Chapter: Biochemistry: Vitamins
Vitamin - A
Vitamin - A
Vitamin A is found only in foods of animal
origin. It is present in almost all species of fish, birds and mammals. The
yellow plant pigments α, β and γ carotenes and cryptoxanthin are
precursors of vitamin A. The body has the ability to convert these carotenoid
compounds present in the diet into vitamin A.
The chemical structure of β - carotene is such that it oxidizes to form two molecules of
vitamin A, the other provitamins form only one. b-carotene is more efficiently converted to
vitamin A than α - or γ - carotene or cryptoxanthin.
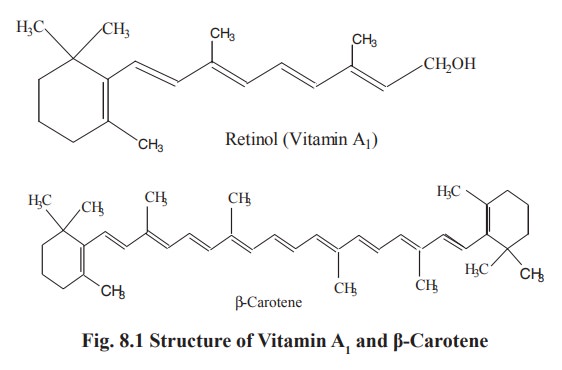
There are two forms of vitamin A: Vitamin A1
which occurs in the liver of marine water fish and Vitamin A2 found
in the liver of fresh water fish. The vitamin A which contain alcoholic group
in the side chain is called as retinol (Fig. 8.1) and which contain aldehyde
group is known as retinal. Though the two vitamins differ slightly in their
chemical structures their physiological functions are the same.
Functions
Vitamin A is essential
·
for the
growth and metabolism of all body cells
·
for the
formation of rhodopsin (visual purple) a complex substance formed from retinol
and protein. Rhodopsin, a pigment found in retina is necessary for vision in
dim light.
·
for the
maintenance of healthy skin, particularly mucous membrane of the cornea and the
lining of respiratory tract.
Sources
The liver of any animal is a rich source of
vitamin A. Fish liver oil is an excellent source. Whole milk, egg yolk, dark
green leafy vegetables and deep yellow vegetables and fruits are rich in
carotenes, which can be converted into vitamin A by the intestinal wall.
Requirements
Vitamin A requirement is based on the intake to
maintain the normal blood level. Adults placed on a vitamin A free diet are
found to show no change in the level for several weeks.The capacity of the body
to store vitamin A provides for an effective emergency supply. Recommended
amount of Vitamin A for different age group is as follows:
Infants - 1500 IU / day
Children - 2000-3000 IU / day
Adults Pregnant and - 5000 IU / day
lactating women - 6000-8000 IU / day (IU = International units)
Absorption and storage
Vitamin A and carotene are absorbed from the
small intestine into the lymph system. The maximum absorption is reached 3 to 5
hours after consumption. The rate of absorption of vitamin A is more rapid than
that of carotene. In the human being about 95% of the vitamin A stored in the
body is found in the liver with small amount in the lungs, adipose tissue and
kidneys.
Deficiency
The earliest sign of vitamin A deficiency is
concerned with vision. Initially there is a loss of sensitivity to green light,
followed by impairment to adapt to dim light. This condition leads to night blindness. More prolonged or
severe deficiency leads to the ulceration of cornea and this condition is known
as xerophthalmia or keratomalacia.
Related Topics