Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: Papovaviruses
Clinical Syndromes - Human Papillomaviruses
Clinical Syndromes
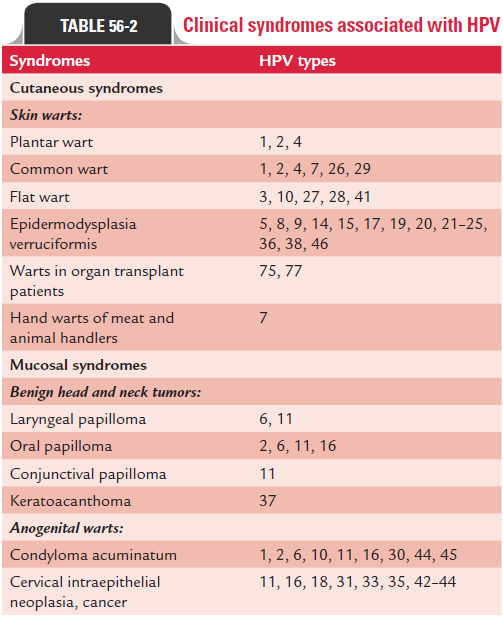
Human papilloma virus infection causes: (a) cutaneous warts, (b) benign head and neck tumors, (c) genital warts, and (d) cancerous conditions in humans (Table 56-2).
◗ Cutaneous warts
Cutaneous warts are commonly caused by HPV-2, HPV-4, and HPV-7. Warts usually develop on the hands and feet after incuba-tion period of 3–4 months depending on the HPV type and the site of infection. They may appear flat, plantar, or dome shaped. The plantar and flat warts are most common in children and young adults. Wart is usually a benign and self-limiting condi-tion, which resolves during the course of time.
◗ Benign tumors of head and neck
These include oral papilloma, laryngeal papilloma, and conjunctival papilloma.
Oral papillomas are usually single but may be multiple. They are sessile, verrucous, and white with raised borders. These lesions usually appear on the lips, hard palate, or gingiva. Focal epithelial hyperplasia or Heck disease is commonly caused by HPV-13 and HPV-32. This condition manifests as multiple, smooth, and sessile nodules present on the mucosal surface of the lower lip or on the buccal mucosa. This condition was described in North American people.
Laryngeal papillomas are life-threatening conditions in children, caused by HPV-6 and HPV-11. This is the most com-mon benign epithelial tumor of the larynx.
◗ Genital warts
Genital warts or condyloma acuminata is caused by HPV-6 and HPV-11. The condition typically manifests as solitary or multiple cerebriform and pink lesions, which appear more commonly on the nonkeratinized mucosa than on the keratin-ized mucosa. These genital lesions may also spread to the oral cavity during sexual activity involving orogenital contact.
◗ Cancerous conditions
Certain types of HPV—commonly, HPV-16 and less frequently, HPV-18, HPV-33, HPV-35—have been associated with oral premalignancy and malignancies in humans. These conditions are associated with verruciform proliferations in the oral cavity. Oral premalignant lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma caused by HPV-16 and HPV-18 are most commonly associated with intraepithelial cervical neoplasia and cancer. The condi-tions progresses from mild to moderate neoplasia to severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ during a period of 1–4 years.
Related Topics