Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Electroconvulsive Therapy
What are the anesthetic agents of choice for ECT?
What are the anesthetic
agents of choice for ECT?
Short-acting intravenous anesthetic agents and
muscle relaxation are used to facilitate ECT. As previously men-tioned, the
goal of ECT is to produce a generalized seizure;
however, anesthetic agents have inherent
anticonvulsant properties. Therefore, the most appropriate agent and dose
should be selected for this short procedure.
Of the barbiturates, the most commonly used
induction agent for ECT is methohexital. It is short-acting and has the least
effect on seizure duration of all the intravenous induction agents. Thiopental
has also been used but its duration of action and side-effect profile is not as
favorable as methohexital.
Ketamine has also been used for ECT, but its
utility is limited by subsequent increases in heart rate and blood pressure.
Etomidate has been shown to increase the seizure duration when compared with
methohexital. However, the usefulness of etomidate is limited by pain on
injection, postprocedural confusion, and emesis. Its use may be appropriate,
however, for patients with limited cardiac reserve.
There has been a long-standing debate over the
role of propofol in ECT. Propofol has a greater anticonvulsant effect on ECT
than other intravenous anesthetics, although propofol may itself be associated
with the induction of seizures when used in higher doses. Propofol has been
shown to be beneficial in patients with a history of pro-longed ECT-induced
seizure, as well as those with a history of post-ECT nausea and vomiting.
Emergence from propo-fol is marginally faster than from other intravenous
anes-thetics when given in equipotent doses.
Remifentanil has recently been demonstrated to
effec-tively attenuate the sympathetic response to ECT without affecting
seizure duration or prolonging recovery time. Induction doses of
benzodiazepines raise the seizure threshold and may prolong emergence. Some
authors have described the use of volatile agents, particularly sevoflu-rane,
for ECT. Sevoflurane may be used in the pregnant patient to prevent preterm
labor. If sevoflurane is used for induction of the pregnant patient beyond 12
weeks gestation, the airway must be secured with an endotracheal tube to
prevent aspiration. The major disadvantage of sevoflurane is the requirement
for an anesthesia machine.
The muscle relaxant of choice for ECT is
succinyl-choline because of its quick onset and short duration of action. If
there are any contraindications to using succinyl-choline, any of the short to
moderate duration nondepo-larizing muscle relaxants can be substituted. The
short duration of action of mivacurium makes it the most commonly used muscle
relaxant when succinylcholine is contraindicated. However, it should not be
used in the patient with pseudocholinesterase deficiency.
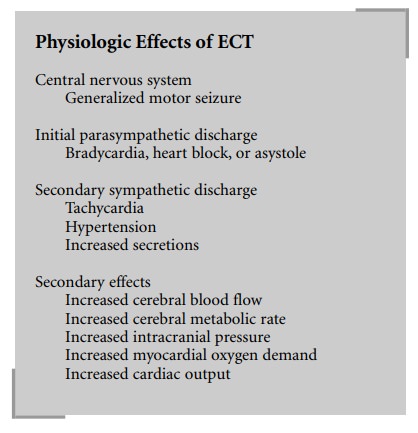
A variety of medications have been used to
control the cardiovascular responses associated with ECT. Anticholinergics,
such as glycopyrrolate and atropine, have been administered as premedications
to block the initial parasympathetic response (bradycardia) of ECT. To con-trol
the tachycardia and hypertension associated with the sympathetic response, β-blockers, calcium channel block-ers, α2
agonists and antagonists, vasodilators, ganglionic blockers, local anesthetics,
and opioids have been used alone or in combination with mixed results.
Short-acting drugs seem to be most appropriate for ECT.
Related Topics