Chapter: Basic Radiology : Scope of Diagnostic Imaging
Nuclear Medicine - Radiology
NUCLEAR
MEDICINE
Nuclear medicine studies, in
general, are very sensitive, but relatively nonspecific in the detection of
pathology. It is very important, therefore, to correlate nuclear medicine
examina-tions with pertinent history, physical findings, laboratory data, and
other diagnostic imaging studies in order to opti-mize the diagnostic utility
of these studies. Nuclear medicine imaging examinations are performed by
administering vari-ous radiopharmaceuticals to the patient and subsequently
recording in vivo distribution. Radiopharmaceuticals consist of two main
components: (1) the main component that is distributed to various organs via a
number of different mech-anisms, and (2) the radionuclide that is tagged to the
main component, which emits gamma rays, permitting detection of the compound in
the body.
Most nuclear medicine studies are
performed with gamma cameras, which provide planar (2D) images. Single photon
emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a special technique that creates
tomographic images using a rotating gamma camera system. Positron emission
tomography (PET) is another unique technique that creates tomographic images by
detecting gamma rays produced when positrons interact with electrons.
Some common
nuclear medicine procedures
includecardiac studies to evaluate myocardial perfusion and/or
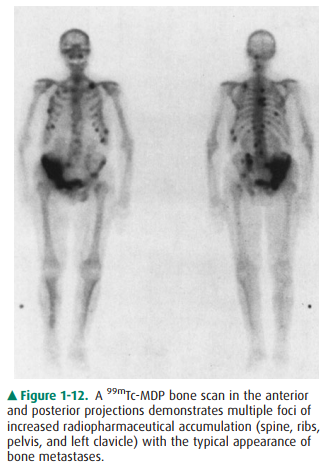
ventricular function; (2) skeletal studies to evaluate for early bony
metastases (Figure 1-12), skeletal trauma, osteomyelitis, and primary bone
neoplasms; (3) renograms and renal scans to evaluate kidney function and
morphology; (4) ventilation-perfusion studies to evaluate for suspected
pulmonary emboli; and (5) PET studies to diagnose or stage tumors (eg, lung,
lymphoma, melanoma, colorectal, breast), evaluate dementia, monitor for brain
tumor recurrence, track post-therapy changes, and evaluate myocardial
viability.
Less common nuclear medicine
studies include (l) thy-roid evaluation of nodules and therapy for
hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer; (2) hepatobiliary studies to evaluate for
acute cholecystitis and bile duct patency; (3) brain imaging to evaluate
dementia and brain death; (4) white blood cell stud-ies to detect infection and
inflammation; (5) gastrointestinal bleeding studies to detect and localize
small gastrointestinal bleeds; (6) lymphoscintigraphy to identify sentinel
lymph nodes for surgery; and (7) parathyroid studies to identify adenomas and
hyperplasia.
Positron Emission Tomography/CT (PET/CT)
Positron emission tomography
(PET) with fluorine (18F) fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is a functional
imaging method that plays an important role in the diagnosis and staging of
malignancy, as well as in treatment monitoring. CT is an anatomic imaging
modality that provides excellent spatial localization of pathology. The first
combined PET/CT scanner was in operation in 2001. Combined PET/CT scanners have
separate individual imaging components that reside in the same unit. In
general, a CT scan is per-formed first and the PET scan follows. Output from
PET/CT imaging includes separate CT and PET images, as well as the coregistered
fused images that overlay the anatomic CT and metabolic data. The combined
anatomic and functional images can be acquired in a single examina-tion. The
use of CT images for attenuation correction of the PET emission data also
significantly reduce PET scan time. The combined PET/CT is more sensitive and
specific for detecting otherwise occult malignancy, tumor staging, and
detecting disease recurrence and/or metastasis. PET/CT has also proven useful
for following post-therapy changes, such as squamous-cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. Fused PET/CT images consistently outperform sepa-rately collected CT
and PET images for the detection of pathology, even when the separate nonfused
imagines are viewed simultaneously.
Related Topics