Chapter: Medical Physiology: Somatic Sensations: II. Pain, Headache, and Thermal Sensations
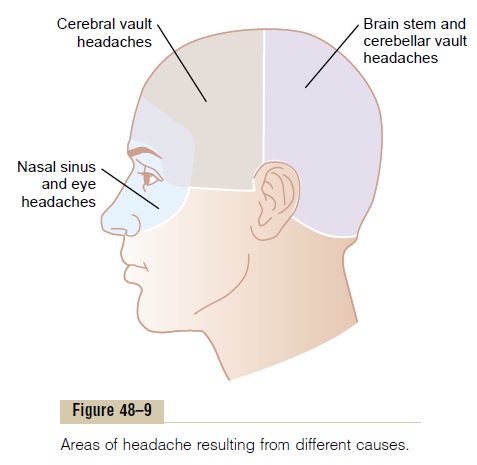
Types of Intracranial Headache
Types of Intracranial Headache
Headache of Meningitis. One of the most severeheadaches of all is that resulting from meningitis, which causes inflammation of all the meninges, including the sensitive areas of the dura and the sensitive areas around the venous sinuses. Such intense damage can cause extreme headache pain referred over the entire head.
Headache Caused by Low Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure.
Removing as little as 20 milliliters of fluid from the spinal canal, particularly if the person remains in an upright position, often causes intense intracranial headache. Removing this quantity of fluid removes part of the flotation for the brain that is normally provided by the cerebrospinal fluid. The weight of the brain stretches and otherwise distorts the various dural surfaces and thereby elicits the pain that causes the headache.
Migraine Headache. Migraine headache is a special typeof headache that is thought to result from abnormal vas-cular phenomena, although the exact mechanism is unknown. Migraine headaches often begin with various prodromal sensations, such as nausea, loss of vision in part of the field of vision, visual aura, and other types of sensory hallucinations. Ordinarily, the prodromal symptoms begin 30 minutes to 1 hour before the beginning of the headache. Any theory that explains migraine headache must also explain the prodromal symptoms.
One of the theories of the cause of migraine headaches is that prolonged emotion or tension causes reflex vasospasm of some of the arteries of the head, including arteries that supply the brain. The vasospasm theoretically produces ischemia of portions of the brain, and this is responsible for the prodromal symptoms. Then, as a result of the intense ischemia, something happens to the vascular walls, perhaps exhaustion of smooth muscle contraction, to allow the blood vessels to become flaccid and incapable of maintaining vascu-lar tone for 24 to 48 hours. The blood pressure in the vessels causes them to dilate and pulsate intensely, and it is postulated that the excessive stretching of the walls of the arteries—including some extracranial arteries, such as the temporal artery—causes the actual pain of migraine headaches. Other theories of the cause of migraine headaches include spreading cortical de-pression, psychological abnormalities, and vasospasm caused by excess local potassium in the cerebral extra-cellular fluid.
There may be a genetic predisposition to migraine headaches, because a positive family history for migraine has been reported in 65 to 90 per cent of cases. Migraine headaches also occur about twice as fre-quently in women as in men.
Alcoholic Headache. As many people have experi-enced, a headache usually follows an alcoholic binge. It is most likely that alcohol, because it is toxic to tissues, directly irritates the meninges and causes the intracra-nial pain.
Headache Caused by Constipation. Constipation causesheadache in many people. Because it has been shown that constipation headache can occur in people whose pain sensory tracts in the spinal cord have been cut, we know that this headache is not caused by nervous impulses from the colon. Therefore, it may result from absorbed toxic products or from changes in the circula-tory system resulting from loss of fluid into the gut.
Related Topics