Chapter: Diseases of The Brain and Nervous System(A Health Education Guide): Infectious diseases of the brain
Tuberculosis of the Brain and its Diagnosis, Drugs
Tuberculosis of the Brain :
Usually, tuberculosis infection of the brain comes from other parts of the body like lungs or stomach. There is a possibility that the tuberculosis in the chest may be there for a long time, buta decrease in the immunity of the body due to any cause may result in TB of the brain. This disease is so common in our country that the TB organism is present in the bodies of most of the people, having entered through milk or air and its immunity is already there in the body. When the immunity of the body is compromised due to any reason, .and the body becomes weak, active disease develops. A patient of AIDS can get infected with innumerable organisms causing variety of diseases in which TB organisms are the main germs.
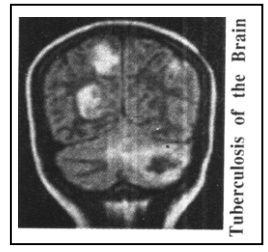
Tuberculosis infection in the membranes of the brain is called TB Meningitis and the TB tumor in brain is called as Tuberculoma. The infection of the cortex of the brain is called Encephalitis (Encephalopathy). Headache, low-grade fever, vomiting, loss of appetite, excessive weakness or anxiety are the initial symptoms of this disease. Gradually, seizures, paralysis of one or more limbs can occur and in advanced stage, coma due to the edema of the brain and even death may occur. If there is an obstruction in any small or big blood vessel of the brain due to TB, it is known as TB arteritis. TB can also cause paralysis. If the pathways of the C.S.F are obstructed, the result is hydrocephalus, in which the cerebral ventricles dilate leading to unconsciousness or loss of eyesight. A tubercular infection in the spinal cord or vertebra may lead to paralysis of the lower limbs.
Diagnosis :
In order to diagnose this disease, a detailed medical examination as well as blood tests are required. The C.T.Scan or/and M.R.I are useful. Lumbar Puncture is almost an essential test for the confirmatory diagnosis of the infectious diseases of the brain. In tubercular meningitis the examination of the C.S.F shows high protein levels, lowsugar levels and high lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) count. In some complicated cases, C.5.F.-P.C.R, C.S.F.-C.R.P, C.S.F-A.D.A tests are conducted for accurate diagnosis. This accuracy is necessary because once the diagnosis is confirmed the patient requires proper treatment for a minimum of one and a half years to two years. Initially, the C.S.F reports may sometimes present a picture of a viral or pyogenic infection and if there is a laxity in the treatment of any of the three infections due to lack of proper diagnosis, it could lead to dangerous consequences. Hence, proper investigations are very essential in these infectious diseases. Almost all the specialist physicians agree that the diagnosis should never be done with guesswork. But in situations where the edema in the brain is considerable, respiration is inadequate and the general condition of the patient is fragile, lumber puncture test can be dangerous and at such times the treatment should be immediately initiated on the basis of CT Scan, MRI and other supportive facts. Lumbar Puncture can be done later, when general condition permits.
Drugs :
The main medicines for the tuberculosis of the bra in are streptomycin (SM) injections, isoniazid (INH), rifampicin (RF), pyrazinamide (PZ), and ethambutol, which are called the primary medicines. In resistant cases, sparfloxacin or ciprofloxacin, kanamycin injection, ethionamide or cycloserine can also be used as secondary medicines. All these drugs have some or the other side effects and therefore along with the symptoms of the patient, laboratory tests are regularly carried out. For example INH, RF or PZ can cause an inflammation in the liver and effects of jaundice. Hence doctors regularly carry out tests like S.G.P.T./S.G.O.T etc.
In case a problem is detected, the particular medicine is stopped for sometime. Vomiting, loss of appetite, red discoloration in the urine because of RF, are the usual side effects in majority of patients, but the drugs need not be discontinued because there is a considerable improvement seen in the patients within 4 to 6 weeks.
In case of an inflammation in the brain or CSF test showing excessive proteins, steroids are given for 4 to 6 weeks and if there are large tumors in the brain, a major surgery may be required. Small tumors can be removed along with biopsy by the latest surgery called stereotaxisbiopsy. Surgery is rarely required for these tumors as they start resolving with the medicines. Normally CT scan or MRI are done after 2 to 3 months to note the improvement. CSF is rarely required to be done frequently. However in selected cases the drugs are given through CSF, which is known as the Intrathecal route. When the pathways of the CSF gets blocked and the ventricles start filling with fluid, the patient loses consciousness, has problems in walking, talking and understanding, vision diminishes or headache and vomiting take place. This is called hydrocephalus and it can be accurately detected with the help of CT Scan. In this case, a small tube is introduced in to ventricles of the brain through the skull, and the extra fluid is drained out through a tunnel beneath the skin up to the stomach via the tube. This process is known as shunt surgery. This is a simple operation with good results. However, problem can arise if the shunt becomes obstructed. If TB organisms are not controlled by the primary drugs, it is called drug resistance and the secondary medicines can be used. However, in some cases if the patient has totally lost the immunitylike in AIDS or if the infectious organisms are very resistant, such patients cannot be helped much.
Related Topics