Chapter: 9th Social Science : Civics : Forms of Government and Democracy
What Is Democracy?
What Is Democracy?
·
Democracy is a form of government that allows people to choose their rulers.
·
Only leaders elected by people should rule the country.
·
People have the freedom to express views, freedom to organise and freedom to protest.
1. Meaning of Democracy
Democracy is a system of government in which the
supreme power is vested in the people of a country and people elect their
representatives either directly or indirectly through fair and free elections,
which are usually held periodically.

2. Definition
According to Mahatma Gandhi, “True democracy cannot
be worked by twenty men sitting at the centre. It has to be worked from below
by the people of every village.”

3. Salient Features of Democracy
1. Elected
representatives of people and final decision-making power to the
representatives.
2. Free and
fair elections.
3. Universal
adult franchise with each vote having equal value.
4. Fundamental
rights and protection of individual freedom.
4. Evolution of Democracy
Democracy began 2,500 years ago in
some of the
city-states of ancient Greece. It is important to know that
democratic institutions existed in India as early as the Vedic period.
Chanakya’s Arthashastra tells us that
in ancient India, an autonomous
village community was the basic unit of the local government. In ancient Tamil
Nadu, Kudavolai system was a very notable and unique feature of the village
administration of the Cholas. The evolution towards a democracy is represented
by the following values: freedom, equality, liberty, accountability,
transparency and trust.

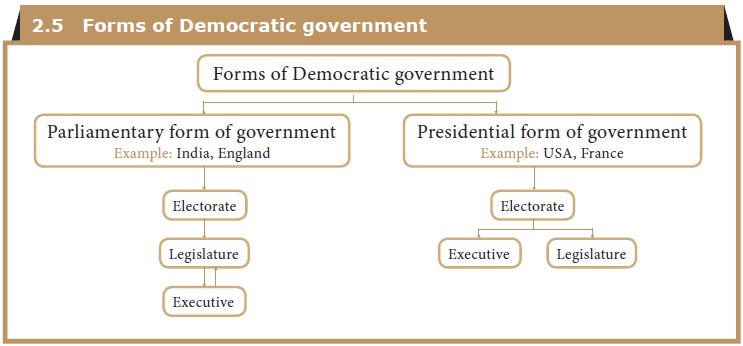
5. Forms of Democratic governmevt
6. Types of Democracy
There are two types of democracies:
1. Direct democracy
2. Indirect (representative) democracy
The types of democracy refers to the kind of
government or social structures which allow people to participate equally.
Direct Democracy
When the people themselves directly express their
will on public affairs, the type of government is called pure or direct
democracy.
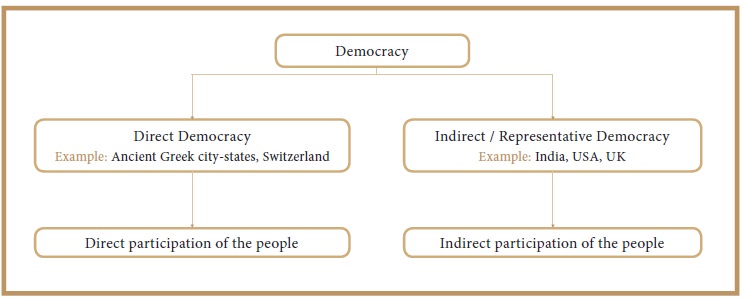
Example: Ancient Greek city-states, Switzerland
Indirect Democracy / Representative Democracy
When the people express their will on public
affairs, through their elected representatives, the type of government is
called indirect or representative democracy.
Example: The prevailing system of democracy in
India, USA and UK
7. Democracy in India
India has a parliamentary form of democracy. The Indian Parliament comprises the elected representatives of people and makes the laws for the country. The participation of people in the decision making and the consent of citizens are the two important elements of the parliamentary form of government in India.

India is the largest democratic country in the
world. Democracy in India works on five basic principles. These are sovereign,
socialist, secular, democratic, republic.
Every person who is a citizen of India and who is
not less than 18 years of age can exercise their right to vote in India, based
on universal adult suffrage. There is no discrimination based on a person’s
caste, creed, religion, region, gender and education when it comes to providing
the right to vote.
8. Merits and Demerits of Democracy
Merits
·
Responsible and accountable government
·
Equality and fraternity
·
Sense of responsibility among common people
·
Local self-government
·
Development and prosperity for all
·
Popular sovereignty
·
Sense of cooperation and fraternal feeling
Demerits
·
Indirect or representative nature of democracy
·
Lack of interest in democratic process and hence
lower turnout in elections
·
Instability in governance due to fractured mandate
·
Delay in decision-making process.
9. Elections in India
India has a quasi-federal government, with elected
representatives at the federal, state and local levels. The general elections
are conducted by the Election Commission of India. At the national level, the
President of India, appoints the Prime Minister, who enjoys majority in the Lok
Sabha, the lower house of the Parliament of India.
All members of the Lok Sabha are directly elected
through general elections, which take place once in every five years, in normal
circumstances.

Two Anglo Indian members can be nominated by the President of
India to the Lok Sabha.
Members of the Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of the
Indian Parliament, are elected by an electoral college consisting of elected
members of the legislative assemblies of the states and the Union Territories of
India. The President of India nominates 12 members for their contributions to
art, literature, science and social services.
10. The First Elections in Democratic India
General elections to the first Lok Sabha since
independence Were held in India between 25 October 1951 and 21 February 1952.
The Indian National Congress emerged victorious by winning 364 of the 489
seats. Jawaharlal Nehru became the first democratically elected Prime Minister
of the country.
11. Major challenges to Indian Democracy
Democracy is the dominant form of government in the
contemporary world. It has not faced a serious challenge or a rival so far. In
the last hundred years, there has been an expansion of democracy all over the
world. The various aspects of democracy and its challenges are:
1. Illiteracy
2. Poverty
3. Gender
discrimination
4. Regionalism
5. Casteism,
communalism and religious fundamentalism
6. Corruption
7. Criminalisation
of politics
8. Political
violence
12. Conditions for the Success of Democracy in India
·
Empowerment of the poor and illiterates to enjoy the goodness of democracy.
·
Willingness among the elected people not to misuse their powerful position and public wealth.
·
Eradication of social evils and dangers from which democracy suffers.
·
An impartial and efficient press to form public opinion.
·
Presence of strong public opinion.
·
Feeling of tolerance and communal harmony among the people.
·
Awareness among the people of the fundamental rights that they are entitled to enjoy.
·
Conscious check and vigilance on the working of the elected representatives.
·
Powerful and responsible opposition.
Though democracy in India has been appreciated
worldwide for its working, there is still a lot of scope for improvement. The
above-mentioned steps must be taken to ensure smooth functioning of democracy
in the country.
Indian democracy can be successful and vibrant only
when its citizens imbibe and reflect in their behavior the basic democratic
values like equality, freedom, social justice, accountability and respect for
all. Their mindset, thinking and behavior are expected to be in tune with the
essential conditions of democracy. They have to appreciate the opportunities
for their desired roles like participation, making the system accountable,
fulfilling obligations, and playing proactive roles to actualize the goals of
democracy.
Recap
·
Government is a group of people who govern a community or unit.
·
Monarchy is a system of government in which one person reigns supreme, usually a king or queen.
·
Types of democracy refer to kind of government or social structures which allow people to participate
equally, either directly or indirectly.
·
When the people themselves directly express their will on public affairs, the type of government is
called pure or direct democracy.
·
Based on universal adult suffrage,
every Indian citizen, above 18 years of age, can exercise the right to
vote in India.
Related Topics