Term 1 Chapter 3 | 4th Science - Work and Energy | 4th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Work and Energy
Chapter: 4th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Work and Energy
Work and Energy
Unit 3
Work and Energy

Learning Objectives
After learning this
lesson students will be able to
• define work
• understand work and energy
• know simple machines
• classify types of machine
• know about three types of lever
Let us Recall
Teacher : Students, you have studied about force in your lower class. What is
force ?
Students : A force is a push or pull that moves an
object at rest or stops an object in motion.
Teacher : There are different kinds of force. What are they?
Students : Frictional force, Gravitational force,
Muscular force and Magnetic force
A force can cause an object to
change its shape, speed or direction.
I. Work
An action in which one exerts a
force to move an object is known as work. What do you understand from
the below pictures?

From these pictures, we
understand that a force is applied to do some work.
Think and say
Teacher: Yesterday I was walking back from school. I found some people
working to lay the road. I found some items in that place. Can you say
something about that place and the machines that were used there? Or
Say something about the machines that were used. When can we say that work
is done or not?
Answer: Machines like road roller, crow bars, spades, pick axe and
shovels are used. The shape of the road is changed by applying force. So we say
that work is done.
When can we say
that work is done or not?
Two main conditions
are needed for work to be done.
• A force should act on an
object.
• Object should move from one
place to another.
When the force
acting on the object makes it move it is said to be done a work.
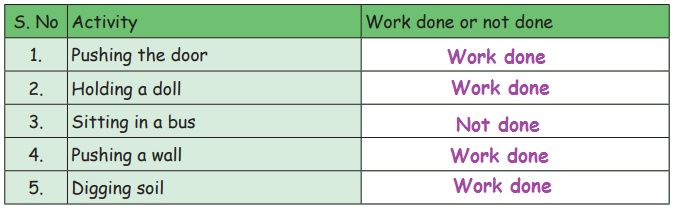
Try to Answer
Observe the picture and put a tick (✓) if work is done and put a cross (x) if work is
not done.

Try to Answer
Mention whether work is done or not in the
following activity.
II. Energy

In the above picture
• A man pulls a luggage. To do so he needs some
energy. What is the source? Food gives energy to humans.
• The car moves by the obtained
from the burning of fuel.
• The escalator moves by using
electricity as energy.
Energy is defined
as capacity for doing work.
Energy must be transferred to an object
in order
to do work.
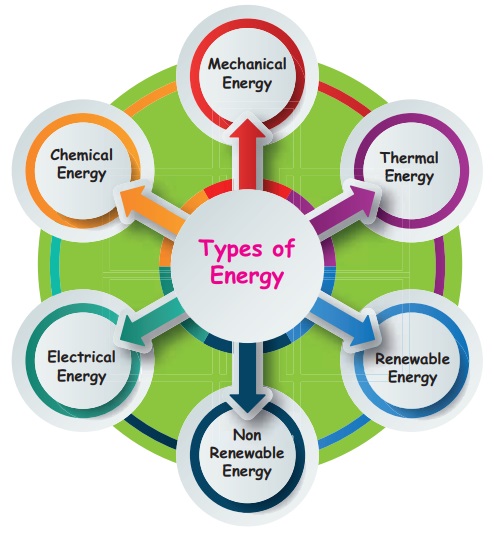
1. Renewable Resources
Renewable sources of energy are
replaced naturally over a period of time. We can keep using these sources for a
long period of time. Since the beginning of human life, we have been using
these resources. We use these resources for light, transport, cooking, heating.
Eg: Sun, Wind and Water.

2. Non-renewable Resources
The resources which are not
easily replaced once used are called the non-renewable resources. Eg: Petrol,
Coal and Natural gas

More to know
The law of conservation of energy
states that energy cannot created nor destroyed. It can be converted from one form to
another.

The
SI unit of energy is joule.
It is named after James Joule who
explained about energy.
III. Simple machine
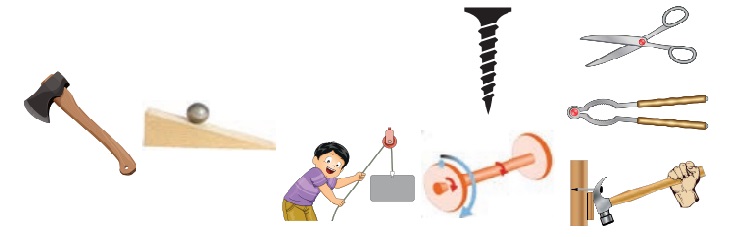
Observe the above
pictures. What are they used for?
In our daily life our effort is
saved with the help of some simple machines.
We draw water from the well with
the help of a wheel and a rope.
Simple machines are tools
which are used to make our work easier. Some examples for simple machines are pulley,
wedge, inclined plane, screw, lever, wheel and axle.
1. Pulley
Observe the picture. Which is
easier? Lifting the load with the help of a pulley or without a pulley?


Answer: Lifting the load with the help of a pulley is
easier.
A pulley is a machine
made up of a wheel with a cut around it. A rope or chain passes around the
pulley. It rotates in the direction with more force. Eg: crane

2. Inclined Plane
Observe the picture and discuss.
Is lifting a box is easier than rolling it on a ramp?


Answer: Rolling a box on a ramp is easier than lifting
it.
An inclined plane is a flat sloping surface with
one end higher than another.
Eg: ramp, slide and slope for wheel chair.

3. Wedge

A
wedge is a tool with a sharp edge which can be used to split materials.
It is used to break wooden logs into two pieces. Eg: knife, scissors and axe.
4. Screw
The
screw is used to raise weights and to hold objects together.
Eg: pencil sharpener, screw-jack,
bottle cap and windmill.

The screw in the bottle cap holds
the cap and the bottle together.
The blade and sharpner are held
together by screw.
5. Wheel and Axle
Wheel and axle consist of a wheel
attached to a small rod so that these two parts rotate together.
Eg: bicycle wheel, door knob,
grinder, axle wheel.

More to know
Simple machines usually exchange
a smaller force to move a heavy object. The work required is the same, but the force
required is less. The idea of a simple machine originated with the Greek
philosopher Archimedes around the 3rd century BC.

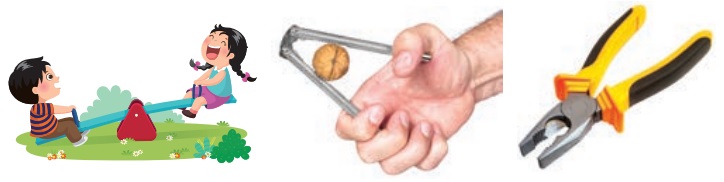
6. Lever
A lever is used to multiply the
force we give on an object.
Eg: see saw, nut cracker and
plier.
Try to Answer
Identify and mention the types of simple machines.

Try to Answer
Complete the table.
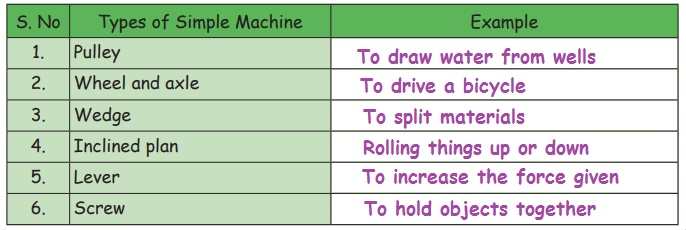
1. Pulley: To draw
water from wells
2. Wheel and axle: To drive a bicycle
3. Wedge: To split
materials
4. Inclined plane: Rolling things up or down
5. Lever: To
increase the force given
6. Screw: To hold
objects together
IV. Types of Lever
To understand the lever, we must
know the following terms.
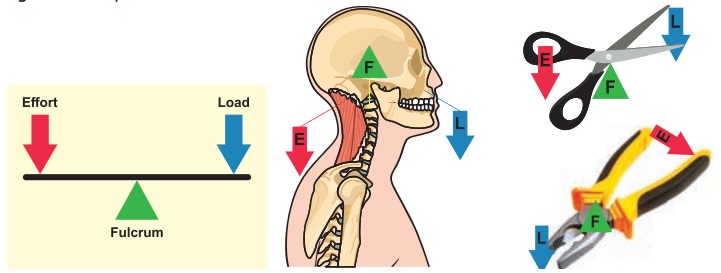
Load is the object on which the force is applied.
Effort is the force we apply on the lever.
Fulcrum is the point on which the lever rotates.
Lever is classified into three types according to where the load and effort are located with respect to fulcrum.
The three types of lever
Class I lever
Class II lever
Class III lever
1. Class I Lever
When the fulcrum is between the
effort and the load, it is known as Class I lever.
Eg: scissors, pliers, seesaw.
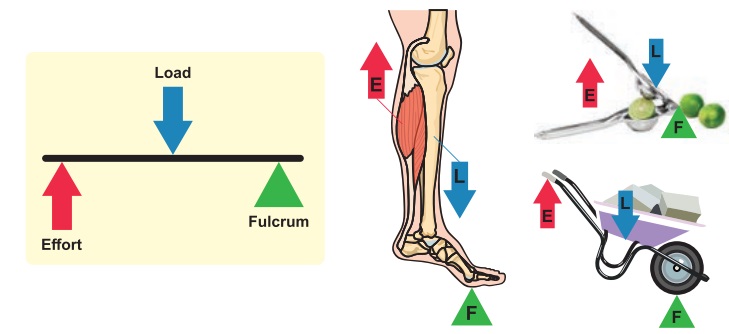
2. Class II Lever
When the load is between the
effort and the fulcrum, it is known as Class II lever.
Eg: wheel barrow, lemon squeezer,
nut cracker.
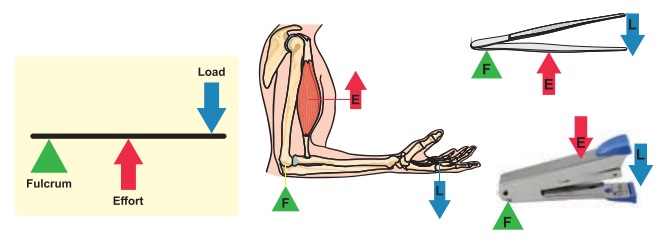
3. Class III Lever
In this lever, the effort is
between the load and the fulcrum.
Eg: stapler, tongs, broom stick,
hockey stick.
Try to Answer
Name the load, effort and fulcrum.

Related Topics