Chapter: Essential Microbiology: Procaryote Diversity
Stalked and budding Proteobacteria
Stalked and budding Proteobacteria
The members of this group of aquatic Proteobacteria differ noticeably in their appearance from typical bacteria by their possession of extracellular extensions known as prosthecae; these take a variety of forms but are always narrower than the cell itself.They are true extensions of the cell, containing cytoplasm, rather than completely ex-tracellular appendages.
In the stalked bacteria such as Caulobacter (Figure 7.5), the prostheca serves both as a means of attaching the cell to its substratum, and to enhance nutrient absorption by
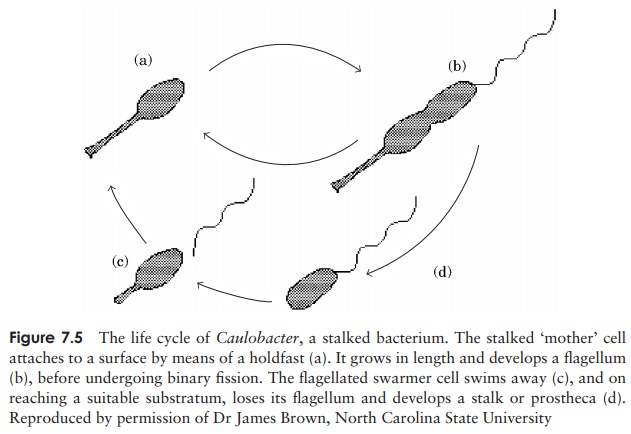
increasing the surface area-to-volume ratio of the cell. The latter enables such bacteria to live in waters containing extremely low levels of nutrient. Caulobacter lives part of its life cycle as a free-swimming swarmer cell with no prostheca but instead a flagellum for mobility.
The iron oxidiser Gallionella (see Nitrifying Proteobacteria above) may be regarded as a stalked bacterium, however it is not truly prosthecate, as its stalk does not contain cytoplasm.
In the budding bacteria, the prostheca is involved in a distinctive form of reproduc-tion, in which two cells of unequal size are produced (c.f. typical binary fission, which results in two identical daughter cells). The daughter cell buds off from the mother cell, either directly, or as Hyphomicrobium spp. at the end of a hypha (stalk) (Figure 7.6). Once detached, the daughter cell grows to full size and eventually produces its own buds. Hyphomicrobium is a methanotroph and a methylotroph, so it also belongs to the methanotrophs described earlier.

In some bacteria, more than one prostheca is found per cell; these polyprosthecate forms include the genus Stella, whose name (‘a star’) derives from its six symmetrically arranged buds.
Representative genera: Caulobacter, Hyphomicrobium
Related Topics