Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes | Geography | Social Science - Distinguish between | 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – I Endogenetic Processes
Distinguish between
LITHOSHERE – I
ENDOGENETIC
PROCESSES
VI. Distinguish
between
1. Core and Crust.
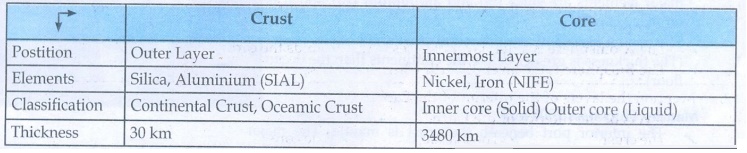
Crust
Postition: Outer Layer,
Elements: Silica, Aluminium (SIAL)
Classification: Continental Crust, Oceamic Crust
Thickness: 30 km
Core
Postition: Innermost Layer
Elements: Nickel, Iron (NIFE)
Classification: Inner core (Solid) Outer core (Liquid)
Thickness: 3480 km
2. Epicentre and Hypocentre.

Epicentre
• Epicentre is a point on the Earth's surface that lies directly
above the focus.
• The impact of the Earthquake is felt the most at the
epicentre.
Hypocentre
• The point of origin of an Earthquake is called Hypocentre
(Focus)
• It generates a series of elastic waves.
3. Divergent and convergent boundaries.

Divergent
boundaries
• In Divergent boundary the plates pull away from each other as
magma pushes up from the mantle
Convergent
boundaries.
• In convergent boundaries the plate moves toward each other and
some times, a plate sinks under another.
4. Primary waves and Secondary waves.
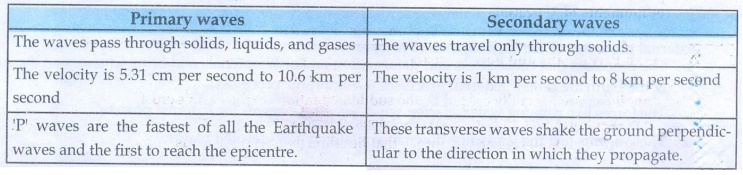
Primary waves
• The waves pass through solids, liquids, and gases
• The velocity is 5.31 cm per second to 10.6 km per second
• 'P' waves are the fastest of all the Earthquake waves and the
first to reach the epicentre.
Secondary waves
• The waves travel only through solids.
• The velocity is 1 km per second to 8 km per second
• These transverse waves shake the ground perpendicular to the
direction in which they propagate.
5. Shield volcano and Volcanic Dome.
Shield Volcano:
• Shield volcanoes are formed by intense viscous lava
• These are shallow depositions with gently sloping sides.
• Hence the lava flows out in all directions to create a shield.
E.g. Mauna Loa, Hawaii
Volcanic Dome:
• A lava dome or volcanic dome is roughly a circular mound
formed due to the slow ejection of viscous lava from a volcano.
• As the lava is rich in silica with intense viscosity, it is
prevented from flowing far from its vent. Eg. Paricutin, Mexico
Related Topics