Term 2 Chapter 2 | 4th Science - Water | 4th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Water
Chapter: 4th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Water
Water
Unit 2
Water

Learning Objectives
After learning this lesson, students will be able to
• understand the change of states in
water
• describe the water cycle
• explain the importance of water cycle
• summarise rainwater harvesting and its uses
Introduction
Water is the most abundant and
precious resource on the Earth. It is found in oceans, seas, rivers, streams,
lakes, ponds and even under the ground. All living things need water to live
and to do many other activities. We have already learnt about this in the
previous classes. Let us learn more about water in this lesson.
I. Change of States
in Water
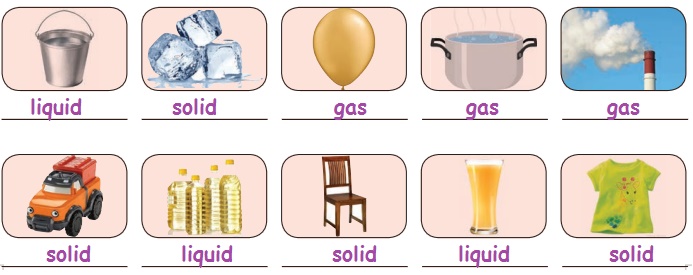
Let us do
See the given
pictures and write down the state of each objects. (Solid, Liquid, Gas )
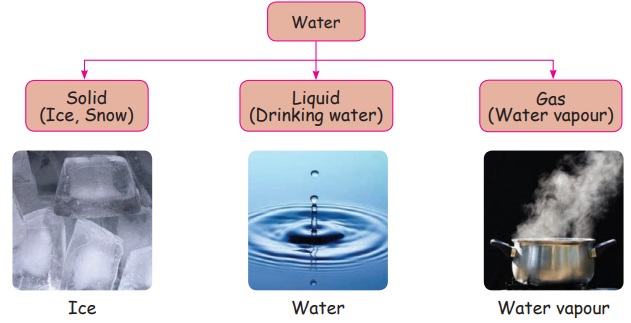
Water occurs naturally in three
forms: ice, water and water vapour.
These forms are also called
states of water. Ice is in solid form, water is in liquid form and watervapour
is in gaseous form.
These states occur naturally
because of temperature changes. Water becomes ice in cold regions, remains as
water in oceans/rivers and becomes water vapour due to the heat of the Sun.
More to know: Human body consists of 75% of water.
Let us do
Fill in the boxes
given below with correct answers.
(Liquid, Solid,
Melting, Freezing, Cooling, Heating, Gas)
Change of States in water
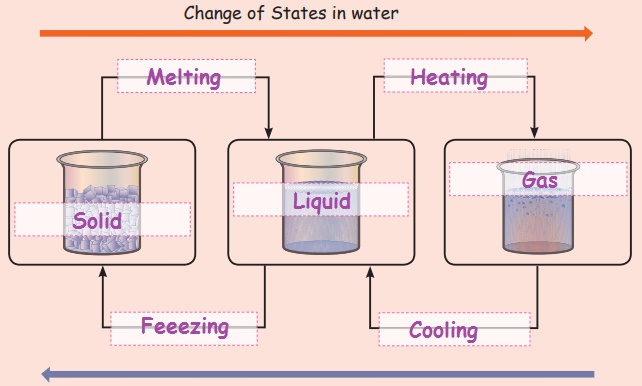
SOLID STATE (Ice)
Ice is a solid form of water. At
temperature below 0° C water becomes ice. This process is called freezing.

LIQUID STATE
(Water)
Water in liquid state is
available in water bodies such as oceans, river, waterfalls etc.
Write any two water
bodies in your area. river, ocean
GASEOUS STATE
(Water vapour)
Water becomes water vapour as the
temperature increases due to heat. Heating forms a white mist of extremely
small water droplets in the air known as water vapour.

Try to Answer
1. Why water is a good example for all states of
matter?
Answer: Because it is the only natural
substance that can exist in all three states of matter at the temperatures
normally found on Earth.
2. Which of the following is in liquid state?
Rain/Ice/Snow
Answer: Rain
Let us do
• Fill water in an ice tray and keep it in the
freezer. After few hours, take it out. What happened to the water?
The water changed from liquid state to solid state. It became
ice.
• Now keep this ice
tray on a table for some time. What happens to the ice?
Ice cubes melt and turn into water. Now water changes from solid
state to liquid state.
• Pour water from the
ice tray into a kettle. Ask an elder at your home to heat the kettle and
observe the mouth of the kettle when the water starts boiling. What do you see?
We see white smoke (water vapour) coming out from the mouth of
the kettle. Water changes from liquid state to gaseous state. It became steam.
II. Water Cycle
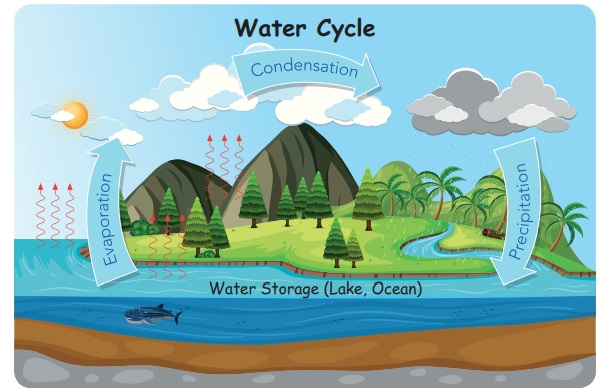
In nature, water keeps changing
its state. Let us see how this happens. Due to the Sun‛s heat, water in oceans
and rivers changes into water vapour and rises up.
Water becoming water vapour on
heating is called evaporation. The
water vapour, when comes into contact with cool air, becomes water droplets.
This is called condensation. The water droplets combine to form clouds. The water
droplets continue to combine, and they become big and heavy. These water
droplets then fall down as rain. This is called
precipitation. In colder places,
combined water droplets come down as snow, sleet or hail. This continuous
change of water from one state to another in nature is called water cycle.
The continuous
cycle through which water is circulated by different processes like
evaporation, condensation and precipitation is called water cycle.
Water Cycle
More
to know
Each
day, we lose a little more than a cup of water when we exhale.
Think and answer
What happens to the
water in a wet cloth?
Answer: The water in a wet cloth gets
evaporated. Hence the cloth gets dried up.
Try to Answer
Choose the correct answer.
In the water cycle ________
a. only evaporation is involved
b. only condensation is involved
c. evaporation and condensation are involved
Answer: (c)
evaporation and condensation are involved
Importance of water
cycle
• To improve the availability of
ground water.
• To control the Earth‛s
temperature.
• To provide water to plants and
animals especially humans.
• To recycle the Earth‛s supply
of water constantly.
Try to Answer
1. Unscramble the words and fill
in the blanks.
ondencsaonti, vaeionorpat,
ecippitatrino
condensation, evaporation, precipitation
2. Is water cycle important for
farming? Yes
3. Why is water cycle important
to human? To improve the availability of ground water.
4. Name the process which is
responsible for the formation of droplets on the surface of a glass of cold
drink. condensation
Do
you Know?
73% of our brain‛s
mass consists of water. The Antartic region has about 70% of the worlds fresh
water.
III. Rain Water
Harvesting
‘Rainwater
harvesting‛ is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use.
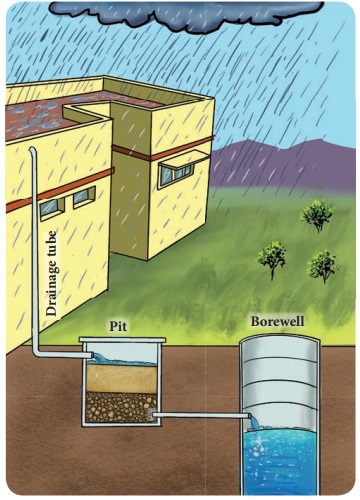
Rainwater can be collected in natural reservoirs or artificial tanks. Roof top harvesting
is also a type of rainwater harvesting. The rainwater on the top of the
building is collected and passed into the ground through pipes. Water passing
through the pipes enters the pit which consist of gravels and Coarse sand. As
it passes impurities are filtered and stored as ground water.
More to know: H2O is the chemical formula of water.
Do you Know? 1 inch of rainfall on a 2,000
sq.ft. roof is equal to 4,800 litres of water.
Benefits
of rainwater harvesting
• It increases
the ground water level
• It can be used
for agriculture
• It increases
the availability of water for living things
Rain water harvesting is the only
way to conserve rain water
More
to know
•
The rain water harvesting was launched in the year 2001 by the Tamil Nadu
government.
•
Tamil Nadu is the first Indian state which made rainwater harvesting as
mandatory.
Try to Answer
1. List out some other benefits
of rain water harvesting.
Answer:
❖ Reduces flooding and Erosion.
❖ It increases ground water
level
❖ It can be used for agriculture
❖ It increases the availability
of water for living things
2. Suggest some ideas to save
rainwater in your school.
Answer:
❖ By making rain water storage
pits.
❖ By collecting rainwater from
roof and allowing it to flow around borewells.
Let us do
Tips to construct a rainwater
harvesting pit at school/home.
Construct a pit of any shape or
size. It may be generally constructed, 1-2 metre wide and 2-3 metre depth. The
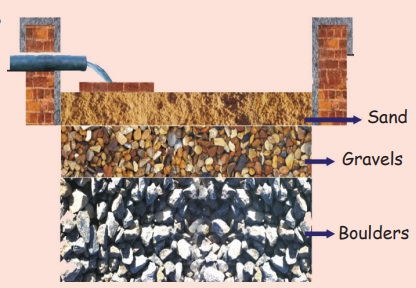
pits can be filled with boulders, gravels and Coarse sand.
Put the boulders in the bottom,
sand in the top and gravels in the middle.
Let
us do
Discuss
with your friends.
Rain
water harvesting has an important role to protect our environment.
Answer: It increases the ground water
level. It reduces flooding and soil erosion and reduces water scarcity.
Related Topics