Chapter: Mechanical : Manufacturing Technology : Metal Forming Process
Metal Forming Process
METAL
FORMING PROCESS
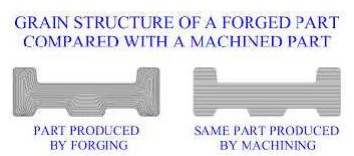
The Materails to be used in
places where the component is subjected to very high Impact load, Shock Load,
intermittant load and in Power transmission lines, Need to be produced with
dense grain structure. This requirement can be acheived by manufacturing
process such as Forging, Rolling,Extrusion and Drawing.
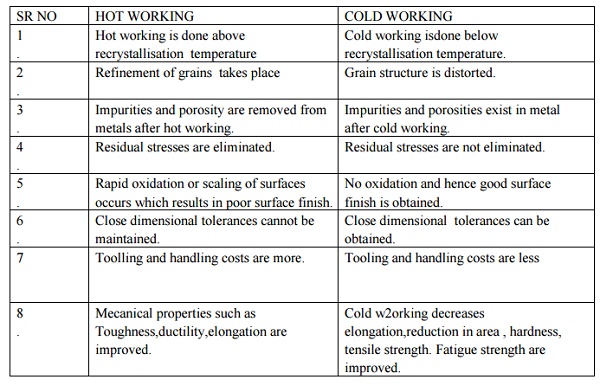
COMPARISION
BETWEEN HOT WORKING AND COLD WORKING
HOT
WORKING
1.
Hot working is done
above recrystallisation temperature
2.
Refinement of
grains takes place
3.
Impurities and porosity
are removed from metals after hot working.
4.
Residual stresses are
eliminated.
5.
Rapid oxidation or
scaling of surfaces occurs which results in poor surface finish.
6.
Close dimensional
tolerances cannot be maintained.
7.
Toolling and handling
costs are more.
8.
Mecanical properties
such as Toughness,ductility,elongation are improved.
COLD
WORKING
1.
Cold working isdone
below recrystallisation temperature.
2.
Grain structure is
distorted.
3.
Impurities and
porosities exist in metal after cold working.
4.
Residual stresses are
not eliminated.
5.
No oxidation and hence
good surface finish is obtained.
6.
Close dimensional
tolerances can be obtained.
7.
Tooling and handling
costs are less
8.
Cold w2orking decreases
elongation,reduction in area , hardness, tensile strength. Fatigue strength are
improved.
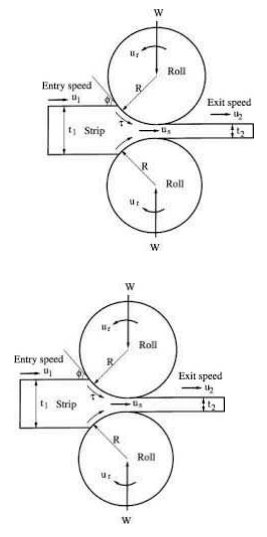
ROLLING
Rolling is the most rapid method
of forming metals into desired shapes by plastic deformation in between rolls.
The
forming of bars, plates , sheets, rails
and other steel sections are produced by
rolling.
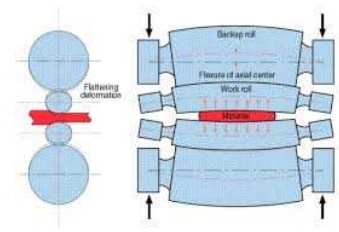
1.Classification
of Rolling mill based on number of
rolls.
1.Two High Rolling Mill.
2.Three high Rolling Mill
3.Four high Rolling Mill
4. Multi Rolling Mill.
5.Universal Rolling Mill
6.Planetary Rolling Mill.
1.Two High Rolling Mill.
2.
DEFECTS IN ROLLED PARTS

There are two types of major defects on the rolled products.
(a) SURFACE
DEFECTS
(b) INTERNAL
SURFACE DETECTS.
(a) SURFACE
DEFECTS Major surface defects on rolled products are scales, rust, scratches,cracks,
and pits. These defects occurs on the rolled products due to the impurities and
inclusions present in the original cast materials.,
(b).INTERNAL SURFACE DEFECTS
i. WAVINESS OR WAVY EDGES.
It occurs due to the bending of rolls. The rolls
acts as a straight beam. If the material flow is continuous and to maintain
this continuity, strains with in the material should adjust with itself. There
are compressive strain on the edges and tensile strain at the centre. The edges
are restrained from expanding freely in the longitudinal direction because of
which wavy edges on the sheet will be produced.
ii. Zipper Cracks
It occurs due to poor material ductility, at the
rolling temperatureCamber is provided to avoid this defect., Camber is
providing slightly large diameter at the center of rolls than that at the
edges.
iii. FOLDS
Folds
occur if the reduction per pass is very less.
iv. Alligatoring.
It is the splitting of work piece along the
horizontal plane on exit, with top and bottom part following the rotation of
their respective rolls.
v. Lamination.
These are
small cracks which may develop when reduction in thickness is excessive.
FORGING
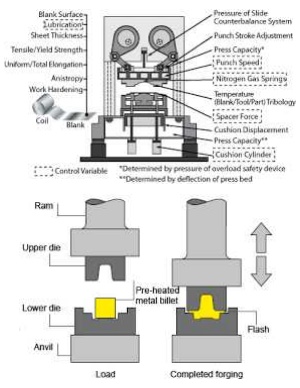
1.
COMPARISON BETWEEN PRESS FORGING AND DROP FORGING.
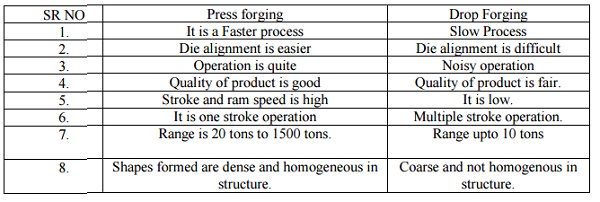
SR NO Press forging : Drop Forging
1. It is
a Faster process : Slow Process
2. Die
alignment is easier : Die alignment is difficult
3. Operation
is quite : Noisy operation
4. Quality
of product is good : Quality of product is fair.
5. Stroke
and ram speed is high : It is low.
6. It is
one stroke operation : Multiple stroke operation.
7. Range
is 20 tons to 1500 tons. : Range upto 10 tons
8. Shapes
formed are dense and homogeneous in structure.
: Coarse and not homogenous in structure.
2.
Forging operations
Forging is a process in which the work piece is
shaped by compressive forces applied through various dies and tools. It is one
of the oldest metalworking operations. Most forgings require a set of dies and
a press or a forging hammer. A Forged metal can result in the following: -
Decrease in height, increase in section - open die
forging Increase length, decrease cross-section, called drawing out.
Decrease length, increase in cross-section on a
portion of the length - upsetting
Change length, change cross-section, by squeezing in
closed impression dies - closed die forging. This results in favorable grain
flow for strong parts
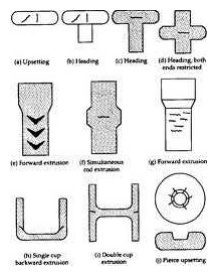
3. Types
of forging
Closed/impression die forging
Electro-upsetting
Forward extrusion
Backward extrusion
Radial forging
Hobbing
Isothermal forging
Open-die forgig
Upsetting
Nosing
Coining
Commonly used materials include
• Ferrous
materials: low carbon steels
• Nonferrous
materials: copper, aluminum and their alloys
3.1Open-Die Forging
Open-die forging is a hot forging process in which
metal is shaped by hammering or pressing between flat or simple contoured dies.
Equipment. Hydraulic presses, hammers.
Materials. Carbon and alloy steels, aluminum
alloys, copper alloys, titanium alloys, all forgeable materials.
Process Variations. Slab
forging, shaft forging, mandrel forging, ring forging, upsetting between
flat or curved dies, drawing out.
Application. Forging ingots, large and
bulky forgings, preforms for finished forgings.
Closed Die Forging
In this process, a billet is
formed (hot) in dies (usually with two halves) such that the flow of metal from
the die cavity is restricted. The excess material is extruded through a
restrictive narrow gap and appears as flash around the forging at the die
parting line.
Equipment. Anvil and counterblow hammers,
hydraulic, mechanical, and screw presses.
Materials. Carbon and alloy steels, aluminum
alloys, copper alloys, magnesium alloys, beryllium, stainless steels,
nickel alloys, titanium and titanium alloys, iron and nickel and cobalt super
alloys.
Process Variations. Closed-die
forging with lateral flash, closed-die forging with longitudinal flash,
closed-die forging without flash.
Application.
Production
of forgings for automobiles, trucks, tractors, off-highway equipment,
aircraft, railroad and mining equipment, general mechanical industry, and
energy-related engineering production.
4.DEFECTS IN FORGED PARTS
1.Unfilled Sections.
In this some of the die cavity are not completely filled by
the flowing metal.
2.Cold Shuts.
This
appears as small cracks at the corners of the forging. Caused due to improper
design of die.
3.Scale Pits.
This is seen as irregular depositions on the
surface of forging. This is primarily caused because of improper cleaning of
the stock used for forging.
The
oxides and scales gets embedded into the finish forging surface.
When the
forging is cleaned by pickling, these are seen
as deputations on the forging
surfaces.
4.Die Shifts.
This is caused by the mis-alignment of the half
dies, making the two halves of te forging to be of improper shape. It is also
called as mismatch.
5..Flakes.
These are basically ruptures caused by the
improper cooling of the large forging. Rapid cooling causes the exterior to
cool quickly causing internal fractures.
6.Improper Grain Flow.
Due to improper design of the
die, which makes the flow of the metal to be not in the final intended
direction?
7.Laps.
Laps are
formed by webbuckling during forging. To avoid laps web thickness should be
increased and properly edesigned.
Related Topics