Chapter: Operating Systems : Storage Management
Thrashing
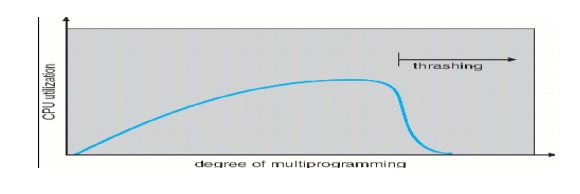
THRASHING
ü High paging activity is called
thrashing.
ü If a process does not have enough pages, the page-fault rate is very high.
ü This
leads to:
o low CPU utilization
o operating system thinks that it needs to increase the degree
of multiprogramming
o another process is added to the system
When the CPU utilization is low, the OS increases the degree
of multiprogramming.
If global replacement is used then as processes enter the
main memory they tend to steal frames belonging to other processes.
Eventually all processes will not have enough frames and
hence the page fault rate becomes very high.
Thus swapping in and swapping out of pages only takes place.
This is the cause of thrashing.
ü To limit
thrashing, we can use a local replacement algorithm.
ü To
prevent thrashing, there are two methods namely ,
· Working
Set Strategy
· Page
Fault Frequency
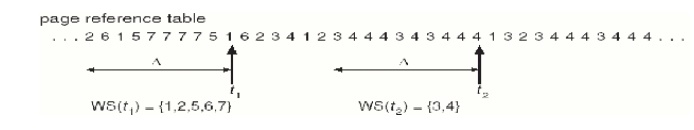
1. Working-Set
Strategy
v It is
based on the assumption of the model of locality.
v Locality
is defined as the set of pages actively used together.
v Working set is the set of pages in the most recent page references is the working set
window.
§ if too small , it will
not encompass entire locality
§ if too large ,it will
encompass several localities
§ if = it will encompass entire program
D=WSSi
SSi is
the working set size for process i.
D is the
total demand of frames
ü if D >
m then Thrashing will occur.
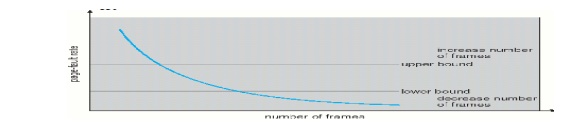
2. Page-Fault
Frequency Scheme
v If actual
rate too low, process loses frame
v If actual
rate too high, process gains frame.
Other Issues
Prepaging
§ To reduce the large
number of page faults that occurs at
process startup
§ Prepage
all or some of the pages a process will need, before they are referenced
§ But if
prepaged pages are unused, I/O and memory are wasted
Page Size
Page size selection must take into consideration:
·
fragmentation
·
table size
·
I/O overhead
·
locality
TLB Reach
• TLB Reach - The amount of memory accessible from the TLB
• TLB Reach = (TLB Size) X (Page Size)
• Ideally, the working set of each process is stored in the
TLB.
• Otherwise there is a high degree of page faults.
• Increase the Page Size. This may lead to an increase in
fragmentation as not all applications require a large page size
• Provide Multiple Page Sizes. This allows applications that
require larger page sizes the opportunity to use them without an increase in
fragmentation.
I/O interlock
Pages must sometimes be locked into memory
Consider I/O. Pages that are used for copying a file from a
device must be locked from being selected for eviction by a page replacement
algorithm.
Related Topics