Chapter: Mobile Networks : Transport and Application Layers
WAP-Architecture
WAP-ARCHITECTURE
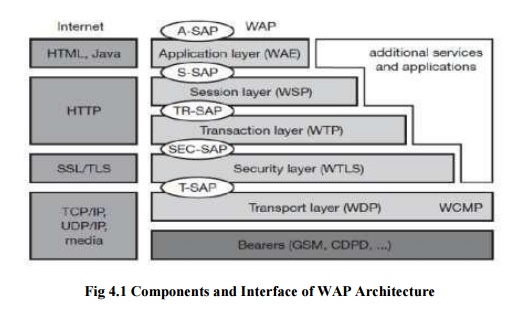
The above
Figure gives an overview of the WAP architecture, its protocols and components,
and compares this architecture with the typical internet architecture when
using the World Wide Web. This comparison is often cited by the WAP Forum and
it helps to understand the architecture (WAP Forum, 2000a). This comparison can
be misleading as not all components and protocols shown at the same layer are
comparable. For consistency reasons with the existing specification, the
following stays with the model as shown in Figure 10.9.The basis for
transmission of data is formed by different bearer services. WAP does not specify bearer services, but uses
existing data services and will integrate further services. Examples are
message services, such as short message service (SMS) of GSM, circuit-switched
data, such as high-speed circuit switched data (HSCSD) in GSM, or packet
switched data, such as general packet radio service (GPRS) in GSM. Many other
bearers are supported, such as CDPD, IS-136, PHS. No special interface has been
specified between the bearer service and the next higher layer, the transport layer with its wireless datagram protocol (WDP) and
the additional wireless control message
protocol (WCMP), because the adaptation of these protocols are bearer-specific.
The
transport layer offers a bearer independent, consistent datagram-oriented
service to the higher layers of the WAP architecture. Communication is done
transparently over one of the available bearer services. The transport layer service access point
(T-SAP) is the common interface to be used by higher layers independent of
the underlying network. The next higher layer, the security layer with its wireless
transport layer security protocol WTLS
offers its service at the security SAP
(SEC-SAP). WTLS is based on the transport layer security (TLS, formerly
SSL, secure sockets layer) already known from the www. WTLS has been optimized
for use in wireless networks with narrow-band channels. It can offer data
integrity, privacy, authentication, and (some) denial-of-service protection.
The WAP transaction layer with its wireless transaction protocol (WTP)
offers a lightweight transaction service at the transaction SAP (TR-SAP). This service efficiently provides
reliable or unreliable requests and asynchronous transactions as explained in
the above section. Tightly coupled to this layer is the next higher layer, if
used for connection-oriented service as described in section 10.3.5. The session layer with the wireless session protocol (WSP) currently offers two services at
the session-SAP (S-SAP), one
connection-oriented and one
connectionless if used directly on top of WDP. A special service for browsing
the web (WSP/B) has been defined that offers HTTP/1.1 functionality, long-lived
session state, session suspend and resume, session migration and other features
needed for wireless mobile access to the web. Finally the application layer with the wireless
application environment (WAE) offers a framework for the integration of
different www and mobile telephony applications. It offers many protocols and
services with special service access.
The main
issues here are scripting languages, special markup languages, interfaces to
telephony applications, and many content formats adapted to the special
requirements of small, handheld, wireless devices.Figure 10.9 not only shows
the overall WAP architecture, but also its relation to the traditional internet
architecture for www applications. The WAP transport layer together with the
bearers can be (roughly) compared to the services offered by TCP or UDP over IP
and different media in the internet. If a bearer in the WAP architecture
already offers IP services (e.g., GPRS, CDPD) then UDP is used as WDP. The
TLS/SSL layer of the internet has also been adopted for the WAP architecture
with some changes required for optimization. The functionality of the session
and transaction layer can roughly be compared with the role of HTTP in the web
architecture. However, HTTP does not offer all the additional mechanisms needed
for efficient wireless, mobile access (e.g., session migration,
suspend/resume).
Finally,
the application layer offers similar features as HTML and Java. Again, special
formats and features optimized for the wireless scenario have been defined and
telephony access has been added.WAP does not always force all applications to
use the whole protocol architecture. Applications can use only a part of the
architecture as shown in Figure 10.9. For example, this means that, if an
application does not require security but needs the reliable transport of data,
it can directly use a service of the
transaction layer. Simple applications can directly use WDP. Different
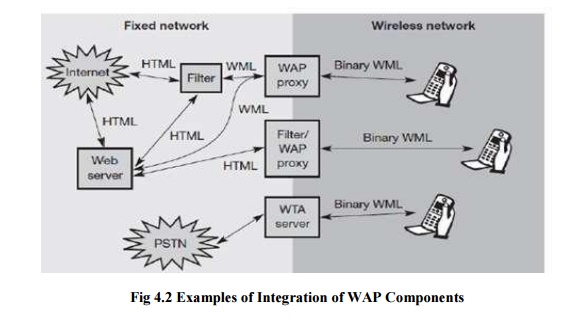
scenarios are possible for the integration of WAP components into existing
wireless and fixed networks (see Figure 10.10). On the left side, different
fixed networks, such as the traditional internet and the public switched
telephone network (PSTN), are shown. One cannot change protocols and services
of these existing networks so several new elements will be implemented between
these networks and the WAP-enabled wireless, mobile devices in a wireless
network on the right-hand side.
The
current www in the internet offers web pages with the help of HTML and web
servers. To be able to browse these pages or additional pages with handheld
devices, a wireless markup language (WML) has been defined in WAP. Special
filters within the fixed network can now translate HTML into WML, web servers
can already provide pages in WML, or the gateways between the fixed and wireless
network can translate HTML into WML. These gateways not only filter pages but
also act as proxies for web access, as explained in the following sections.WML
is additionally converted into binary WML for more efficient transmission. In a
similar way, a special gateway can be implemented to access traditional
telephone services via binary WML. This wireless telephony application (WTA)
server translates, e.g., signaling of the telephone network (incoming call
etc.) into WML events displayed at the handheld device. It is important to
notice the integrated view for the wireless client of all different services;
telephony and web, via the WAE.
Related Topics