Chapter: Health Management in Aquaculture: Viral diseases
Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN) - Viral Infections In Fish
Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN)
CAUSATIVE AGENT:
Nodavirus (20-25 nm)
SPECIES AFFECTED:
Grouper (Epinephelus spp.), sea bass (Lates spp.) (Fig. 2-5), barfin flounder (Verasper moseri), European bass (Dicentrarchus labrax), parrotfish (Oplegnathus fasciatus), striped jack (Pseudocaranx dentex), turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), Japanese flounder(Paralicthys olivaceus), barfinflounder (Verasper moseri), red sea bream (Pagrus major), sea bream (Sparusaurata), shi drum(Umbrina cirrosa), cod (Gadus macrocephalus), Atlantichalibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus), purplish amberjack (Seriola dumerili), and tiger puff (Takifugu rubripes) in Thailand, Japan, Taiwan, Singapore, Ta-hiti, Greece, Australia and Europe.
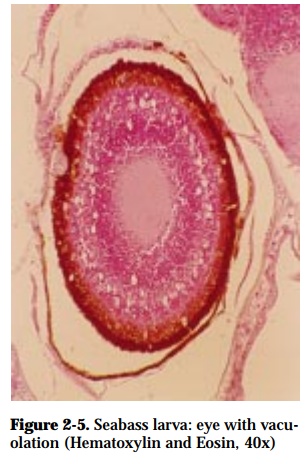
GROSS SIGNS:
Affected larvae and juveniles show lethargy, pale color, loss of appetite, thin-ness, loss of equilibrium and corkscrew swimming. Some fish sink to the bot-tom then float to the surface again.
EFFECT ON HOST:
This viral infection is also known as Paralytic Syndrome, Viral Encephalopathy and Retinopathy, Spinning Grouper Disease, Piscine Neuropathy or Fish En-cephalitis. The disease is more severe in less than 20 days old larvae. Diseased fish had pale livers, empty digestive tracts, the intestines filled with greenish to brownish fluid and the spleens are red-spotted. The virus replicates in the eye, the brain, and the distal spinal cord of affected fish causing vacuolating en-cephalopathy and retinopathy. It also multiplies in the gonad, liver, kidney, stomach and intestine. This disease caused 50-95% mortalities among fish lar-vae and juveniles at 26-30oC in Taiwan and Thailand. It can be transmitted from diseased to healthy fish within 4 days of contact. The virus is more viru-lent at 28oC than at 16oC. Fish broodstocks can be virus reservoirs.
DIAGNOSIS:
Histopathology showing vacuolations in the nerve cells of the eye retina and the brain of affected fish is diagnostic for this disease. The virus can be isolated in SSN-1 and barramundi cell lines on which it induces CPE. The virus can be identified by EM, PCR, RT-PCR, ELISA, FAT and by in-situ hybridization assay.
Related Topics