Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 15 : Nervous System
Transmission of Nerve Impulse
Transmission of Nerve Impulse
All the information from
the environment are detected by the receptors located in our sense organs such
as the eyes, the nose, the skin etc. Information from the receptors is
transmitted as electrical impulse and is received by the dendritic tips
of the neuron. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then
along the axon to its terminal end. On reaching the axonal end, it causes the
nerve endings to release a chemical (neurotransmitter) which diffuses
across a synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrites of
the next neuron, then to their cell body to be carried along the axon.
In this way, the
electrical signal reaches the brain or spinal cord. The response from brain (or
spinal cord) is similarly passed on to the effector organs such as the muscle
or gland cell, that undergoes the desired response.
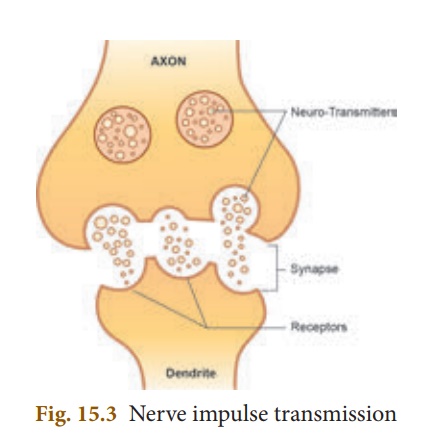
The flow of nerve
impulses from axonal end of one neuron to dendrite of another neuron through a synapse
is called synaptic transmission.
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are
the chemicals which allow the transmission of nerve impulse from the axon
terminal of one neuron to the dendron of another neuron or to an effector
organ. The important neurotransmitter released by neurons is
called Acetylcholine.
Related Topics