Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes | Geography | Social Science - Write answers in a paragraph | 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes
Write answers in a paragraph
LITHOSHERE – I
ENDOGENETIC
PROCESSES
VII. Write answers
in a paragraph
1. Describe the structure of the
Earth.
Structure of the
Earth's interior is
• The Crust
• The mantle
• The Core
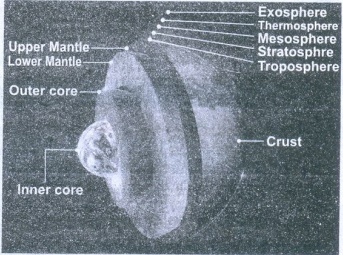
Crust (Thickness 5
km to 30 km)
• Crust is the outer layer of the Earth. It is solid and rigid.
The major elements are silica (Si) and aluminium (Al) and it is termed as SIAL.
• The crust is classified as continental crust and oceanic
crust.
(The thickness is greater below the continents than the ocean
floor)
Mantle (Thickness
2900 km)
• The interior port beneath the crust is mantle. The major
elements are silica (Si) and Magnesium (Mg) and it is termed as SIMA.
• In the upper part the rock remains solid and in the lower part
rocks are in molten form. (Molten rock 'Magma')
Core (Thickenss
3480 km)
• The core is the inner most and hottest layer of the Earth. The
major elements are Nickel (Ni) and Iron (Fe) and it is termed NIFE.
• The inner core is solid and the outer core is Liquid. It is
responsible for Earth’s gravitational force and Earth's magnetic field.
2. Write a note on the internal
and external processes of Earth.
Internal Processes
of Earth (Endogentic Processes)
• The forces that act from the Earth's interior towards the
Earth's surface are called "Internal Processess". These forces build
the landscape and create topographic relief.
• By the heat generated, the materials from deep below the
Earth's crust are ejected.
• The movement of tectonic plates, Earthquake and volcanic
eruptions are internal processes.
External processes
of Earth (Exogenetic Processes :
• The processes that cause stress and deformation on Earth
materials and bring Changes on the surface of the Earth are called
"External processes (Geomorphic processes)
• The forces like running water, glacier, wind, waves are agents
for External process.
• These agents tear the landscape down into relatively low
elevated plains.
3. How are volcanoes classified
based on the periodicity of their eruptions?
Volcanoes
• Hot solid, liquid and gaseous materials from the Earths
interior erupt out to the surface through a vent or an opening on the crust.
• Based on the periodicity of eruptions volcanoes are classified
into
• Active volcano
• Dormant volcano
• Extinct Volcano
Active volcano:
• The Volcanoes that constantly eject volcanic lava, gases and
fragmented materials are called active Volcanoes.
• Ex. Mount St. Helens - United States of America.
Dormant Volcano:
• The Volcanoes that do not show any sign of volcanic activity
for a long period of time are called 'Dormant' volcanoes. (Sudden explosion;
May cause loss to life and property.)
Ex. Mt. Fuji, Japan
Extinct volcano:
• The volcanic that permanently stop volcanic activities are
called 'Extinct' Volcanoes.
Ex. Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
4. Explain the effects of
Volcanoes :
Effect of
Volcanoes:
Constructive
effects:
• Volcanic materials are used as building materials ; Enrich the
soil fertility that promotes agricultural activities.
• The hot volcanic region helps in generating geothermal energy.
• Many Dormant and Active volcanoes are the most attractive
tourist spots of the world.
Destructive
effects:
• Volcanic eruption causes Earthquakes, fast floods, mud slide
and rock fall. Lava can travel very far and burn, bury, damaging anything in
its path.
• The large amount of dust and ash makes breathing hard and
irritable.
• They can alter the weather conditions and disrupt transport in
and around the volcanic region.
Related Topics