its terminals which opposes the current
flow and hence called as Back e.mf.
Basic
Classification
Basically
d.c. servo motors are classified as:
(i) Variable
magnetic flux motors.
(ii)Constant
magnetic flux motors
Derivation
of transfer functions for
(i) Field
controlled d.c. servo motor
(ii)Armature
controlled d.c. servo - motors.
i. Field
Controlled DC Servo motor Assumptions
(1)Constant
armature current is fed into the motor.
(2)Nf % If.
Flux produced is proportional to field current. Nf = Kf If
(3)Torque is
proportional to product of flux and armature current.
% N Ia .
Tm = K` N
Ia = K’
Kf If Ia
Tm = Km
Kf If
Where
Km = K`
Ia =
constant
Now shaft torque Tm is used for driving load against the
inertia and frictional torque
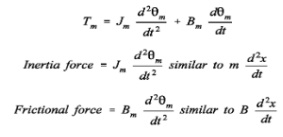
finding Laplace Transforms of equations Tm (s) =
Km Kf If(s)
Ef (s) =
(SLf + Rf) If (s)
Tm (s) = Jms 2m (s) + Bms2m (s)
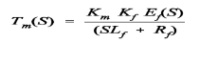
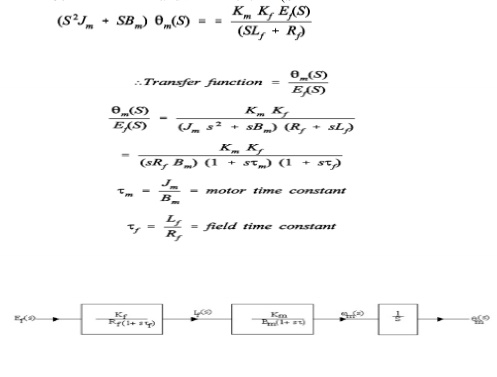
Eliminate
If (s) from equations (4) and (5)Input = Ef(S)
Output = Rotational displacement 2m (S
ii.Armature
Controlled D.C. Servo Motor
Assumptions:
(i)Flux is directly proportional to current
through field winding. Nm = Kf If = constant
(ii) Torque
produced is proportional to product of flux and armature current.
T = K`m N Ia
T = K`mKf If Ia
(iii)Back
e.m.f is directly proportional to shaft velocity Tm, as flux N is constant
Related Topics