Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 11 : Types of Banks
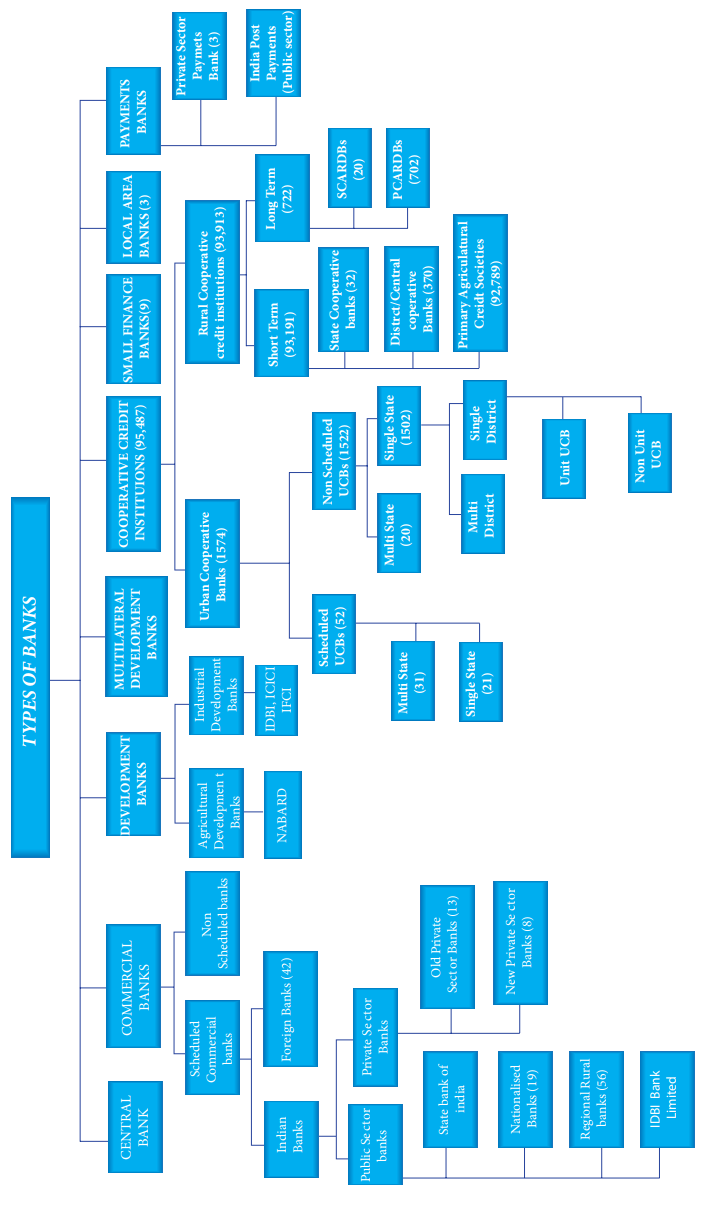
Types of banks
Types of banks
Banks can be classified as follows.
C. Based on the functions of banks
B. Based on the status given by the RBI
- Reserve Bank of India
C. Based on the ownership pattern
A. Based on the functions of banks
1. Central Bank
2. Commercial Banks
Banks which accept deposits from the
public and grant loans to traders, individuals, agriculture, industries,
transport, etc. in order to earn profit. Their lending is in comparatively
small amounts and mostly for short and medium period. They also provide other
services like remittance of funds, safe keeping of valuables, collection of
cheques, s, issue of letters of credit, etc. They operate with a head office and
a network of branch offices spread throughout the country. They also
issue guarantees to businessmen. When a businessman or
industrialist buy machinery on credit or apply for a big contract bank
guarantees that in case the customer fails the bank will make the payment.
Examples:
i.
State Bank of India
ii.
Karur Vysa Bank
iii.
Standard Chartered Bank
3. Development Banks
Huge finance required for investment,
expansion and modernisation of big industries and others are granted by a
separate type of banks called development Banks. They are also called
industrial banks. The objective of development banks is not profit. Their aim
is to develop the country and create employment opportunities. Finance is
provided by them for medium and long terms ranging from five to twenty years.
Development banks do not accept deposits from the public. They subscribe the
shares and debentures of the industries. They provide technical and managerial
consultancy services to industrialists. IDBI Bank established as the apex
development bankin I964 and was transformed into public sector commercial bank
in 2004. Currently it performs both development bank and commercial bank
functions. Its name changed into IDBI Bank Limited in 2008. When a development
bank is established for the development of agriculture industry it is called
agricultural development bank. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural
Development is such a bank
Examples:
i. Industrial Finance Corporation of
India - IFCI
ii. Small Industries Development Bank of
India -SIDBI
iii. MUDRA bank (for the development of
micro industries)
4. Cooperative Banks
All cooperative banks in India are owned
by its customers or members who are farmers, small traders and others.
Cooperative banks in India are either urban based or rural based. Rural
cooperative banking structure in India has three tier structure for short term
loans and two tier structure for long term loans (refer chart). For both these
structures the apex body is National Bank for Agricultural and Rural
Development - NABARD. All cooperative banks in Tamil Nadu are registered under
Tamil Nadu Cooperative Societies Act
1983. They are controlled by both
RBI and the State Government. Their foremost objective is providing service to
its members for rural and agricultural development and not profit earning. They are set up in towns and
villages rather than cities. Compared to the commercial banks they offer less variety of services as the bye laws do
not permit all commercial bank
activities. National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) established in
1963 is providing loans and grants to
State Governments for financing
cooperative societies. NCDC
concentrates on projects like water conservation, irrigation, agri-insurance,
rural sanitation, etc.
Examples:
·
National Agricultural Cooperative
Marketing Federation of India Ltd. (NAFED) was set up in 1958 and registered
under the Multi State Co- operative Societies Act.
·
Tamil Nadu State Apex Cooperative Bank -
Head Office, Chennai
·
Madurai District Central Cooperative
Bank Ltd.
·
Batlagundu Cooperative Urban Bank Ltd.
Dindigul District
5. Foreign Banks
Banks which have registered office in a foreign country and branches in India are called foreign banks. These banks open their offices in big cities and port towns only. Mostly they serve the interests of the multinational companies, employees and other business institutions. Their profitability is higher than Indian banks. In 2017, there were 42 Foreign Banks in India and all of them were scheduled banks. They have to oblige both their home country banking regulations and the RBI regulations.
Examples:
i.
Bank of America - The USA
ii.
Barclays Bank - The UK
iii.
Deutsche Bank - Germany
6. Regional Rural Banks - RRBs
The RRBs were formed under the Regional
Rural Bank Act 1976, jointly by the Central Government, State Government, and a
sponsor bank. Their share capital is contributed by these sponsors in the ratio
of 50:15:35. They are established as low cost institutions in rural areas.
Their objective is to develop rural economy and play supplementary role to
cooperative societies. They mobilise deposits from the rural public and provide
finance to rural artisans, small entrepreneurs and farmers and try to avoid
their dependency on money lenders. As on 31.3.2016, there were 56 RRBs in India
with 14,494 branches. They are regulated and supervised by NABARD.
Examples:
i. Pallavan Grama Bank, Salem,Tamil Nadu
ii. Pandian Grama Bank,Thirumangalam, Madurai Dirstict, Tamil Nadu
iii. Vallalar Grama Bank, Chidambaram,Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu
iv. Paduvai Bharathiyar Grama Bank,
Villiyanur, Puducherry.
7. Specialised Banks
Some banks are created for special
purposes by the Government. Export and Import Bank of India was set up through
Export- Import Bank of India Act, 1981. Its main objective is to facilitate
international trade of Indian businessmen. EXIM Bank provides finance for
import of technology, export product development, pre-shipment and
post-shipment and overseas investment. National Housing Bank was established
under the National Housing Bank Act, 1987. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of
the RBI. The objective of NHB is to promote housing finance institutions at
local and regional levels in India.
Example:
(i) Export - Import Bank of India (EXIM
Bank)
(ii) National Housing Bank (NHB)
8. Local Area Banks
Local Area Bank (LAB) scheme was
introduced by the RBI in August 1996. LABs are small private sector banks
established in rural and semi-urban areas. Each bank serves two or three
adjoining districts only. Their main objective is to mobilise rural savings
(accept deposits) and invest them in the same areas. They have to follow the
priority sector lending targets, including the targets on loans to weaker
sections. RBI received 227 applications
for setting up LABs. 10 were considered for approval and six were given license
under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. Only three LABs are
functioning now.
Exmaples:
1.
Coastal Local Area Bank, Vijayawada,
Andhra Pradesh.
2.
Krishna Bhima Smruddhi Local Area Bank, Mahabubnagar,
Telangana.
3.
Subhadra Local Area Bank Limited,
Kolhapur, Maharashtra.
Deficiencies are found in the original
model of LABs. There are practical difficulties in the operation of these
banks. Even after 20 years (1996-2017) LABs could not make an impact in rural
development. Therefore further licensing to LAB has been stopped.
9. Small Finance Banks
Small Finance Banks(SFBs)
areprivatesector banks set up in unbanked and underbanked regions of the
country to achieve financial inclusion. Their objectives are;
a. mobilising rural savings (accepting
deposits) and
b. providing credit to
i. small and marginal farmers
ii. to micro and small industries and
iii other unorganised sector entities.
In September 2015, RBI granted provisional
licenses to 8 Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs) already engaged in
microfinance to be converted into SFBs and 2 others. SFBs are low cost
structure banks. They are formed under section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act
1949.
Examples:
i. ESAF SFB, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala.
ii. Ujjivan SFB Limited, Bengaluru,
Karnataka, (has 10,000 employees)
iii. Fincare SFB, Ahmedabad, Gujarat,
has 25 branches spread over several states.
10. Payment Bank
Payment banks are formed to widen the spread of payment and financial services to small businesses, low-income households, and migrant labourers.
These banks should be fully networked from
the beginning. They offer doorstep banking payment for a small fees
prescribed on the basis of the amount.
They issue ATM/ debit cards, internet banking and third party fund transfers.
They can’t lend money and issue credit cards. In August 2015, the RBI gave ‘in
principle’ licenses to Payment Banks.
Examples:
i. Airtel Payment Bank Limited
ii. Paytm Payment Bank Limited and
iii. India Post Payment Bank Limited -
IPPBs (Public Sector Bank).
11. Multilateral Development Banks - MDBs
A Multilateral Development Bank is
formed by the Governments of a group of countries.
The member countries consist of
developed donor countries and borrower countries. International Bank for
Reconstruction and Development, Asian Development Bank, African Development
Bank, and European Investment Bank are some of the MDBs.
B. Based on the Status given by the RBI
Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks
All banks which satisfied the norms and
included in the Second Schedule to the RBI Act, 1934 are called scheduled
banks. Such banks are given financial accommodation and remittance facilities
at concessional rates by the RBI.
There is no non-scheduled commercial bank (private sector, public sectorandforeign banks) in India.
There are five Urban
Cooperative Banks and three Local Area Banks which function as non-scheduled
banks in India. Small Finance Banks and Payments Banks have not been licenses
under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
C. Based on the Ownership Pattern
Any bank in which not less than 51
percent of shares are owned by the
Government are called Government banks or public sector commercial banks
(Total 21). All nationalized banks (19 banks, in 2017), SBI and IDBI Ltd. are
public sector commercial banks. All of them are joint stock company type banks.
There are corporation type banks. Each corporation type bank is established by
a separate Act of Parliament and is fully owned by Government of India.
Examples:
IFCI, SIDBI, EXIM Bank, etc.
All banking companies owned by private
people are called private sector commercial banks. All cooperative banks are
owned by its members from the public.
1n 1969, there were 14 private banks which were concentrated in cities and towns. Their objective was to earn more profits. In order to channelize the funds with these commercial banks towards national priorities and to develop agricultural and rural sector nationalization of banks was undertaken. Government paid the share capital of those banks to the private owners and took over as Government banks. This is called nationalization of banks. 6 more banks were nationalised in 1980. New Bank of India one of the nationalised bank merged with Punjab National Bank in 1980 and today there only 19 nationalised banks (2017). Examples:
a.
Nationalised Banks: Indian bank, Indian Overseas Bank,
Oriental Bank of Commerce.
b.
Public Sector Banks: State Bank of India, IDBI Bank Ltd. and
all nationalised banks
c.
Private Sector Banks: Lakshmi Vila Bank, Karur Vysya Bank,
Kotak Mahindra bank.
Note: Bharatiya Mahila Bankwas
established on 19, November 2013 to serve exclusively women members of the
public was merged with SBI on 31 March, 2017.
A detailed study on the functions of
commercial banks is given in the next chapter.
On the basis of organisation the banking
may be unit banking or branch banking.
On the basis of lending practices, it may
be pure banking or mixed
banking. On the basis of their products it can be retail
banking or wholesale banking. On the basis of activities undertaken it may be
narrow banking or universal banking. From the ownership point of view it can be
chain banking or group banking. There are some peculiar types of banks such as
investment banking, Islamic banking, etc. In modern times virtual banking or
internet banking and mobile banking are very popular.
Related Topics