Chapter: 11th Computer Applications : Chapter 14 : Introduction to JavaScript
JavaScript Variables
JavaScript
Variables:
Variable
is a memory location where value can be stored. Variable is a symbolic name for
a value. Variables are declared with the var
keyword in JavaScript. Every variable has a name, called identifier.
Basic Data types and Declaring variables:
Every
variable has a data type that indicates what kind of data the variable holds.
The basic data types in JavaScript are Strings, Numbers, and Booleans.
•
A
string is a list of characters, and
a string literal is indicated by enclosing the characters in single or double
quotes. Strings may contain a single character or multiple characters,
including whitespace and special characters such as \n (the newline).
•
Numbers can be integer or floating-point
numerical value and numeric literals are specified in the natural way.
•
Boolean can be any one of two values: true or false. Boolean literals are indicated by using true or false directly in the source code.
Variables
are declared in JavaScript using var keyword that allocates storage space for
new data and indicates to the interpreter that a new identifier is in use.
Declaring a variable in JavaScript as follows:
var no;
var no1,no2;
The
var no; statement tells the
interpreter that a new variable no
is about to be used and var no1,no2;
tells the interpreter that no1 and no2 are variables.
Rules for naming variable
1. The first character must be a letter
or an underscore (_). Number cannot be as the first character.
2. The rest of the variable name can
include any letter, any number, or the underscore. You can't use any other
characters, including spaces, symbols, and punctuation marks.
3. JavaScript variable names are case
sensitive. That is, a variable named RegisterNumber
is treated as an entirely different variable than one named registernumber.
4. There is no limit to the length of
the variable name.
5. JavaScript's reserved words cannot
be used as a variable name. All programming languages have a supply of words
that are used internally by the language and that cannot be used for variable
names.
Scope of variables
The
scope of a variable is the life time of a variable of source code in which it
is defined.
•
A
global variable has global scope; it can be defined everywhere in the
JavaScript code.
•
Variables
declared within a function are defined only within the body of the function.
They are local variables and have local scope.
Assigning values to variables
Variables
can be assigned initial values when they are declared as follows:
var
numericData1 = 522;
var
stringData = "JavaScript has strings\n It sure does";
var
numericData = 3.14;
var
booleanData = true;
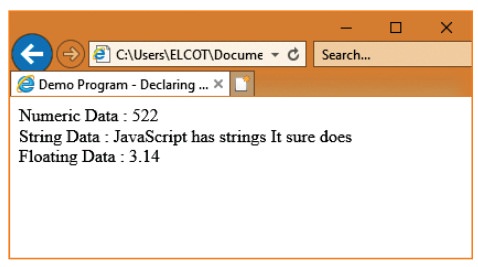
Illustration 14.2 Declaring Variables
<Html>
<Head>
<Title>Demo
Program - Declaring Variables in JavaScript </Title>
</Head>
<Body>
<script
language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var numericData1 = 522;
var stringData = " JavaScript has
strings\n It sure does";
var numericData = 3.14;
var booleanData = true;
document.write("Numeric Data :
"+numericData1);
document.write("<br> String
Data :
"+stringData);
document.write("<br> Floating
Data : "+numericData);
</script>
</Body>
</Html>
Output
In
addition, multiple variables can be declared with one var statement, if the variables are separated by commas:
var no1=50, no2=5065;
JavaScript
allows the implicit declaration of variables by using them on the left-hand
side of an assignment. In JavaScript there is no need to indicate data type
during variable ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() declarations. JavaScript variables are untyped and it is
dynamically datatyped which means initially you can assign a value of any data
type to a variable and later you can assign a value of different data type to
the same variable. For example:
declarations. JavaScript variables are untyped and it is
dynamically datatyped which means initially you can assign a value of any data
type to a variable and later you can assign a value of different data type to
the same variable. For example:
var
value=100;
var
value=”JavaScript”;
JavaScript Literals
A
literal is a fixed value given to a variable in source code. Literals are often
used to initialize variables. Values may be Integer, Floating point, Character,
String and Boolean. For Example,
var
int_const=250; //Integer constant//
var
float_const=250.85; //Floating point constant//
var
char_const=’A’; //Character constant//
var
string_const=”Raman”; //String constant//
var
boolean_const=true; //Boolean constant//
write statement:
General Syntax:
document
write ("string " + var);
Type casting in JavaScript.
Type
conversion is the act of converting one data type into a different data type
which is also called as casting. In JavaScript there are two type of casting,
•
Implicit
casting and
•
Explicit
casting
Implicit
casting occurs automatically in JavaScript when you change the data stored in a
variable:
Related Topics